Carnitine and Acylcarnitine Analysis Service
Submit Your Inquiry
Carnitine is widely distributed in all organs of the body. The main role of carnitine is to combine with fatty acids or deamination products of branched-chain amino acids to form acylcarnitine. These metabolites are then transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where they are completely degraded by beta-oxidation and produce energy. Abnormalities in the metabolic enzymes or transport proteins involved in fatty acid and amino acid metabolism in patients with inherited metabolic defects can result in abnormal plasma concentrations of carnitine and acylcarnitine. Thus, disorders of fatty acid or branched-chain amino acid metabolism result in characteristic alterations in one or more acylcarnitine levels.
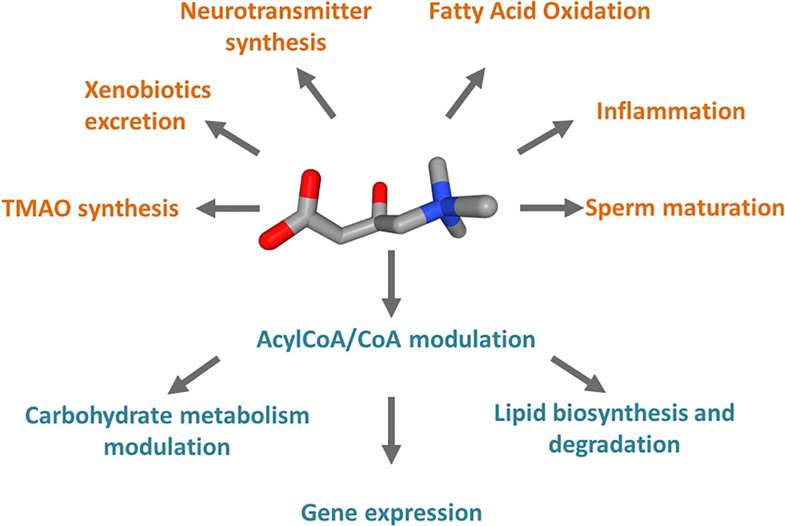 Schematic representation of the cell processes linked to carnitine (Console et al., 2020)
Schematic representation of the cell processes linked to carnitine (Console et al., 2020)
Creative Proteomics has established a method for the quantification of carnitine and acylcarnitine and related metabolites from C0 to C18. It allows for the one-time determination of more than thirty carnitine and ester-based carnitines in samples. The solution uses an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry platform, using multiple carnitine and acylcarnitine isotopic standards and non-isotopic standards as internal standards, providing a solution for the simultaneous quantitative detection and analysis of multiple carnitines and acylcarnitines in biological samples, significantly improving the accuracy of qualitative and quantitative determination while greatly increasing throughput and stability. The method is applicable to a wide range of biological samples and can meet multiple needs.
Detectable carnitine and acylcarnitine metabolites
| L-carnitine | C2-carnitine | C3-carnitine | C4-carnitine |
| C5-carnitine | C8-carnitine | C10-carnitine | C10:1-carnitine |
| C12-carnitine | C12:1-carnitine | C14-carnitine | C14:1-carnitine |
| C14:2-carnitine | C16-carnitine | C16:1-carnitine | C18-carnitine |
| C18:1-carnitine | C18:2-carnitine | C20-carnitine | C20:1-carnitine |
| C20:2-carnitine | C20:3-carnitine | C20:4-carnitine |
|
| L-carnitine | Acetylcarnitine | Propinoylcarnitine | Butyrylcarnitine |
| Valerylcarnitine | Glutarylcarnitine | Hexanoyl- (caproyl-)carnitine | Octanoylcarnitine |
| Octenoylcarnitine | Decanoylcarnitine | Decenoylcarnitine | Lauroylcarnitine |
| Dodecenoylcarnitine | Hydroxydodecanoylcarnitine | Myristoylcarnitine | Tetradecenoylcarnitine |
| Tetradecenoylcarnitine | Tetradecadienoylcarnitine | Tetradecenoylcarnitine | Hydroxymyristoylcarnitine |
| Palmitoylcarnitine | Hydroxyhexadecanoylcarnitine | Stearoylcarnitine | Oleoyl-(Elaidic-,Vaccenyl-)carnitine |
| Linoleyl-(linoelaidyl-)carnitine | Hydroxylinoleylcarnitine | Arachidoylcarnitine | Eicosenoylcarnitine |
| Eicosadienoylcarnitine | Eicosatrienoylcarnitine | Arachidonoylcarnitine |
|
Service Workflow
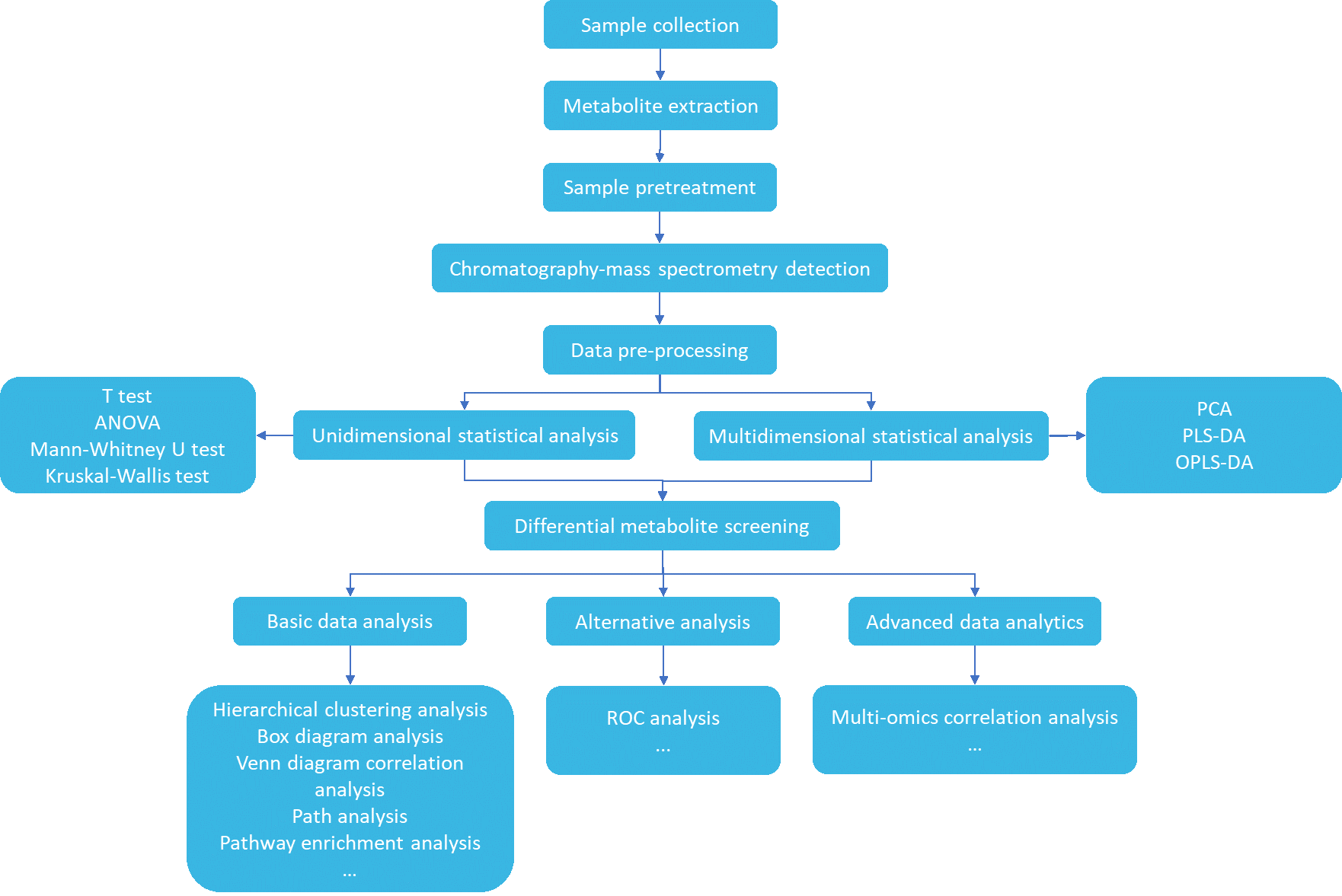
Deliverables
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
- MS raw data files and MS data quality checks
- Custom analysis report
Project Cycle
A standard experiment and analysis process takes about 2~6 weeks.
If you would like to analyze other metabolites or learn more, please contact us. We look forward to working with you.
Reference
- Console, L., Scalise, M., Mazza, T., Pochini, L., Galluccio, M., Giangregorio, N., ... & Indiveri, C. (2020). Carnitine traffic in cells. Link with cancer. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 981.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.


 Schematic representation of the cell processes linked to carnitine (Console et al., 2020)
Schematic representation of the cell processes linked to carnitine (Console et al., 2020)

