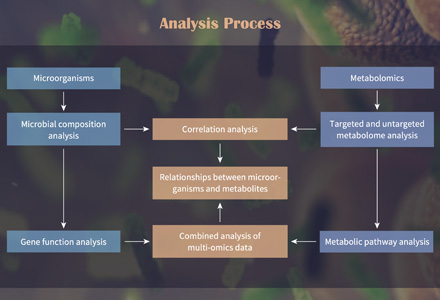
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) refers to the use of genomic resequencing technology to obtain millions of SNPs as molecular genetic markers, which are analyzed jointly with phenotypic data, from which SNPs associated with diseases are screened and genetic variants affecting complex traits are identified. GWAS has identified a large number of associated genomic variant loci and have identified many associated genes in practice, but explain only a small fraction of heritability. The establishment of high-throughput and sensitive methods for large-scale metabolomics studies has enabled the combined analysis of metabolome and genome-wide association studies (mGWAS).
Creative Proteomic has established the mGWAS analysis platform. We use second-generation sequencing technology to obtain genotype data of population materials combined with metabolome data to perform genome-wide association analysis of metabolites.
mGWAS can be applied to the localization of genes with high genetic effects as well as gene function studies, revealing many genetic variants that affect human metabolism and providing new ideas for disease mechanism research. The analysis of genetically influenced metabolic types will accelerate metabolic personalization studies and help analyze the ability of different individuals to cope with environmental challenges and their susceptibility to specific diseases. mGWAS is currently used in the study of many diseases (e.g. cancer, obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression and Alzheimer's disease).
In plant and animal research, mGWAS can bulk pinpoint relevant candidate genes controlling metabolic phenotypes (quality, functional nutritional molecules, etc.) and uncover mechanisms regulating relevant metabolic pathways such as nutrition and quality, helping to gain insight into metabolic genetic mechanisms, as well as breeding new high-quality varieties.
Technology Roadmap for
Integrative Metabolome and LncRNA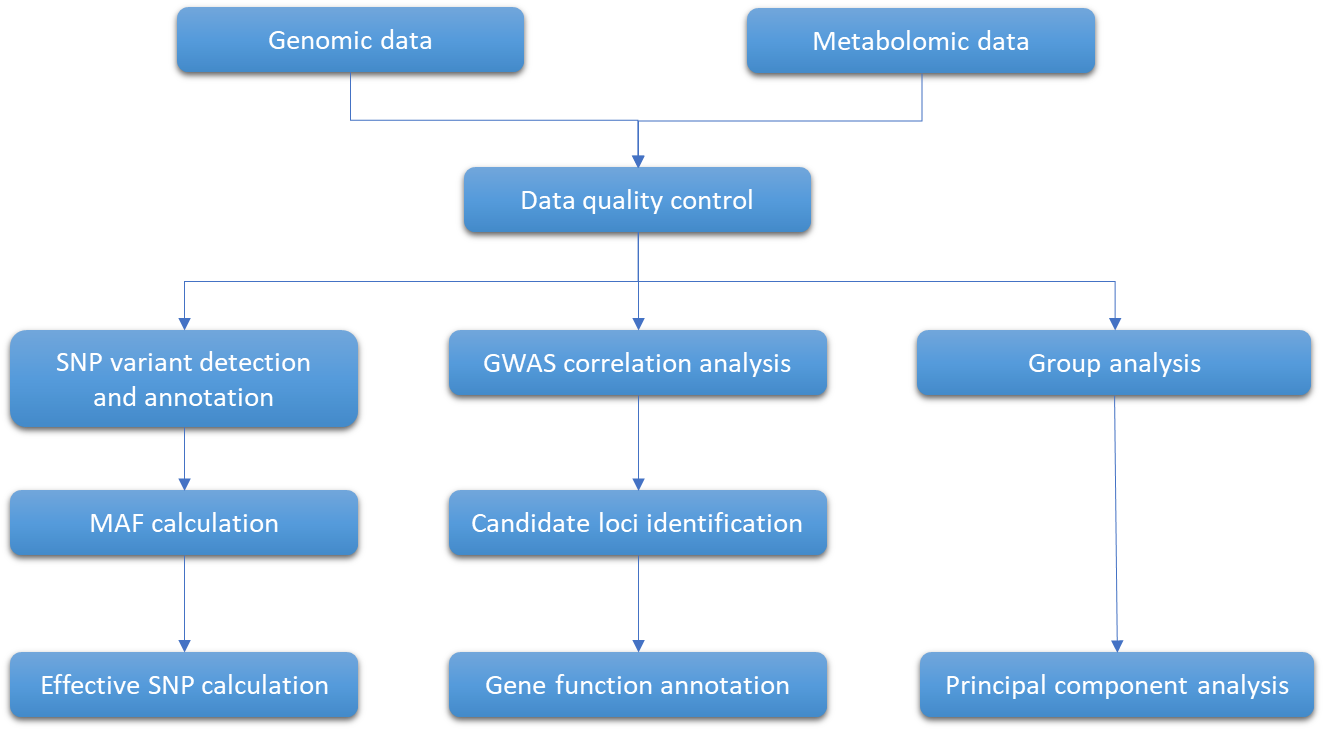
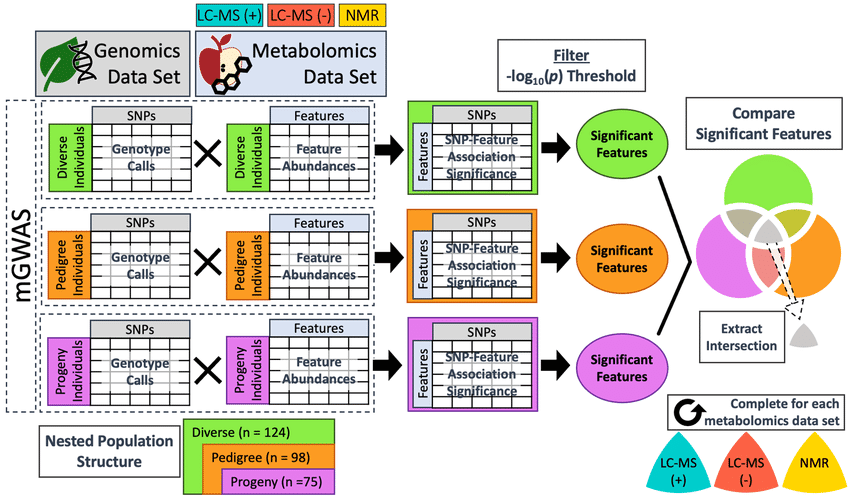 Workflow for integration of one metabolomics dataset with genomics data (Bilbrey et al., 2021).
Workflow for integration of one metabolomics dataset with genomics data (Bilbrey et al., 2021).
Sample Submission
| Sample Types |
| GWAS | - Tissue samples: ≥ 100mg
- Blood sample: ≥ 0.5ml, EDTA anticoagulation tube is recommended to avoid heparin anticoagulation.
- Saliva sample: ≥ 1ml
- Cell sample: ≥ 1×107
- gDNA samples: concentration ≥ 30ng/ul, total amount ≥ 2ug, OD260/280 between 1.8-2.0. No degradation, no contamination.
|
| Metabolomics | - Serum/plasma: 200ul/sample
- Cerebrospinal fluid: 300ul/sample
- Urine: 200ul/sample
- Tissue: 100 mg/sample
- Stool: 5-10g/sample
- Cells: ≥1x107/sample
|
If you want to know more, please contact us. Looking forward to cooperating with you.
Reference
- Bilbrey, E. A., Williamson, K., et al. (2021). Integrating genomics and multi-platform metabolomics enables metabolite QTL detection in breeding-relevant apple germplasm. bioRxiv.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.



 Workflow for integration of one metabolomics dataset with genomics data (Bilbrey et al., 2021).
Workflow for integration of one metabolomics dataset with genomics data (Bilbrey et al., 2021).