What Is Food Metabolomics?
Food metabolomics (often called foodomics or nutritional metabolomics) is the comprehensive analysis of small molecules (metabolites) in food and food-related matrices.
Using our foodomics LC-MS/MS services, you can:
This approach is ideal for data-driven decision-making in product development, process optimization and food research.
When Do You Need Food Metabolomics?
Typical questions that bring clients to a food metabolomics service include:
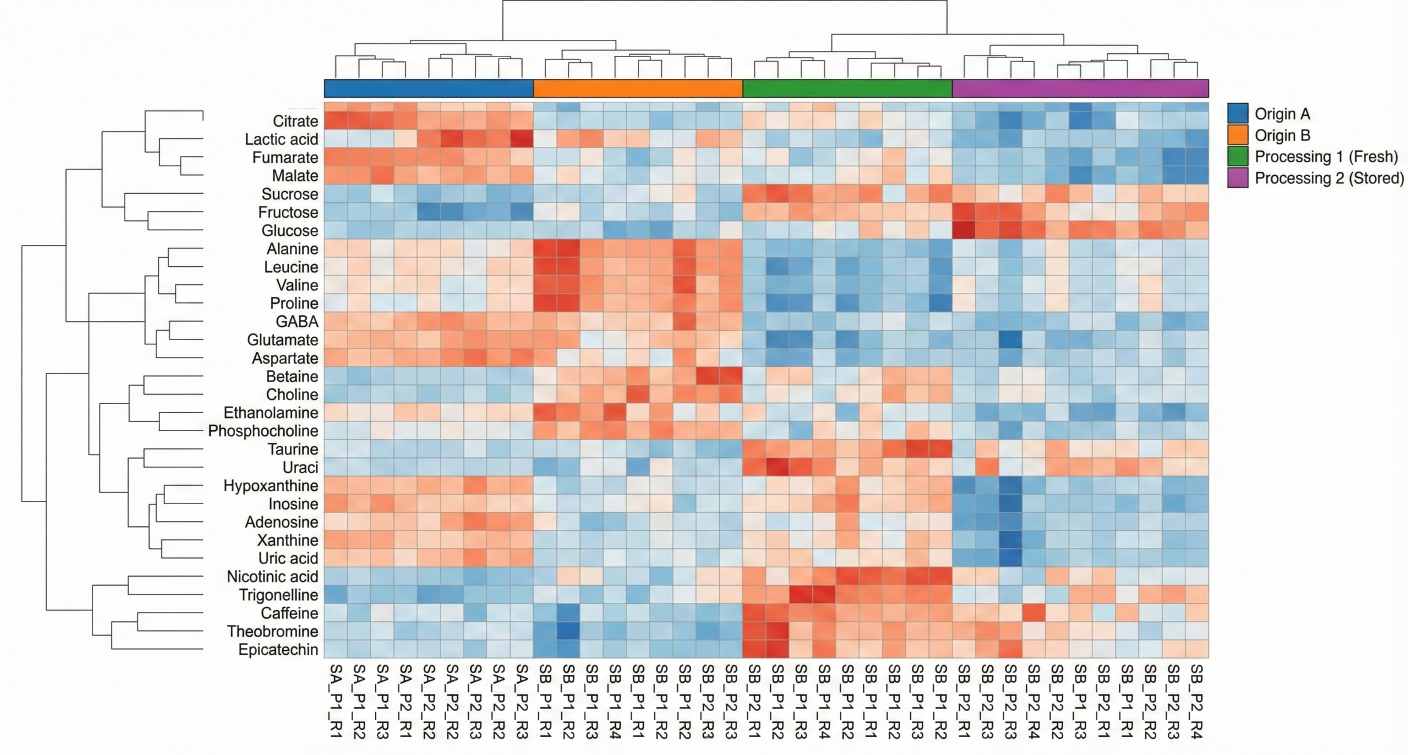
- How do origin, variety or harvest year change the chemical profile of my product?
- Can I use food authenticity metabolomics testing to distinguish genuine from adulterated samples?
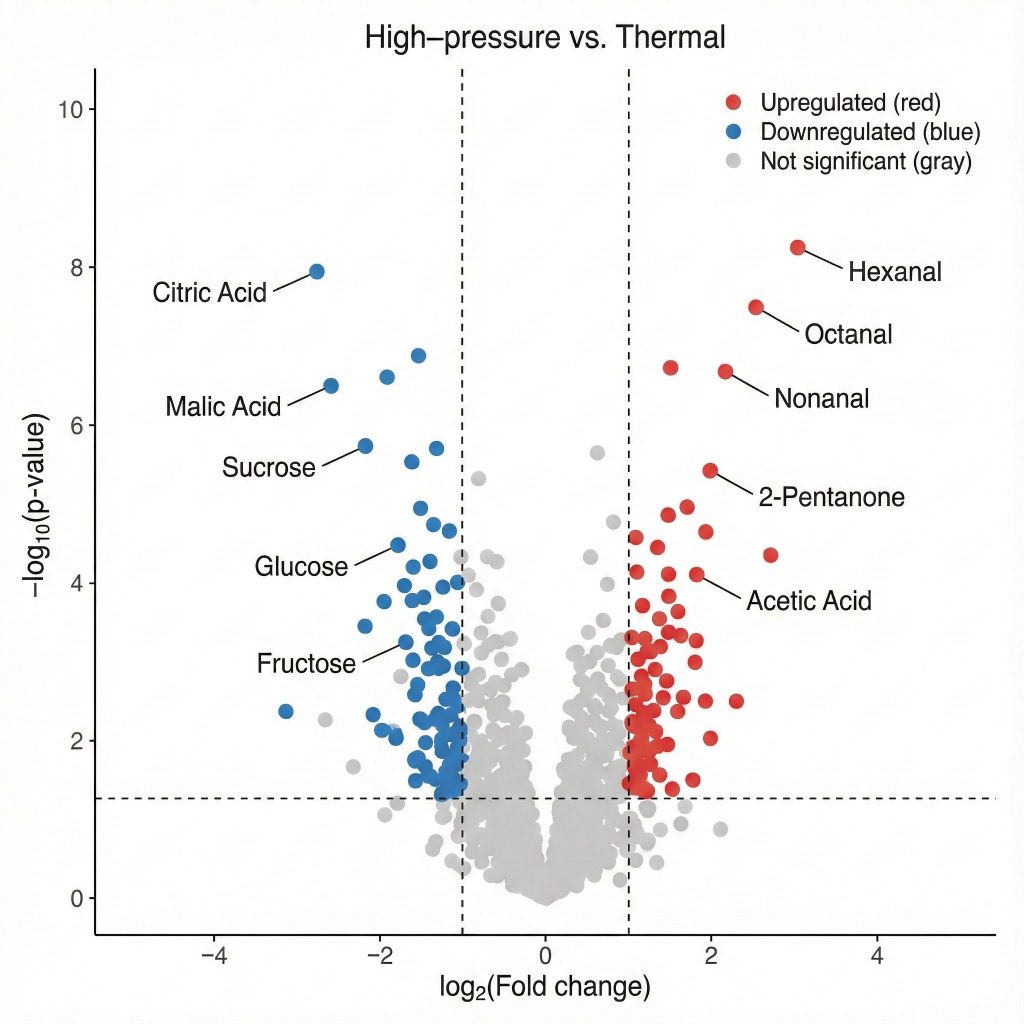
- What is the impact of processing, formulation or packaging on flavor and shelf-life?
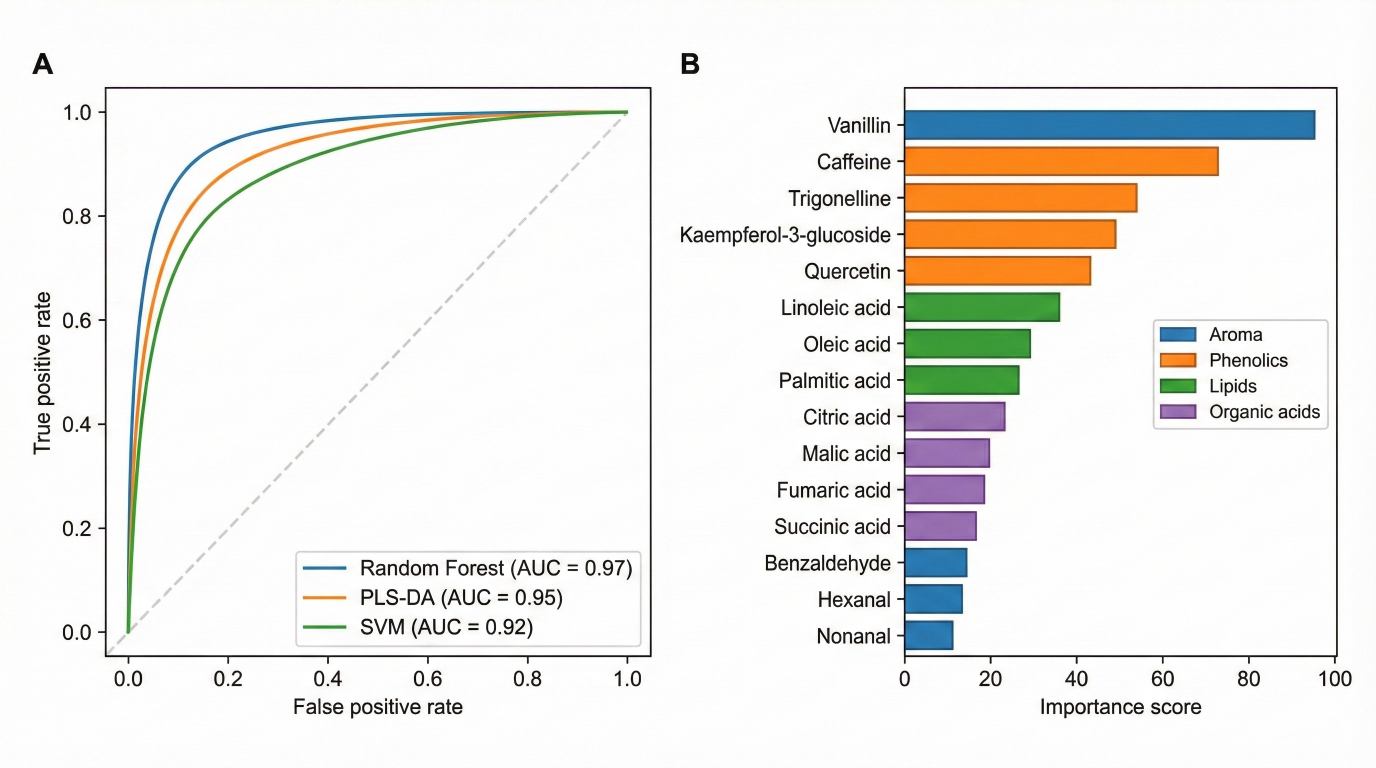
- Which metabolites are associated with consumer liking or sensory scores?
- How do different recipes or ingredients affect the nutritional and functional composition of a food?
Our role is to convert complex spectra into clear comparisons, markers and models that answer these practical questions.
Core Application Areas of Our Food Metabolomics Services
Why Choose Our Food Metabolomics Services?
- Built for Food Matrices
Extraction efficiency and signal stability optimized for complex foods—typically 20–40% higher feature recovery than generic biological protocols.
- Statistically Powered Study Design
We calculate effect size and replicate needs upfront, helping reduce unnecessary samples by 15–30% while maintaining statistical confidence.
- Quantified, Decision-Ready Outputs
Every project includes fold-changes, ranked markers, and validated models (e.g., 70–90% classification accuracy in multi-origin studies), not just raw feature lists.
- Reliable Multi-Factor Insights
Our workflow handles origin × process × storage designs with >90% batch alignment consistency, allowing clean interpretation across complex variables.
- Seamless Discovery-to-Target Workflow
Untargeted to targeted confirmation stays within one pipeline—typically cutting verification time by 25–40% compared with switching vendors.
High-Performance LC–MS/GC–MS Platform for Food Metabolomics
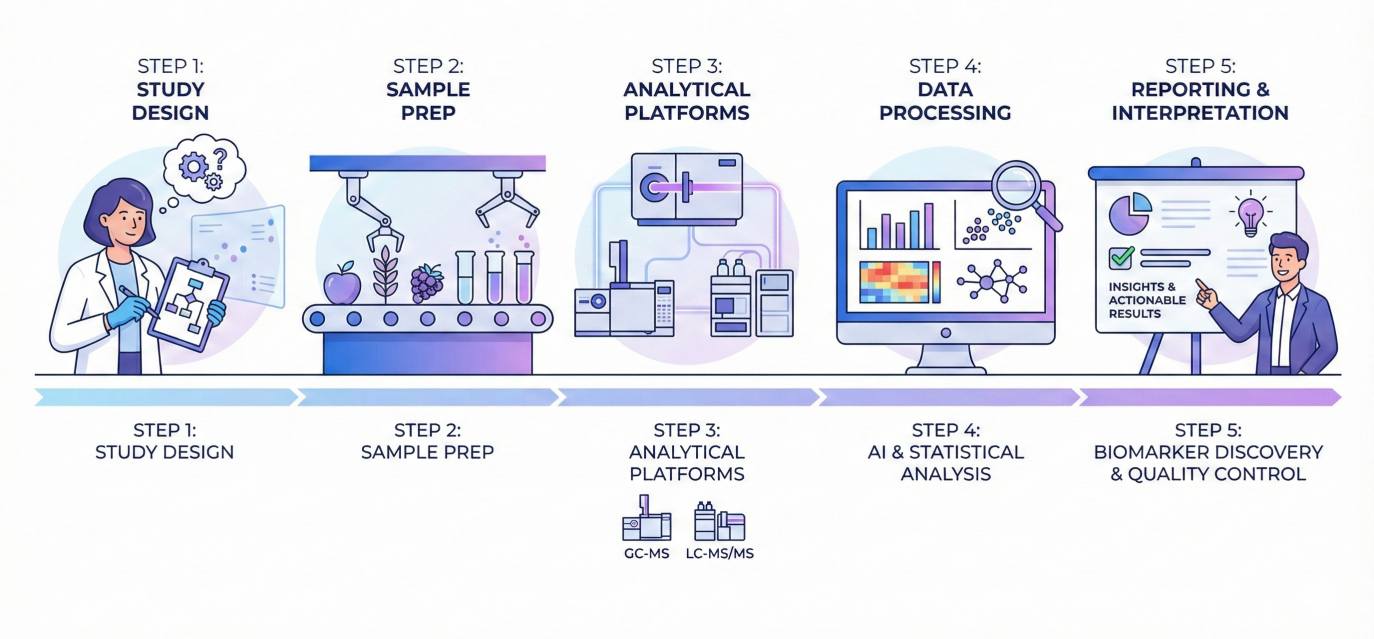
How Our Food Metabolomics Service Works
Sample Submission Requirements for Food Metabolomics
Sample Types & Minimum Amount
| Sample type |
Recommended minimum amount |
| Solid / semi-solid foods |
10–20 g per sample |
| Liquids / beverages |
20–50 mL per sample |
| Extracts / concentrates |
1–2 mL or 50–100 mg per sample |
Handling, Storage & Shipping
| Item |
Recommendation |
Notes |
| Containers |
Use clean, inert polypropylene tubes/bottles; avoid glass for frozen shipment where possible |
Remove packaging, stones, metal pieces and other obvious foreign materials |
| Sample preparation |
Mix heterogeneous products thoroughly to obtain a representative aliquot |
If grinding/homogenizing, avoid contamination from tools (e.g., metal shavings, plastic dust) |
| Storage before shipping |
Store perishable samples at –20 °C or below; high-fat/unstable matrices preferably at –80 °C |
Minimize freeze–thaw cycles; aliquot if you expect multiple uses |
| Labeling |
Clearly label each tube with a sample ID matching your sample list |
Avoid full project names or confidential info on labels |
| Shipping conditions |
Ship frozen samples on dry ice in insulated containers; stable dry products may go ambient |
Please confirm ambient shipment suitability with us before sending |
Deliverables: What You Receive from Food Metabolomics Analysis
- Raw LC–MS/MS or GC–MS data files (by agreement)
- Processed data matrices (features × samples)
- Statistical outputs: PCA/PLS-DA plots, volcano plots, heatmaps, VIP scores and more
- Tables of candidate biomarkers with detailed meta-information
- A comprehensive report, ready to be used in internal decision-making, presentations or manuscripts
- Optional follow-up meeting to discuss results and next steps (e.g. validation experiments or targeted assays)
Multiomics of a rice population identifies genes and genomic regions that bestow low glycemic index and high protein content
Badoni, S., Pasion-Uy, E. A., Kor, S., Kim, S. R., Tiozon Jr, R. N., Misra, G., ... & Sreenivasulu, N.
Journal: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2410598121
Comparative metabolite profiling of salt sensitive Oryza sativa and the halophytic wild rice Oryza coarctata under salt stress
Tamanna, N., Mojumder, A., Azim, T., Iqbal, M. I., Alam, M. N. U., Rahman, A., & Seraj, Z. I.
Journal: Plant-Environment Interactions
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pei3.10155
Physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic insights of three extremophyte woody species living in the multi-stress environment of the Atacama Desert
Gajardo, H. A., Morales, M., Larama, G., Luengo-Escobar, A., López, D., Machado, M., ... & Bravo, L. A.
Journal: Planta
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04484-1
Effects of Aronia melanocarpa juice-powder on hindgut function and performance in post-weaned pigs
Pearce, S. C., Anderson, C. L., & Kerr, B. J.
Journal: Journal of Functional Foods
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2024.106196
Prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a standardized oral pomegranate extract on the gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acids
Sivamani, R. K., Chakkalakal, M., Pan, A., Nadora, D., Min, M., Dumont, A., ... & Chambers, C. J.
Journal: Foods
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010015