What Are Bile Acids?
Bile acids are cholesterol-derived amphipathic molecules that act as detergents, modulators of nutrient absorption, and potent signaling ligands (e.g., via FXR and TGR5). Their chemistry is intricate: primary and secondary species exist as free acids and as glycine/taurine conjugates, with additional sulfated and glucuronidated forms and numerous positional isomers. Because biological matrices contain wide concentration ranges and strong matrix effects, a purpose-built, isomer-aware LC-MS/MS method is essential for robust quantification.
Creative Proteomics provides a customer-oriented bile acids analysis solution that delivers absolute quantitation and isomer-level resolution across human and preclinical matrices, optimized for discovery, mechanism-of-action studies, biomarker research, microbiome–host interaction projects, nutrition science, toxicology, and pharmaceutical R&D.
What Problems We Solve for Our Clients
- Differentiate challenging isomers such as CA vs CDCA or DCA vs UDCA, avoiding data misinterpretation.
- Quantify at ultra-low concentrations in complex matrices like feces, plasma, or bile.
- Minimize matrix effects using optimized extraction and isotope-labeled internal standards.
- Measure a broad spectrum of bile acid species (primary, secondary, conjugated, sulfated, glucuronidated, and muricholic acids) in a single run.
- Deliver decision-ready results with full traceability, validation, and documentation.
Service Scope — Creative Proteomics Bile Acids Analysis
Bile Acids and Related Metabolites – Target Panel Overview
| Category |
Representative Compounds |
Notes |
| Primary Bile Acids |
Cholic acid (CA), Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) |
Synthesized in liver from cholesterol; key in lipid digestion |
| Secondary Bile Acids |
Deoxycholic acid (DCA), Lithocholic acid (LCA), Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA), Isodeoxycholic acid (IDCA), Allocholic acid (ACA), Alloisolithocholic acid (AILCA) |
Formed via gut microbial metabolism of primary bile acids |
| Glycine-Conjugated Bile Acids |
Glycocholic acid (GCA), Glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA), Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA), Glycolithocholic acid (GLCA), Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA), Glycohyodeoxycholic acid (GHDCA), Glycohyocholic acid (GHCA), Glycodehydrocholic acid (GDHCA), Glycoallocholic acid (GACA) |
Increased solubility; facilitates reabsorption in enterohepatic circulation |
| Taurine-Conjugated Bile Acids |
Taurocholic acid (TCA), Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA), Taurodeoxycholic acid (TDCA), Taurolithocholic acid (TLCA), Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), Taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA), Taurohyocholic acid (THCA), Taurodehydrocholic acid (TDHCA) |
Increased solubility; important in bile acid transport |
| Sulfated Bile Acids |
Lithocholic acid-3-sulfate (LCA-3S), Deoxycholic acid-3-sulfate (DCA-3S), Cholic acid-3-sulfate (CA-3S), Glycolithocholic acid-3-sulfate (GLCA-3S), Glycodeoxycholic acid-3-sulfate (GDCA-3S), Taurolithocholic acid-3-sulfate (TLCA-3S), Taurodeoxycholic acid-3-sulfate (TDCA-3S), Tauroursodeoxycholic acid-3-sulfate (TUDCA-3S) |
Phase II metabolism products; more water-soluble, excretory forms |
| Glucuronidated Bile Acids |
Deoxycholic acid-3-glucuronide (DCA-3G), Lithocholic acid-3-glucuronide (LCA-3G), Chenodeoxycholic acid-3-glucuronide (CDCA-3G), Chenodeoxycholic acid-24-β-D-glucuronide (CDCA-24G), Lithocholic acid-24-glucuronide (LCA-24G) |
Detoxification products; aid excretion via urine/bile |
| Rodent-Specific Bile Acids |
Alpha-muricholic acid (α-MCA), Beta-muricholic acid (β-MCA), Omega-muricholic acid (ω-MCA), Lambda-muricholic acid (λ-MCA, Hyocholic acid), Tauro-alpha-muricholic acid (TαMCA), Tauro-beta-muricholic acid (TβMCA), Tauro-omega-muricholic acid (TωMCA), Tauro-lambda-muricholic acid (TλMCA, Taurohyocholic acid) |
Predominant in mouse/rat bile acid profiles |
| Bile Acid Precursors & Intermediates |
7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (C4), 3α,7α-dihydroxycholestenoic acid (DHCA), 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxycholestenoic acid (THCA), 3β-hydroxycholestenoic acid (3βHCA), 3β,7α-dihydroxycholestenoic acid (3β,7αDHCA), 7α-hydroxy-3-oxo-4-cholestenoic acid (7αOH-3O-4CA), Norcholic acid (NorCA), Nordeoxycholic acid (NorDCA), Norursodeoxycholic acid (NorUDCA), Ursocholanic acid (UCA) |
Key biosynthetic intermediates in cholesterol-to-bile acid pathway |
 Don't see a metabolite? We can extend the panel with additional standards or develop a fit-for-purpose assay.
Don't see a metabolite? We can extend the panel with additional standards or develop a fit-for-purpose assay.
Why Choose Our Bile Acids Analysis Service: Key Advantages
- Targeted coverage, isomer aware — Chromatographic methods resolve critical isobaric pairs, protecting data integrity.
- Absolute quantitation with stable-isotope internal standards — Matrix-matched calibration and isotope correction for reliable quantification.
- Dual analytical modes — UPLC-QQQ MRM for sensitivity and throughput; UPLC-HRMS for structural confirmation.
- Method validation data included — R² ≥ 0.99, accuracy/precision within ±15% (±20% at LLOQ).
- Cross-matrix expertise — Harmonized workflows for serum, plasma, feces, bile, liver, cells, and culture media.
- Decision-ready deliverables — Quantitative tables, QC summaries, chromatograms, and pathway analysis.
Bile Acids Assay Technical Details & Coverage
Creative Proteomics quantifies and profiles bile acids using UPLC–MS/MS platforms, including Waters ACQUITY UPLC™ + Sciex Triple Quad™ 5500+/6500+ and Agilent 1290 Infinity II UHPLC + QTRAP® 6500. For high-resolution confirmation, we employ Thermo Scientific™ Q Exactive™ Orbitrap.
Chromatography: Reversed-phase UPLC (C18), gradient elution optimized for bile acid families; isomer-separation conditions applied where needed.
Ionization & detection: Negative-mode ESI for most species; APCI available where advantageous. Triple-quadrupole MRM transitions are established per analyte (quantifier + qualifier).
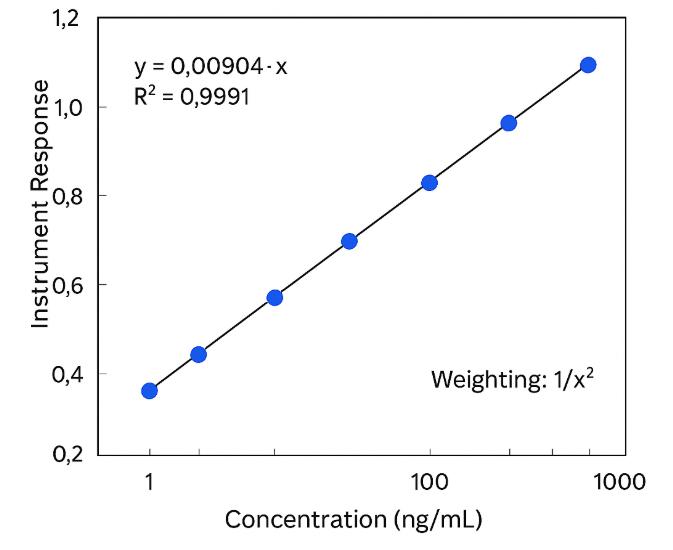
Calibration: 6–8 matrix-matched levels; R² ≥ 0.99; isotope-labeled internal standards (e.g., D₄-CA, D₄-CDCA).
QC: Pooled-matrix QC at low/mid/high levels, spike-recovery, and matrix-effect checks.
Sensitivity & range (typical): LLOQs in low ng/mL (serum/plasma) and low ng/mg (feces/tissue); dynamic range spanning 3–4 orders of magnitude (analyte- and matrix-dependent).
Acceptance targets: Accuracy and precision within ±15% for QCs (±20% at LLOQ); back-calculated calibrators within predefined limits; retention-time and ion-ratio tolerances monitored.
Flexible Service Configurations for Targeted Bile Acid Studies
- Standard Targeted Panel (absolute quantitation)
Primary/secondary bile acids and glycine/taurine conjugates quantified with stable-isotope internal standards where available; optional add-ons for sulfates/glucuronides and muricholic acids.
- Extended Panel (with precursors & intermediates)
Adds C4 and cholestenoic acids to study biosynthetic flux and pathway regulation.
- Hybrid Identification Mode (targeted + HRMS)
For projects requiring additional structural confidence, high-resolution MS/MS libraries and retention-time matching can be enabled.
- Data Analysis Add-Ons
Group stats, volcano plots, enrichment analysis (bile acid pathways), microbiome-linked interpretation with fecal/serum ratioing, and publication-ready visualizations.
How Our Bile Acids Analysis Works — Step-by-Step Process
How to Prepare Your Samples for Bile Acids Quantification
| Matrix / Species |
Minimum Amount |
Container & Handling |
Storage & Shipping |
| Serum / Plasma |
≥50 µL |
PP or glass vials; EDTA or heparin plasma acceptable |
Freeze promptly; ship on dry ice |
| Urine |
≥50 µL |
No additives/detergents |
Freeze; ship on dry ice |
| Feces |
≥20 mg (homogenized preferred) |
Sterile, screw-cap tube |
Freeze; ship on dry ice |
| Bile |
≥50 µL |
Low-bind tubes |
Freeze; ship on dry ice |
| Liver / Tissue |
≥10 mg |
Pre-weighed cryovials or foil |
Snap-freeze; ship on dry ice |
| Cells |
≥2×10⁶ (pellet) |
PBS rinse; remove media |
Snap-freeze pellet; ship on dry ice |
| Culture Supernatant |
≥200 µL |
Clarify by centrifugation |
Freeze; ship on dry ice |
| Dried Blood Spot |
2–3 punches (3–6 mm) |
Card in gas-permeable pouch with desiccant |
Keep dry & cool; cold-chain preferred |
Applications of Bile Acids Profiling & Quantification
Deliverables: What You Get from Our Bile Acids Analysis Service
Comprehensive Concentration Tables — Absolute values in ng/mL, nmol/L, or ng/mg as appropriate.
QC Performance Summary — Calibration curve metrics, QC recoveries, and precision data.
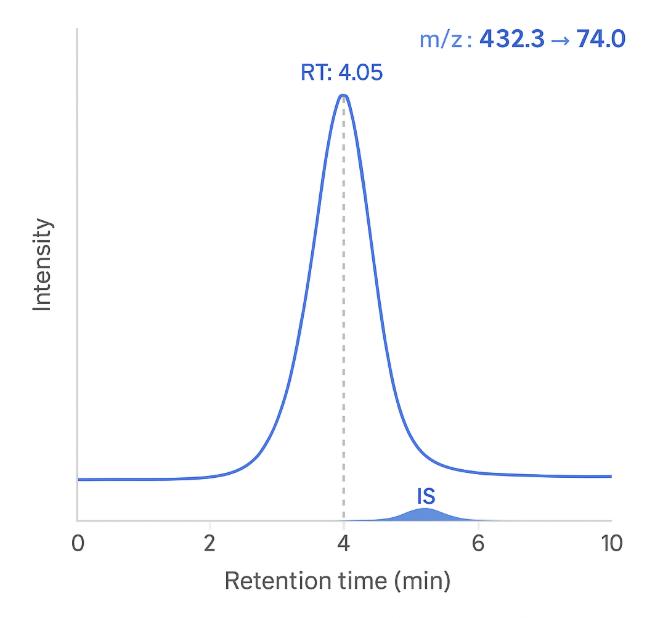
Annotated Chromatograms — Demonstrating analyte resolution and peak quality.
Method Sheet — Key parameters for transparency and reproducibility.
Optional Data Analysis — Statistics, fold-change, volcano plots, pathway enrichment, and microbiome-related interpretation.
Publication-Ready Visuals — Box plots, heatmaps, and bile acid pathway diagrams.
Comprehensive Bile Acids Profiling in a High-Fat Diet Rodent Model
Objective
A pharmaceutical research team sought to evaluate the impact of a high-fat diet (HFD) on bile acid composition in a murine model, aiming to understand gut–liver axis alterations and potential metabolic dysregulation. The study required isomer-level resolution, quantitation across multiple biological matrices, and comparative analysis against control animals.
Approach
Creative Proteomics applied its extended panel bile acids analysis using UPLC–Triple Quad™ 6500+ MS/MS. Sample matrices included serum, feces, and liver extracts from HFD-fed and control mice.
- Sample Preparation: Matrix-specific extraction with protein precipitation and SPE clean-up to minimize matrix effects.
- Chromatographic Separation: Reversed-phase C18 UPLC with optimized gradient to resolve critical isomers such as α-, β-, and ω-muricholic acids.
- Detection & Quantitation: Negative-mode ESI with MRM transitions validated for each analyte; stable-isotope-labeled internal standards for accuracy.
- Data Analysis: Concentration normalization per matrix type, fold-change calculations, and bile acid pathway enrichment mapping.
Key Findings
- Significant Elevation of taurine-conjugated muricholic acids (TαMCA, TβMCA) in feces of HFD-fed mice, indicating altered bile acid metabolism and reduced microbial deconjugation activity.
- Reduced Levels of secondary bile acids such as deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), suggesting microbiota compositional shifts.
- Pathway Analysis revealed downregulation of bile salt hydrolase–related metabolism and altered FXR/TGR5 signaling potential.
Deliverables to Client
- Absolute quantitation tables for >40 bile acid species across all matrices.
- QC performance summary (R² ≥ 0.99, precision within ±15%).
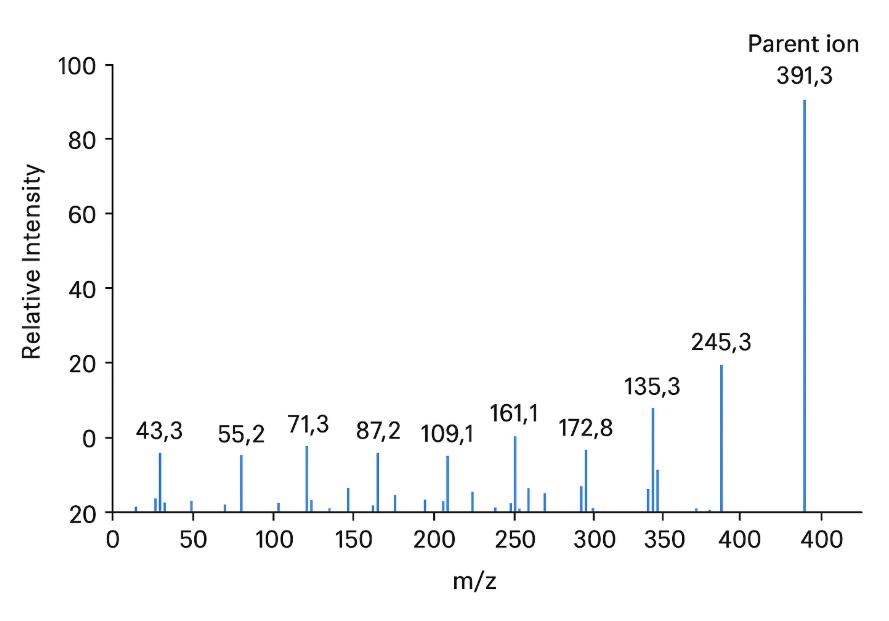
- Extracted ion chromatograms and representative product ion spectra for key compounds.
- Pathway enrichment diagrams highlighting differences between HFD and control groups.
Reference
- Liu, Jui-Tung, et al. "A human iPSC-derived hepatocyte screen identifies compounds that inhibit production of Apolipoprotein B." Communications Biology 6.1 (2023): 452.
Quantifying forms and functions of intestinal bile acid pools in mice
Sudo, K., Delmas-Eliason, A., Soucy, S., Barrack, K. E., Liu, J., Balasubramanian, A., … & Sundrud, M. S.
Journal: bioRxiv
Year: 2024
A human iPSC-derived hepatocyte screen identifies compounds that inhibit production of Apolipoprotein B
Liu, J. T., Doueiry, C., Jiang, Y. L., Blaszkiewicz, J., Lamprecht, M. P., Heslop, J. A., … & Duncan, S. A.
Journal: Communications Biology
Year: 2023