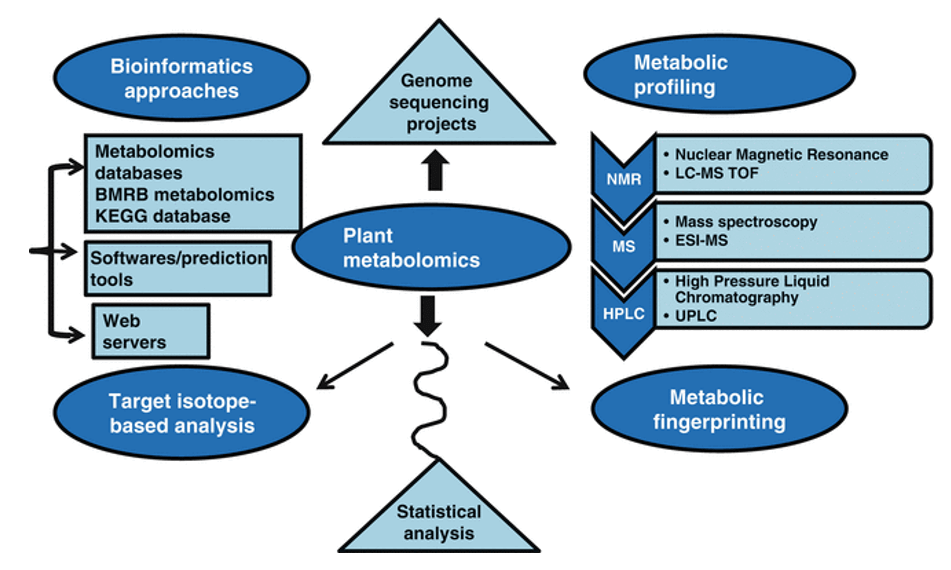
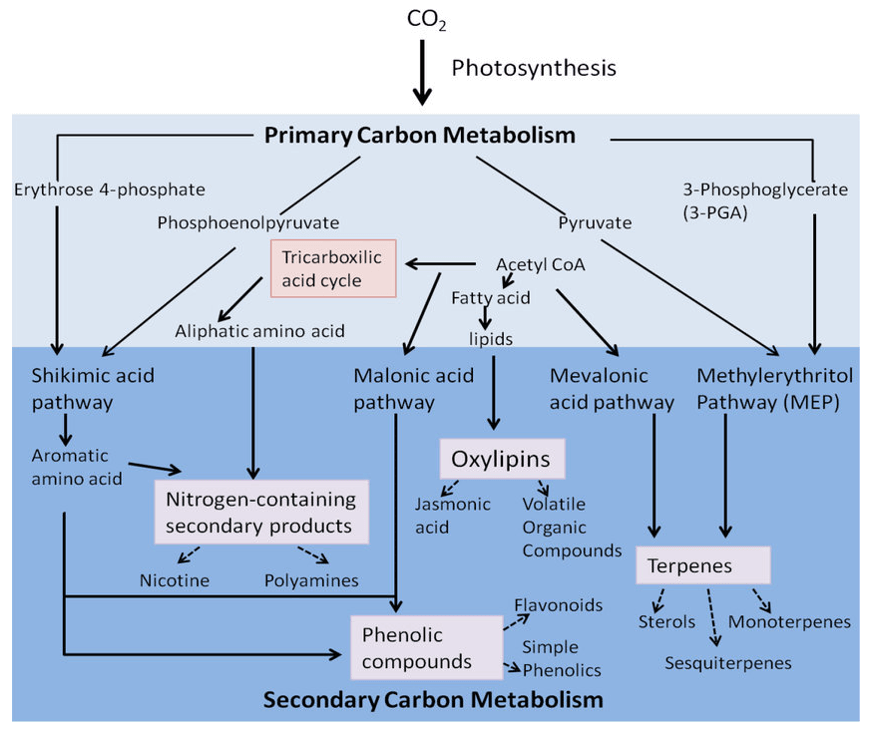
What is Saponin?
Saponins are plant glycosides that can form aqueous or colloidal solutions and soap-like foam. Saponins consist of saponin, sugar and uronic acid or other organic acid. According to the known molecular structure of saponin, saponins can be divided into two categories, one is steroid saponins, and the other is triterpenoid saponins. Saponins are mostly white or milky amorphous powder, a few are crystal, and have irritation to mucosa. Saponins are generally soluble in water, methanol and dilute ethanol, very soluble in hot water, hot methanol and hot ethanol, insoluble in ether, chloroform and benzene. Ginsenoside is the most effective medicinal ingredient of ginseng. There are nearly 30 kinds of ginsenoside, and each kind of ginsenoside has its specific pharmacological function. Soyasaponins have many beneficial physiological functions on human body. In addition to being used as medicine, soyasaponins can also be used in chemical industry as advanced cosmetics, food additives and surfactants. Mass spectrometry is a sensitive analytical technique that enables detection, identification and quantification of a variety of saponins by measuring their mass and characterizing their chemical structure, even at low abundance. MS instruments combine with either high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or electrospray ionization (ESI) to effectively separate organic molecules from complex samples.
Advantages of Our Saponins Analysis Service
Excellent saponins qualitative and quantitative capabilities. Creative Proteomics has rich experience in saponins sample handling and can analyze saponins present in a variety of plant species at cell/tissue level.
Professional data analysis skills. Our professional and technical personnel can analyze the HPLC-MS and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS data accurately, in detail and comprehensively to ensure the scientific nature and consistency of the results.
Years of plant metabolomics project management experience and mature SOP. We have professional and scientific SOP analysis procedures, which can ensure the efficient progress of customers' projects, saving time and money. We can also make one-to-one one-stop personalized service plan according to the special needs of customers.
Workflow of Saponins Analysis Service
Since different tissues have different matrix properties, Creative Proteomics has developed multiple novel sample preparation techniques. Our services allow the profiling of various types of saponins, including ginsenoside, soyasaponins, etc.
Mode: MRM
Precision: pmol
Linear: R2 > 0.99
Saponins Analysis Content
Saponin Extraction: Efficient extraction of saponins from various samples using optimized methods to capture these natural compounds effectively.
Saponin Purity Analysis: Determination of the purity of saponin samples through quantitative analysis techniques such as chromatography or spectroscopy.
Saponin Structural Identification: Utilization of advanced techniques such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance for the structural identification of saponins.
Saponin Content Determination: Accurate quantification of saponin content in samples, providing precise concentration information for further research and development.
Herbal Medicine Saponin Analysis: Analysis of saponin components in herbal medicines and plant extracts, contributing to quality control and standardization.
Biological Activity Assessment: Evaluation of the biological activity of saponins, exploring potential applications in pharmacology, antioxidation, and anti-inflammation.
Environmental Sample Saponin Analysis: Extraction and analysis of saponins from environmental samples such as soil or water, supporting environmental monitoring and ecological studies.
Saponin Detection in Food and Beverages: Detection of saponin content in food and beverages, ensuring product quality compliance with regulatory standards.
Customized Analysis Services: Tailored saponin analysis services designed to meet specific requirements, addressing the unique needs of various industries and research areas.
List of Detectable Saponins at Creative Proteomics
| Astragaloside | Betulinic Acid Saponin | Dioscin | Escin | Ginsenoside |
| Hederagenin | Quillaja Saponin | Saikosaponin | Soyasaponin | Tea Saponins |
| Digitonin | Triterpenoid Saponins |
|
|
|
Sample Requirements of Saponins Analysis
| Sample Type | Sample Quantity (g) |
|---|
| Plant Extract | 5-10 |
| Herbal Powder | 2-5 |
| Plant Leaves | 10-20 |
| Plant Roots | 10-15 |
| Seeds | 5-8 |
| Commercial Product | 5-10 |
Applications of Saponins Analysis
Drug Development: Unlock the therapeutic potential of medicinal plants through precise saponin content analysis, facilitating the identification of compounds for anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer drug development.
Quality Control in Food and Beverage Industry: Ensure the excellence and safety of food products with thorough saponin content analysis, preventing undesirable flavors and maintaining the sensory profile of our culinary offerings.
Cosmetics and Personal Care: Craft superior formulations in cosmetics and personal care products by leveraging saponin content analysis, enabling the optimal use of natural surfactant and foaming properties for a luxurious user experience.
Agriculture for Plant Protection: Spearhead environmentally friendly pest control strategies by analyzing saponin levels in plants, harnessing their disruptive effects on pest cell membranes to safeguard crops.
Environmental Monitoring for Phytoremediation: Contribute to environmental cleanup with saponin content analysis, identifying plant species rich in saponins for effective phytoremediation in contaminated areas.
Detergent Industry for Bio-based Detergents: Ensure the efficacy of eco-friendly bio-based detergents through saponin content analysis, harnessing the natural cleaning power of saponins in detergent formulations.
Livestock Nutrition in Animal Feed Industry: Optimize animal diets with precise saponin content analysis, considering the impact of saponins on the nutritional value of plant materials in animal feed for enhanced livestock well-being.
Biomedical Research for Cell Membrane Studies: Propel advancements in biomedical research by studying cell biology and membrane dynamics through saponin content analysis, capitalizing on saponins' ability to disrupt cell membranes.
Herbal Medicine Production for Standardization: Elevate the quality and efficacy of herbal medicines through saponin content analysis, ensuring standardized preparations with therapeutic saponins for holistic well-being.
Biotechnology for Emulsification: Drive innovation in biotechnological processes with saponin content analysis, optimizing fermentation and bioconversion through the emulsifying properties of saponins.
Delivery
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- Purity analysis report
- HPLC-MS/ HPLC-ESI-MS/MS raw data files and HPLC-MS/ HPLC-ESI-MS/MS data quality checks
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Mass spectrometry-based profiling of saponins enables quantitative analyses of saponins in a faster, convenient, and sensitive manner. With decades of experience in mass spectrometry services, Creative Proteomics has a proven track record supporting diverse saponins detection and quantification. We can meet your specific project requirements, from sampling to bioinformatics.
Case: Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus Terrestris Fruit Against Ischemic Stroke: Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology Approach.
Background
Ischemic stroke, a leading cause of death and disability globally, primarily results from interrupted blood supply to the brain. Despite thrombolysis being the primary treatment, there is a lack of universally accepted and effective therapies. Traditional Chinese herbal medicine, specifically Gross Saponins of Tribulus Terrestris Fruit (GSTTF), has shown promise in protecting against cerebral ischemia. This study aims to evaluate the protective effect of GSTTF using metabolomics and network pharmacology techniques.
Samples
Thirty adult male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into sham, MCAO (middle cerebral artery occlusion), and GSTTF-treated groups. Urine samples were collected for LC-MS metabolomics analysis.
Technical Methods
- Animals were acclimatized and treated with GSTTF via tail vein injection before and after MCAO surgery.
- Infarct volume and neurological defect scores were measured to assess the protective effect.
- LC-MS analysis of urine samples, employing a Vanquish Duo UHPLC system and Q-Orbitrap mass spectrometer, was performed to profile endogenous metabolites.
- Multivariate statistical analysis, including PLS-DA, was applied to identify metabolite differences among groups.
- Biomarker selection criteria included VIP values (>2), fold change (>2), and statistical significance (p < 0.05).
- Metabolite annotation was achieved by matching accurate mass and MS/MS data with databases.
- Network pharmacology analysis utilized the TCMSP database to establish compound–target and disease–target networks.
- A compound–target–disease network was constructed to identify potential therapeutic targets.
Results:
GSTTF demonstrated a neuroprotective effect against MCAO-induced ischemic stroke, as evidenced by reduced neurological defects and infarct volume in rats.
LC-MS-based metabolomics identified 14 biomarkers associated with MCAO, including altered levels of branched-chain amino acids, citric acid, and phenylalanine.
Network pharmacology analysis highlighted NOS2 and GSK3B as potential therapeutic targets for the protective effect of GSTTF.
The identified biomarkers and their related pathways provided insights into the metabolic changes associated with ischemic stroke and the potential mechanisms of GSTTF.
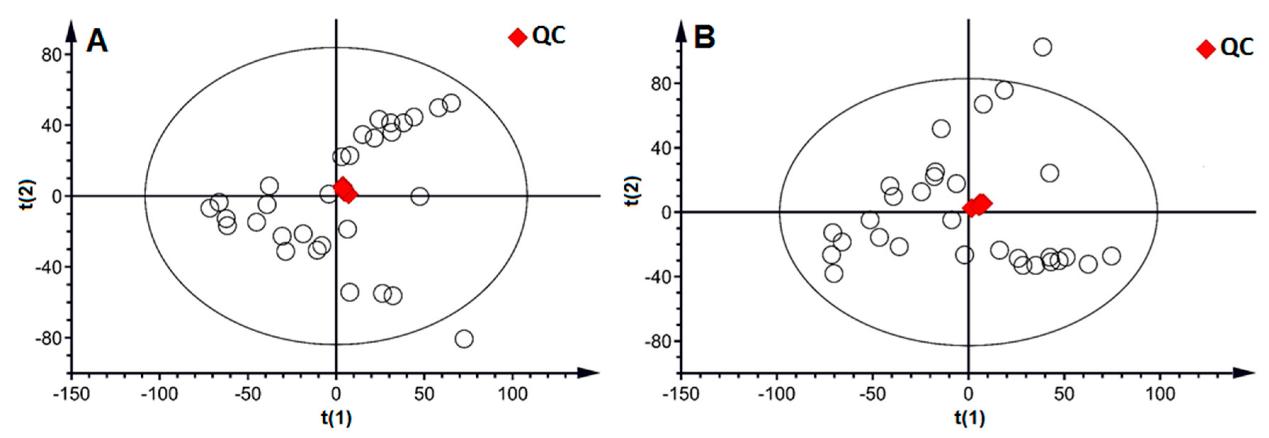 The PCA score plot of all samples (○) with the highlight of the QC (♦) sample in positive ion mode (A) and negative ion mode (B).
The PCA score plot of all samples (○) with the highlight of the QC (♦) sample in positive ion mode (A) and negative ion mode (B).
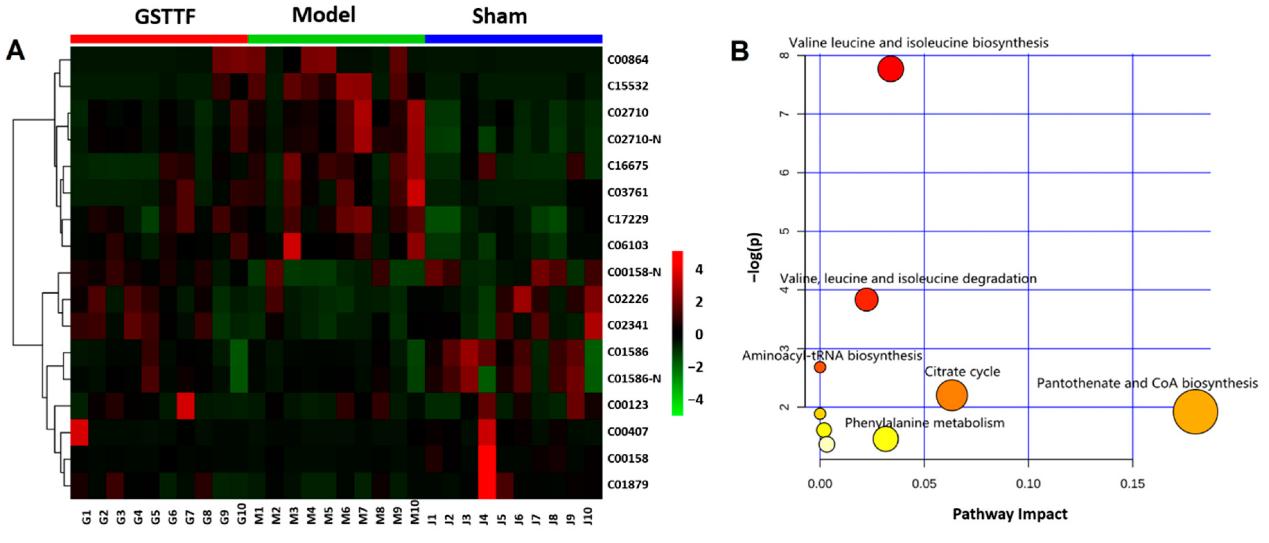 Heat map (A) visualizing the changes in the intensities of potential biomarkers and bubble plot (B) of the main perturbed pathway response to MCAO.
Heat map (A) visualizing the changes in the intensities of potential biomarkers and bubble plot (B) of the main perturbed pathway response to MCAO.
Reference
- Wang, Yang, et al. "Investigating the protective effect of gross saponins of Tribulus terrestris fruit against ischemic stroke in rat using metabolomics and network pharmacology." Metabolites 9.10 (2019): 240.



 The PCA score plot of all samples (○) with the highlight of the QC (♦) sample in positive ion mode (A) and negative ion mode (B).
The PCA score plot of all samples (○) with the highlight of the QC (♦) sample in positive ion mode (A) and negative ion mode (B). Heat map (A) visualizing the changes in the intensities of potential biomarkers and bubble plot (B) of the main perturbed pathway response to MCAO.
Heat map (A) visualizing the changes in the intensities of potential biomarkers and bubble plot (B) of the main perturbed pathway response to MCAO.