Overview
Polyketide is a general term for compounds synthesized by polyketide biosynthetic pathway. Polyketides have great application value in anti-infection, anti-fungal, anti-tumor and immunosuppressive aspects. Polyketides are mainly synthesized by polyketide synthase(PKS), which can be divided into PKS I, PKS II, and PKS III. Polyketides are divided into two types: aromatic cyclic polyketides and non-aromatic cyclic polyketides, that is, macrocyclic polyketides. These two types of compounds are synthesized by type II polyketide synthase synthesis pathway(PKS II) and type I polyketide synthase synthesis pathway(PKS I) respectively. N-methylation plays an important role in the biosynthesis of aromatic polyketides, when 4-amino anhydrotetracycline(ATC) is used as a substrate and incubated with purified oxo thiamine (OxyT) in the reaction system. HPLC/MS results show that ATC is only produced in the presence of OxyT(Figure 1). Experiments show that OxyT is a catalytically active substance with N-methylation, which can catalyze monomethylation and demethylation reactions, which proves the potential of OxyT in the biosynthesis of innovative aromatic polyketides. Among them, PKS I is mainly composed of functional domains such as keto synthase(KS), enol reductase(ER), acyltransferase(AT), dehydrogenase (DH), and ketoreductase(KR); PKS II mainly catalyzes Synthesis of tetracyclic and anthracycline compounds; PKS III is mainly chalcone synthase, mainly exists in the plant kingdom, and is responsible for the synthesis of flavolin and other components(Figure 2). With the LC-MS/MS method, neutral loss(NL) detects polyketides which is characterized via their fragmentation patterns, and then selection reaction monitoring(SRM) quantify its contents.
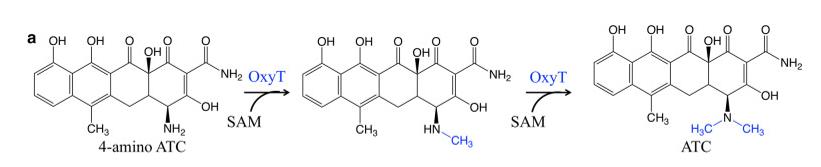 Figure 1. N-methyltransferase OxyT involved in biosynthesis of ATC. (Wang 2020).
Figure 1. N-methyltransferase OxyT involved in biosynthesis of ATC. (Wang 2020).
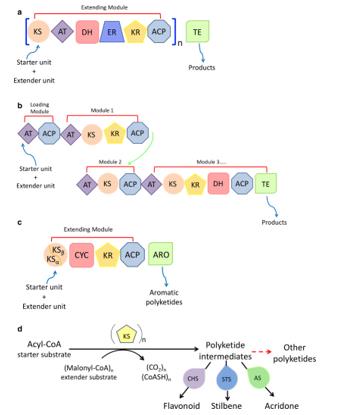 Figure 2. Catalytic reaction of PKSs. (Wang 2020).
Figure 2. Catalytic reaction of PKSs. (Wang 2020).
Applications of Polyketides Analysis
- Polyketide compound identification analysis application
- Research on the biological activity functions of polyketides in anti-infection and anti-fungal effects
- Study on the molecular mechanism of metabolic drugs such as immunosuppressive and anti-cancer activity of polyketides
- Increase the molecular identification and understanding of the molecular mechanism and the metabolic activity of polyketides
- Improvement of polyketide compound application products
- Analysis of the content of polyketides
- Ensure the quality and safety of polyketide products
- Product development of polyketide metabolites
Advantages of Our Polyketides Analysis Service
Use the LC-MS platform to accurately detect and quantify polyketides
First-class laboratory equipment and mature technical methods to ensure extreme sensitivity and selectivity
Fast turnaround time and flexible statistical analysis methods
Provide one-stop service and competitive price
Service Workflow
Our operation technology process meets the requirement of lower detection limit (minimum limit of quantification is 0.0002-0.01μg/kg), and calmly copes with the detection and analysis of polyketides in complex matrix. The sample does not need to be derivatized and the automatic mode is used for detection and analysis, which can ensure the integrity of the sample and reduce human error, so it can achieve high-throughput detection and obtain more accurate analysis reports.
 Figure 3. Polyketides analysis service workflow.
Figure 3. Polyketides analysis service workflow.
Detection method: LC-MS/MS
Monitoring phase: A: acetonitrile, B: water (containing 0.1% formic acid, 2.0 mM ammonium acetate)
Flow rate: 0.4 ml/min
Running time: 10 min
Elution mode: gradient elution
Ion source mode: electrospray ion source, positive ion mode (ESI+)
Back blow: 75
Atomization gas: 220
Ion source spray voltage: 5000 V
Recovery rate: 92.25-105.87%
Method reproducibility: 1.53-4.78%
Lowest limit of quantification: 0.0002-0.01μg/kg
Analysis content:
- Construction of standard curve
- Optimization of elution conditions
- Chromatographic separation condition screening
- Repeatability measurement analysis
- Repeated stability analysis
- Chromatogram raw image and data collection
- Chromatographic peak analysis
- Quantitative analysis of polyketides and its metabolites
Sample Requirements
1. Tissues such as leaves, roots, stems, flowers, fruit pulp, peel tissue, etc., larger leaves need to be quickly cut into pieces with scissors, and the separated samples are quickly washed with sterilized water, and the absorbent paper is immediately put into the liquid after absorbing the excess water. Quickly freeze in nitrogen for more than 2 minutes, and then transfer to -80°C for storage to avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
2. Cell samples, centrifuge after sampling, remove the culture medium, immediately put them in liquid nitrogen for quick freezing for more than 2 minutes, and then transfer to -80°C for storage.
3. For each sample, take no less than 3 g for fresh samples, no less than 1 g for dry samples. At least three biological replicates in each group, prepare a backup. The measured sample will not be returned, please keep a backup.
Delivery
- Complete experimental steps
- Sample purification processing analysis
- Chromatographic separation and screening conditions analysis
- Analysis of optimized parameters of LC equipment
- Chromatogram raw image and data collection and analysis
- Identification and content analysis report of polyketides
- Quantitative data of polyketide metabolites
- Customized analysis report
Using the combined method of LC and MS can obtain high-quality identification and quantitative analysis reports of polyketides and their metabolites, which can help researchers to increase their understanding of the types of active molecules and molecular mechanisms of polyketides. Creative Proteomics strives to provide you with more valuable and innovative research tools and solutions in the analysis and application of polyketide related fields.
References
- Wang J, Zhang R, et al. Biosynthesis of aromatic polyketides in microorganisms using type II polyketide synthases. Microbial Cell Factories. 2020;19(1):110.
- Chen H, Bian Z, et al. Biosynthesis of polyketides by trans-AT polyketide synthases in Burkholderiales. Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 2019;45(2):162-181.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.


 Figure 1. N-methyltransferase OxyT involved in biosynthesis of ATC. (Wang 2020).
Figure 1. N-methyltransferase OxyT involved in biosynthesis of ATC. (Wang 2020). Figure 2. Catalytic reaction of PKSs. (Wang 2020).
Figure 2. Catalytic reaction of PKSs. (Wang 2020). Figure 3. Polyketides analysis service workflow.
Figure 3. Polyketides analysis service workflow.