What is TMAO?
Trimetlylamine oxide (TMAO) is a small molecule compound widely found in aquatic products in nature, but also in mammals, plants, and fungi. TMAO is involved in a variety of important biological functions of the organism, such as osmoregulation and maintenance of intracellular homeostasis.
In recent years, with the in-depth study of intestinal flora, scientists have found that the levels of TMAO and related metabolites are closely related to various diseases such as cardiovascular disease, myocardial infarction, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and cancer. The complete quantitative analysis of TMAO and related metabolites can provide a reliable basis for the diagnosis and prediction of related diseases, etiology and pathogenesis research, and efficacy assessment.
In humans, TMAO is mainly derived from the oxidation of trimethylamine (TMA) by intestinal flora. Intestinal microorganisms metabolize and produce TMAO from ingested nutrients such as lecithin and choline. TMAO enters the liver via the portal circulation, where it is oxidized by flavin monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) or other flavin monooxygenases (FMOx) to produce TMAO. TMAO precursors also include carnitine, betaine, creatinine, etc.
Based on the UHPLC-MS technology platform, Creative Proteomics can perform absolute qualitative and quantitative analysis of TMAO, TMA, choline, betaine, creatinine and l-carnitine, ensuring good separation of multiple isoforms. The use of representative isotopes as internal standard calibration significantly improves the accuracy of qualitative and quantitative detection with excellent sensitivity, precision, reproducibility and accuracy.
Applications of TMAO Quantitative Analysis
- Disease marker screening
- Diagnosis and typing of diseases
- Diagnosis of disease recurrence
- Etiology and pathological mechanism investigation
- Clinical efficacy evaluation
- Drug toxicology evaluation
List of Substances Detectable by Creative Proteomics
| Betaine |
Choline |
Creatinine |
Imidazolepropionic acid |
| L-Carnitine |
Trimethylamine (TMA) |
Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) |
Dimethylamine |
| Dimethylglycine |
Glycine |
Methionine |
Proline |
| N,N-Dimethylglycine |
N,N-Dimethylarginine |
|
|
Technical Advantages of TMAO Analysis
- Isotope internal standard correction, absolute quantification by external standard method, providing absolute concentration data.
- Provide PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA, one-dimensional test, Random Forest and SVM screening, ROC and other analytical results.
- Strict quality control system to ensure the reliability of the data
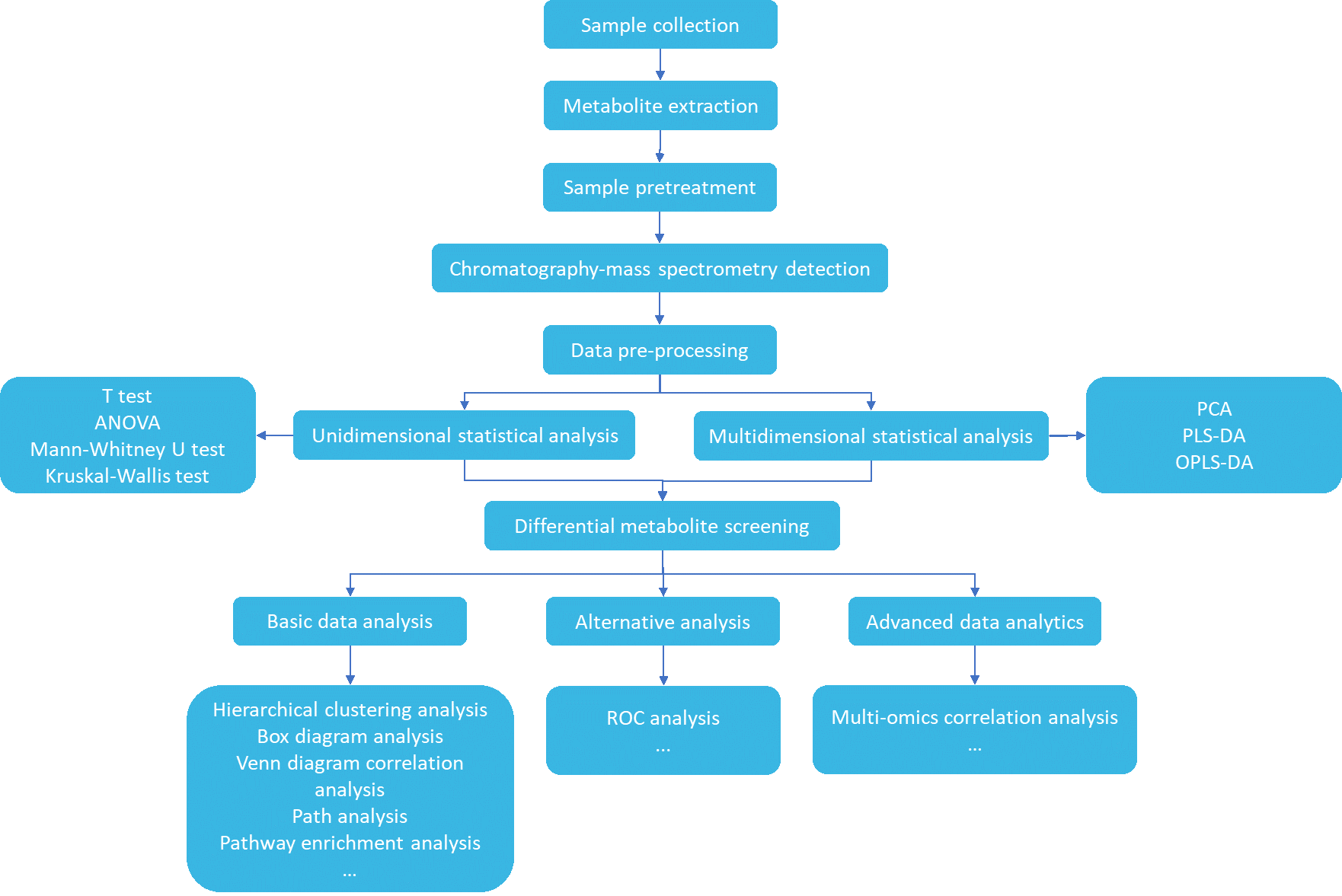
Service Workflow of TMAO Quantitative Analysis
Sample Requirements for TMAO Detection
| Sample Type |
Recommended Volume |
Preservation Requirements |
| Blood Plasma |
0.5 - 1 mL |
Collect in EDTA tubes; Store at -80°C |
| Serum |
0.5 - 1 mL |
Collect in serum separator tubes; Store at -80°C |
| Urine |
1 - 5 mL |
Collect in sterile containers; Freeze immediately at -20°C or below |
| Tissues (e.g., liver) |
20 - 100 mg |
Flash freeze in liquid nitrogen and store at -80°C |
| Microbial Cultures |
Varies |
Preserve with appropriate buffers; Freeze immediately at -80°C |
| Saliva |
0.5 - 1 mL |
Collect in sterile containers; Freeze immediately at -20°C or below |
| Feces |
Varies |
Collect in sterile containers; Freeze immediately at -20°C or below |
| Cell Culture Supernatant |
Varies |
Freeze immediately at -80°C |
Deliverables
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
- MS raw data files and MS data quality checks
- Absolute quantitative data
- Custom analysis report
Project Cycle
A standard experiment and analysis process takes about 2~6 weeks.
Creative Proteomics provides TMAO and related metabolite quantification services with accurate and detailed data and analytical reports. If you want to detect other metabolites, you can tell us through the inquiry form, and our technicians will communicate with you.
Case: Multi-Omic Analysis Reveals Complex Associations of Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) with Cardiovascular Disease Markers and Gut Microbiome Patterns
Background
Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) has emerged as a potential risk factor in cardiovascular disease (CVD) development. This study aims to comprehensively investigate the associations between TMAO and various biological factors, including blood markers, metabolites, proteins, diet, and gut microbiome patterns.
Samples
The study includes a large-scale, cross-sectional analysis of 648 individuals participating in a lifestyle intervention program. De-identified multi-omic data, encompassing clinical labs, metabolites, proteins, and gut microbiome sequencing, were collected from these individuals. The cohort offers a diverse representation for a robust investigation.
Techniques Methods
Clinical Laboratory Tests: Blood samples were collected up to three times over a 12-month period, measuring clinical markers and anthropometric parameters. Rigorous protocols were followed, including fasting and lifestyle restrictions before blood draws.
Gut Microbiome Sequencing: Stool specimens were collected using standardized kits, and microbial DNA was isolated and sequenced using MiSeq profiling of the 16S V4 region. Predicted KEGG profiles were employed to assess the functional composition of the gut microbiome.
Metabolomics: Metabolon conducted assays on plasma samples, involving extensive sample handling, quality control, and data extraction. The metabolome analysis included biochemical identification, curation, quantification, and normalization of metabolite data.
Proteomics: Plasma concentrations of proteins were measured using arrays, and ComBat normalization was applied to adjust for potential batch effects.
Results
Kidney Function Association: TMAO is confirmed as a prognostic biomarker for kidney function, independent of age and sex.
Age and Sex Correlations: Males exhibit significantly higher TMAO levels, even after adjusting for age and kidney function.
Lack of Correlation with Traditional CVD Markers: TMAO does not show significant correlations with established blood markers for CVD.
Dietary Associations: TMAO levels are correlated with omega-3 fatty acids, mercury, and vitamin D, indicating potential links with fish consumption and animal-rich diets.
Microbiome and Metabolite Patterns: Associations between TMAO and gut microbiome composition, specific metabolites, and microbial pathways are identified. Clustering analysis reveals diverse metabolic profiles among individuals with elevated TMAO levels.
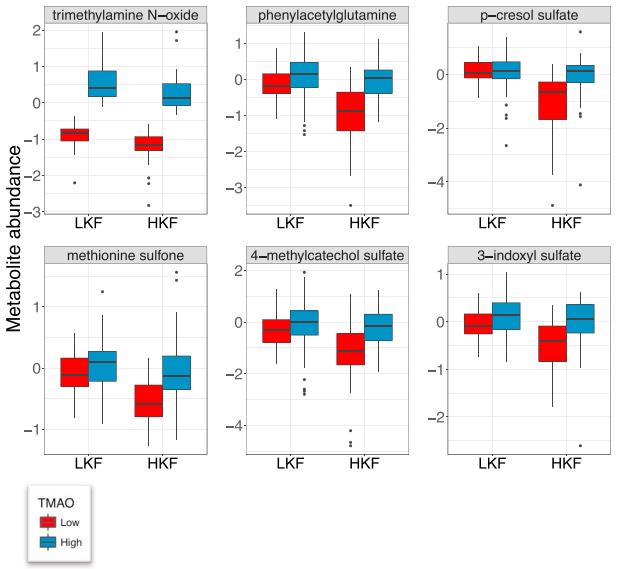 Metabolites that Are Significantly Higher Only in High Kidney Function Individuals with Elevated TMAO Levels
Metabolites that Are Significantly Higher Only in High Kidney Function Individuals with Elevated TMAO Levels
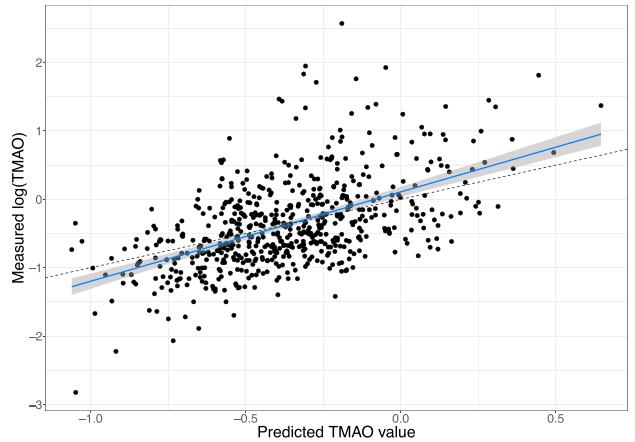 Random Forest Model Predicting TMAO Value
Random Forest Model Predicting TMAO Value
Reference
- Manor, Ohad, et al. "A multi-omic association study of trimethylamine N-oxide." Cell reports 24.4 (2018): 935-946.



 Metabolites that Are Significantly Higher Only in High Kidney Function Individuals with Elevated TMAO Levels
Metabolites that Are Significantly Higher Only in High Kidney Function Individuals with Elevated TMAO Levels Random Forest Model Predicting TMAO Value
Random Forest Model Predicting TMAO Value