Puerarin is an isoflavone compound extracted from the dried roots of the legume pueraria lobata or pueraria lobata, which can improve myocardial metabolism and vascular microcirculation, and dilate coronary blood vessels. Puerarin has low toxicity, clear and extensive pharmacological effects. It has the functions of improving immunity, dilating blood vessels, lowering blood pressure, protecting myocardial cells, anti-tumor, anti-aging, promoting blood circulation, producing body fluid and anti-platelet aggregation. It is widely used in a variety of applications of pharmaceutical products. The UPLC-MS/MS method has the characteristics of strong specificity and high sensitivity. It can make the anti-interference ability strong through the correspondence between the characteristic parent ions and product ions of different compounds, and realize the functions of separation and identification, which provides a reference for the quality control and evaluation of puerarin.
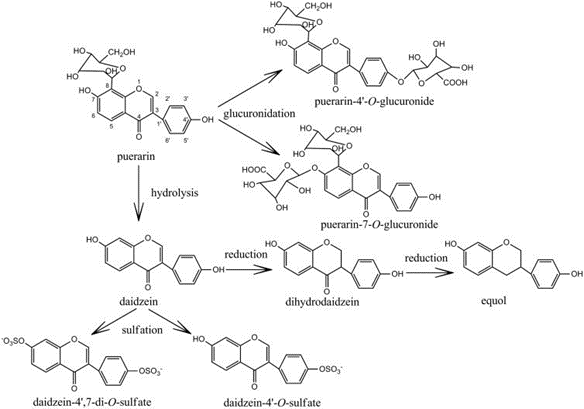 Figure 1. Chemical structures of puerarin and its metabolites. (Zhang 2019)
Figure 1. Chemical structures of puerarin and its metabolites. (Zhang 2019)
Applications of Puerarin Analysis
- The content analysis and application of puerarin
- Quality control of active molecules in drugs
- Development of medicinal value and evaluation of efficacy
- Improve the understanding of the mechanism of puerarin's biological activity
Advantages of Our Puerarin Analysis Service
- Highly selective determination of puerarin content using first-class UPLC-MS/MS platform
- Provide innovative technical tools and experienced scientific research team
- Meet the testing needs of multiple types of complex samples
- Fast turnaround time and low price
- Provide one-stop service and high-quality service level
Service Workflow
Our operation technology process adopts the method of switching between positive and negative ions. The acquisition mode selects MRM to scan the sample to be tested, and the most abundant product ion is used as the quantitative ion, which ensures the specificity and accuracy of the method.
 Figure 2. Puerarin analysis service workflow.
Figure 2. Puerarin analysis service workflow.
Detection method: quantitative analysis by external standard method
Mobile phase: acetonitrile-4mmol/l ammonium formate aqueous solution
Elution method: isocratic elution
Volume flow: 1ml/min
Average sample recovery rate: 98.75%-100.86%
Injection volume: 4ul
Reaction mode: positive ion multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode
Analysis content:
- Standard curve drawing
- Selection of chromatographic conditions
- Precision, repeatability and stability test
- Sample recovery test
- Chromatogram and mass spectrum raw image and data collection
- Determination of Puerarin
Sample Requirements
1. The samples from the separated roots, stems and other tissues are quickly rinsed with sterile water, and the absorbent paper is immediately placed in the liquid after absorbing the excess water. Quickly freeze in nitrogen for more than 2 minutes, then transfer to -80°C for storage, avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
2. For each sample, take no less than 3 g for fresh samples, no less than 1 g for dry samples. At least three biological replicates in each group, prepare a backup. The measured sample will not be returned, please keep a backup.
Delivery
- Comprehensive experimental procedure
- Sample pretreatment analysis
- UPLC-MS/MS chromatogram and mass spectrum and data analysis report
- Quantitative determination of puerarin
- Customized analysis report
UPLC-MS/MS can realize highly sensitive and selective determination and analysis of the content of puerarin, which can meet the determination and analysis of actual samples with low content of puerarin. The simple and fast operation steps can greatly shorten the analysis cycle. Creative Proteomics has rich biological resources and a first-class UPLC-MS/MS determination platform, and we are dedicated to providing you with quality services.
Reference
- Jung HR, Kim SJ, Ham SH, et al. Simultaneous determination of puerarin and its active metabolite in human plasma by UPLC-MS/MS: application to a pharmacokinetic study. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences. 2014;971:64-71.


 Figure 1. Chemical structures of puerarin and its metabolites. (Zhang 2019)
Figure 1. Chemical structures of puerarin and its metabolites. (Zhang 2019) Figure 2. Puerarin analysis service workflow.
Figure 2. Puerarin analysis service workflow.