What is Targeted Metabolomics?
Targeted metabolomics is a highly precise analytical approach focused on the absolute or relative quantification of a specific set of known metabolites. Unlike untargeted metabolomics—which profiles the global metabolome—targeted analysis delivers quantitative data for metabolites of interest, with exceptional sensitivity and reproducibility. This precision is critical for biomarker validation, pharmacokinetic studies, regulatory submissions, and mechanistic research.
Whether you’re monitoring key metabolic pathways, verifying hypotheses, or ensuring regulatory compliance, targeted metabolomics empowers you to achieve robust, actionable insights with unparalleled confidence.
Why Choose Targeted Metabolomics for Your Research?
Targeted metabolomics is the right choice when your research requires:
- Precise Quantification
You need accurate, absolute concentrations of specific metabolites for biomarker validation, clinical studies, or regulatory submissions.
- Detection of Low-Abundance Compounds
Some key metabolites exist at trace levels and demand high sensitivity and selectivity for reliable detection.
- Focused Pathway Analysis
Your project targets specific metabolic pathways linked to diseases, biological processes, or treatment effects.
- Reproducibility Across Batches
Consistent, comparable data is essential for multi-sample or multi-center studies.
- Minimal Sample Volumes
Your samples are precious or limited, requiring efficient analysis without compromising quality.
Targeted metabolomics helps transform these research needs into actionable insights, supporting decision-making across biomedical research, drug development, nutrition, and other fields.
How We Help You Achieve Reliable Results
Our Targeted Metabolomics Service is designed around your needs, helping you move from data to discovery with confidence and clarity.
Here’s how we support your research:
- Precision and Reproducibility
We use advanced LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS platforms, along with carefully optimized protocols, to deliver consistent, high-quality data you can rely on.
- High Sensitivity for Low-Abundance Metabolites
Our methods can detect metabolites present at very low levels, enabling accurate measurement of biomarkers or pathway-specific compounds that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Biological Interpretation Included
We provide more than just raw numbers. Our reports connect your quantitative results to biological pathways, trends, and potential implications for your study.
- Minimal Sample Requirements
Our workflows are optimized for small sample volumes, helping you conserve valuable material without compromising data quality.
- Custom Panels for Your Goals
We can tailor metabolite panels to your research focus—whether you’re investigating specific pathways, disease mechanisms, or particular classes of metabolites.
- Rigorous Quality Control
Every project includes thorough checks for accuracy, consistency, and data integrity, ensuring you receive trustworthy results.
- Expert Support at Every Step
Our team is available to discuss your goals, recommend optimal strategies, and help interpret your results to keep your project moving forward.
List of Detected Metabolites
Targeted metabolomics detectable substances include but are not limited to:
Indoles and Indole-sulfur Compounds
5
Cofactors and Vitamins
12
Carbohydrate Metabolism
14
Targeted Metabolomics Technical Details & Coverage
Our targeted metabolomics services employ industry-standard instruments and methods to deliver precise, reliable data for a wide range of research and industrial applications. Here’s a quick guide to help you choose the optimal platform for your specific needs:
| Platform |
Typical Instruments |
Suitable Metabolites |
LOD / LOQ |
Common Applications |
| LC-MS/MS |
- Agilent 6495C Triple Quad
- SCIEX 6500+ Triple Quad
- Thermo TSQ Altis |
Amino acids, bile acids, organic acids, lipids, steroids |
< 1–2 ng/mL |
Biomarker quantification, clinical studies, pharmacokinetics, targeted pathway analysis |
| GC-MS/MS |
- Agilent 7890B + 5977A MSD |
Organic acids, sugars, volatile metabolites, FAMEs |
< 10 ng/mL |
Organic acid profiling, food safety, environmental analysis |
| UHPLC-QTOF-MS |
- Agilent 6546 Q-TOF
- Waters Xevo G2-XS |
Lipids, polyphenols, flavonoids, complex metabolites |
~ ng/mL – low pg/mL |
High-resolution targeted profiling, structural elucidation, confirmation of unknowns |
| HPLC (LC) |
- Agilent 1260 Infinity II
- Waters ACQUITY UPLC |
Chromatographic separation of diverse metabolites |
N/A (non-MS detection) |
Sample preparation, method development, pre-MS separation |
| NMR |
- Bruker AVANCE III HD 600 MHz
- JEOL ECZ Series |
Central carbon metabolites, sugars, lipids |
~ 1–10 μM |
Broad-spectrum metabolic profiling, comparative studies without internal standards |
How to Choose?
- Need ultra-sensitive quantification of biomarkers? → LC-MS/MS
- Working with volatile metabolites like organic acids or sugars? → GC-MS/MS
- Interested in high-resolution profiles and structural information? → UHPLC-QTOF-MS
- Seeking robust, label-free profiling with minimal prep? → NMR
- Need solid separation before MS analysis? → HPLC (LC)
Workflow for Targeted Metabolomics Service
Sample Requirements for Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
| Sample Type |
Recommended Volume/Amount |
Storage Temperature |
Notes |
| Plasma / Serum |
≥ 50 µL |
-80°C |
Collect in EDTA or heparin tubes; avoid hemolysis |
| Urine |
≥ 200 µL |
-80°C |
Midstream collection preferred; avoid preservatives |
| Tissue |
≥ 20 mg |
-80°C |
Snap-freeze in liquid nitrogen; store dry |
| Cell Pellets |
≥ 1 million cells |
-80°C |
Wash with PBS, remove media before freezing |
| Cell Culture Supernatant |
≥ 500 µL |
-80°C |
Collect at desired time points; avoid repeated freeze-thaw |
| Feces / Stool |
≥ 50 mg |
-80°C |
Store in airtight containers; minimize air exposure |
| Plant Material |
≥ 50 mg |
-80°C |
Freeze immediately after harvest; dry if necessary |
How Targeted Metabolomics Supports Your Research and Development
What Results Will You Receive from Targeted Metabolomics?
Quantitative Data Tables
Detailed tables showing absolute or relative concentrations of each targeted metabolite, enabling precise comparisons across your samples and groups.
Quality Control Reports
Information on internal standards, calibration curves, and QC samples to demonstrate the reliability and consistency of your results.
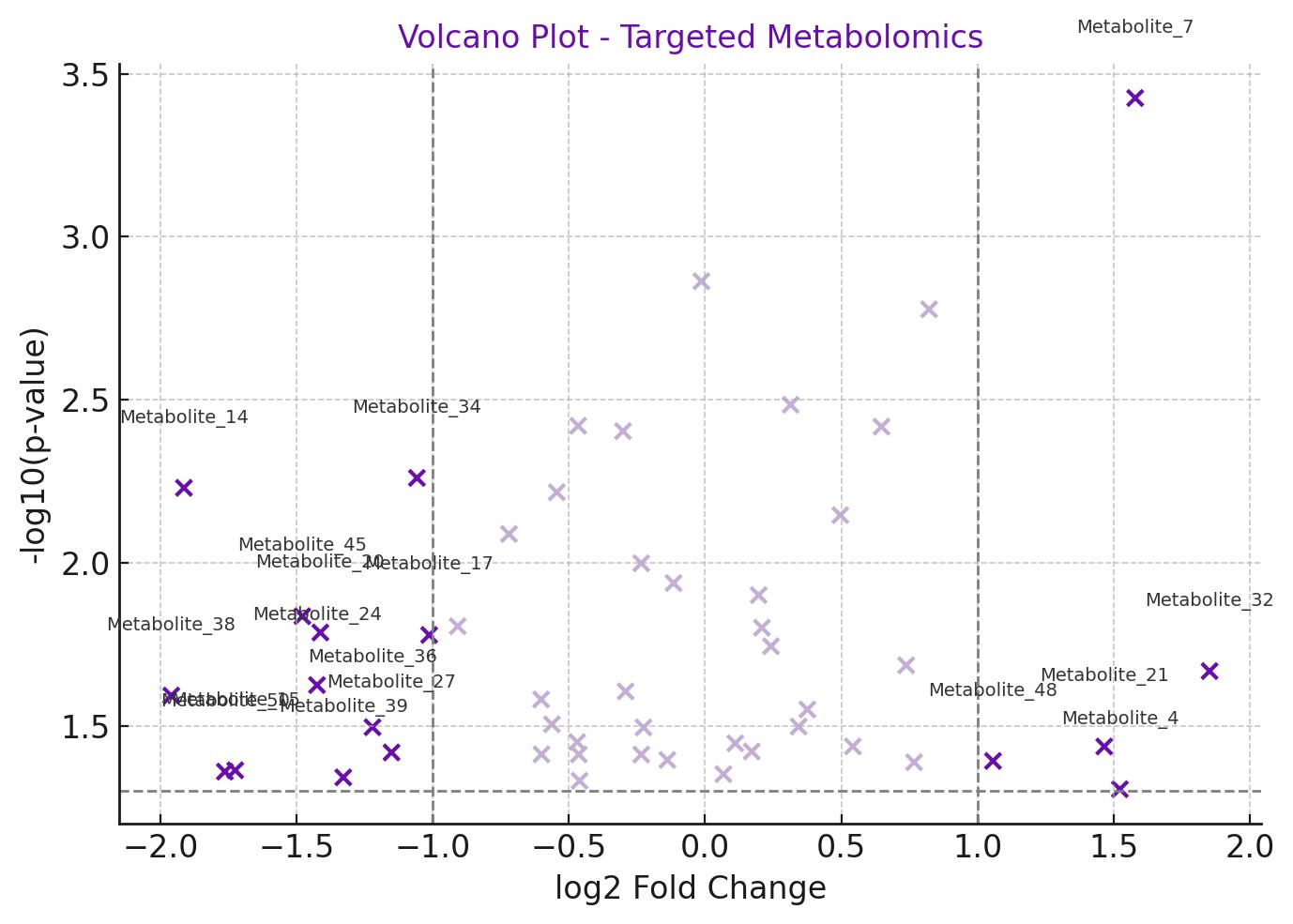
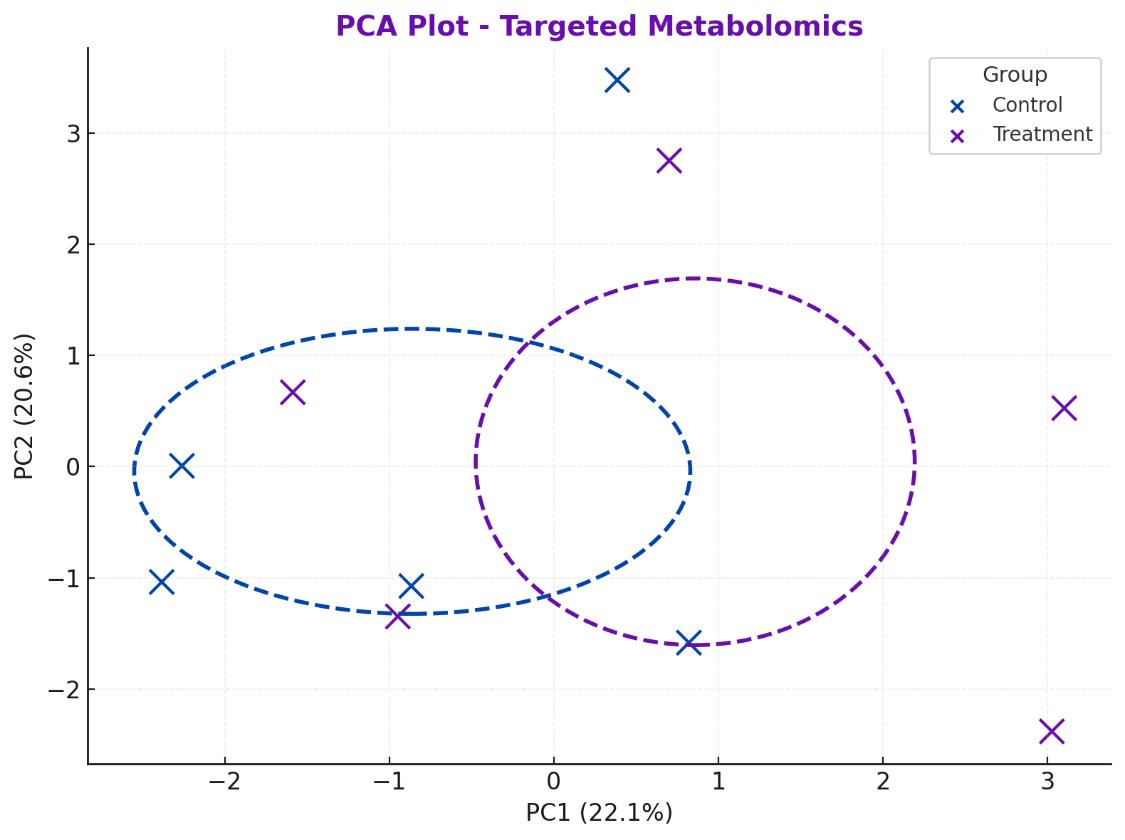
Data Visualizations
Clear charts and plots, such as heatmaps, volcano plots, or PCA plots, to help you quickly identify trends, significant changes, and metabolic patterns.
Biological Interpretation
Expert analysis connecting metabolite changes to biological pathways, helping you understand the potential implications of your data.
Raw Data Files
Access to raw instrument files (e.g., .raw, .wiff, .d) if you wish to perform your own analysis or data integration.
Targeted Metabolomics Supports Discovery of Methyl Donor Benefits in Neurodegeneration
Background
A leading neuroscience research team investigating neurodegenerative tauopathies sought to determine how methyl donor supplementation—specifically L-methylfolate, choline, and betaine—affects one-carbon metabolism and tau pathology in a transgenic mouse model (TAU58/2 mice).
Challenge:
The researchers required:
- Accurate quantification of low-abundance metabolites linked to one-carbon metabolism and oxidative stress.
- Data sensitive and reproducible enough for correlating metabolic changes with tau pathology.
- Fast turnaround to align with behavioral testing timelines in their animal study.
Our Solution
Creative Proteomics developed a customized targeted metabolomics panel tailored to the client's experimental goals. The panel included:
- One-carbon metabolism markers: betaine, choline, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), total plasma homocysteine (tHcy).
- Antioxidant markers: glutathione (GSH).
- Neurotransmitters: acetylcholine (Ach).
Leveraging HPLC-MS/MS on the Agilent 1290 UHPLC coupled with the Sciex 4000 QTRAP mass spectrometer, our team delivered:
- Highly sensitive and precise quantification via multiple reaction monitoring (MRM).
- Triplicate measurements for statistical robustness.
- Timely data delivery that matched the researchers' project schedule.
Results & Findings
Through our targeted metabolomics analysis, the client discovered:
- A ~1.5-fold increase in betaine, ~1.3-fold increase in choline, and ~2.4-fold increase in 5-MTHF in mice receiving methyl donor supplementation.
- A significant ~20% reduction in total plasma homocysteine levels.
- Dramatically elevated glutathione levels in the supplemented group, suggesting improved antioxidant defenses.
These metabolic changes were directly associated with reduced pathological phosphorylation of tau and improved motor and learning performance in the tauopathy mouse model. The data provided critical biochemical insights supporting the therapeutic potential of methyl donors in neurodegenerative diseases.
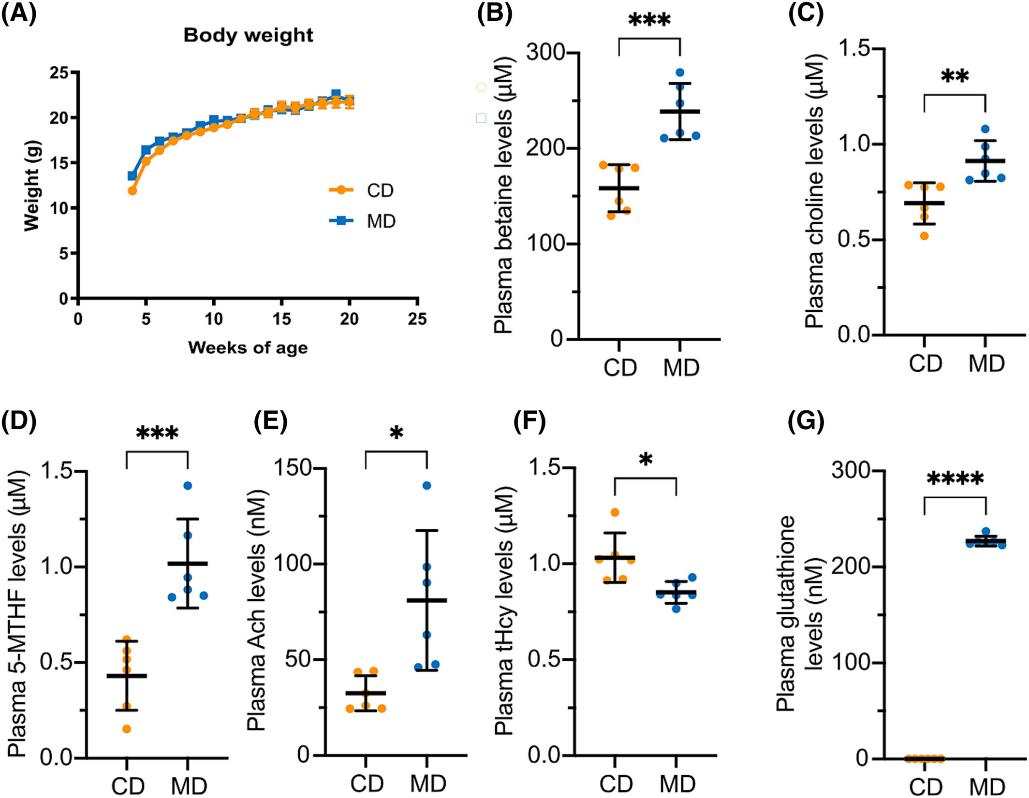 Impact of methyl donor supplementation on one-carbon metabolism in TAU58/2 mice. (A) Body weight unchanged between methyl donor (MD) and control diet (CD) groups. (B–G) Plasma levels of betaine, choline, 5-MTHF, acetylcholine, total homocysteine, and glutathione. Data: mean ± SD (n=6); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001.
Impact of methyl donor supplementation on one-carbon metabolism in TAU58/2 mice. (A) Body weight unchanged between methyl donor (MD) and control diet (CD) groups. (B–G) Plasma levels of betaine, choline, 5-MTHF, acetylcholine, total homocysteine, and glutathione. Data: mean ± SD (n=6); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001.
Reference
- van Hummel, Annika, et al. " Methyl donor supplementation reduces phospho‐Tau, Fyn and demethylated protein phosphatase 2A levels and mitigates learning and motor deficits in a mouse model of tauopathy." Neuropathology and applied neurobiology 49.4 (2023): e12931.
High Levels of Oxidative Stress Early after HSCT Are Associated with Later Adverse Outcomes
Cook, E., Langenberg, L., Luebbering, N., Ibrahimova, A., Sabulski, A., Lake, K. E., ... & Davies, S. M.
Journal: Transplantation and Cellular Therapy
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtct.2023.12.096
Multiomics of a rice population identifies genes and genomic regions that bestow low glycemic index and high protein content
Badoni, S., Pasion-Uy, E. A., Kor, S., Kim, S. R., Tiozon Jr, R. N., Misra, G., ... & Sreenivasulu, N.
Journal: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2410598121
The Brain Metabolome Is Modified by Obesity in a Sex-Dependent Manner
Norman, J. E., Milenkovic, D., Nuthikattu, S., & Villablanca, A. C.
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063475
UDP-Glucose/P2Y14 Receptor Signaling Exacerbates Neuronal Apoptosis After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats
Kanamaru, H., Zhu, S., Dong, S., Takemoto, Y., Huang, L., Sherchan, P., ... & Zhang, J. H.
Journal: Stroke
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.123.044422
Pan-lysyl oxidase inhibition disrupts fibroinflammatory tumor stroma, rendering cholangiocarcinoma susceptible to chemotherapy
Burchard, P. R., Ruffolo, L. I., Ullman, N. A., Dale, B. S., Dave, Y. A., Hilty, B. K., ... & Hernandez-Alejandro, R.
Journal: Hepatology Communications
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/HC9.0000000000000502
Comparative metabolite profiling of salt sensitive Oryza sativa and the halophytic wild rice Oryza coarctata under salt stress
Tamanna, N., Mojumder, A., Azim, T., Iqbal, M. I., Alam, M. N. U., Rahman, A., & Seraj, Z. I.
Journal: Plant‐Environment Interactions
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pei3.10155
Teriflunomide/leflunomide synergize with chemotherapeutics by decreasing mitochondrial fragmentation via DRP1 in SCLC
Mirzapoiazova, T., Tseng, L., Mambetsariev, B., Li, H., Lou, C. H., Pozhitkov, A., ... & Salgia, R.
Journal: iScience
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110132
Physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic insights of three extremophyte woody species living in the multi-stress environment of the Atacama Desert
Gajardo, H. A., Morales, M., Larama, G., Luengo-Escobar, A., López, D., Machado, M., ... & Bravo, L. A.
Journal: Planta
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111098
A personalized probabilistic approach to ovarian cancer diagnostics
Ban, D., Housley, S. N., Matyunina, L. V., McDonald, L. D., Bae-Jump, V. L., Benigno, B. B., ... & McDonald, J. F.
Journal: Gynecologic Oncology
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2023.12.030
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis is prevented by dietary prune in female mice
Chargo, N. J., Neugebauer, K., Guzior, D. V., Quinn, R. A., Parameswaran, N., & McCabe, L. R.
Journal: Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1324649
Proteolytic activation of fatty acid synthase signals pan-stress resolution
Wei, H., Weaver, Y. M., Yang, C., Zhang, Y., Hu, G., Karner, C. M., ... & Weaver, B. P.
Journal: Nature Metabolism
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-023-00939-z







 Impact of methyl donor supplementation on one-carbon metabolism in TAU58/2 mice. (A) Body weight unchanged between methyl donor (MD) and control diet (CD) groups. (B–G) Plasma levels of betaine, choline, 5-MTHF, acetylcholine, total homocysteine, and glutathione. Data: mean ± SD (n=6); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001.
Impact of methyl donor supplementation on one-carbon metabolism in TAU58/2 mice. (A) Body weight unchanged between methyl donor (MD) and control diet (CD) groups. (B–G) Plasma levels of betaine, choline, 5-MTHF, acetylcholine, total homocysteine, and glutathione. Data: mean ± SD (n=6); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001.