Brassinosteroid (BR) Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryOverview
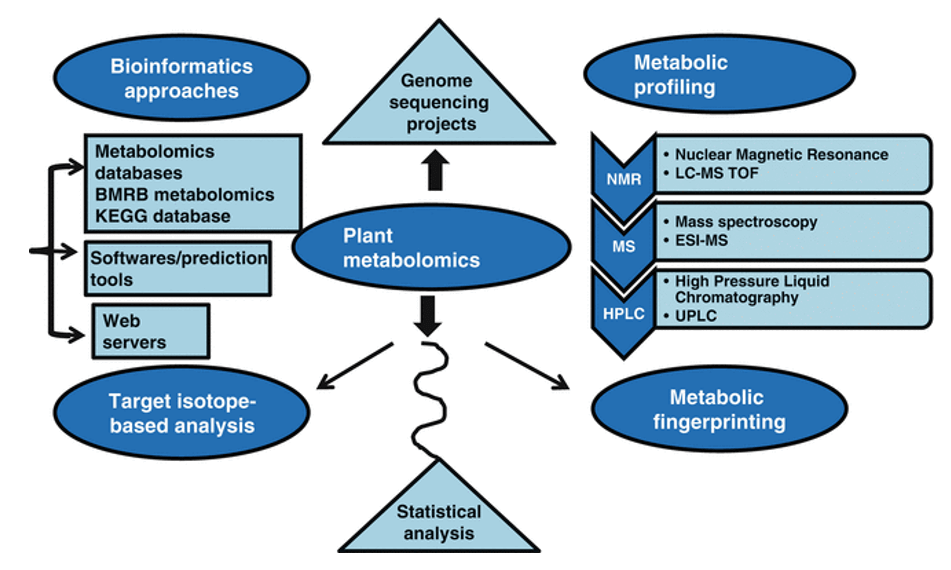
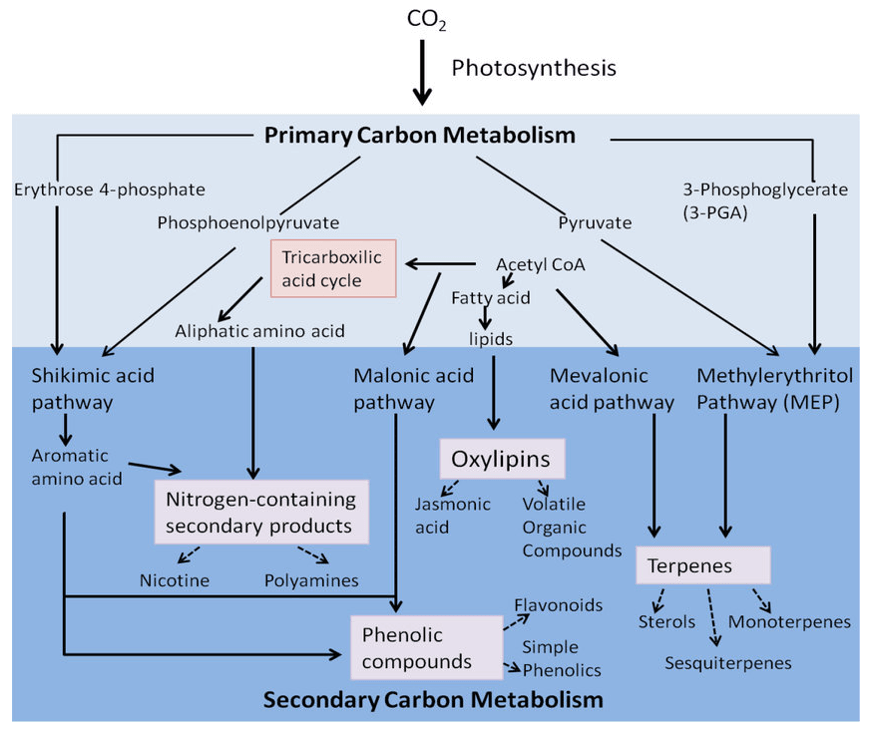
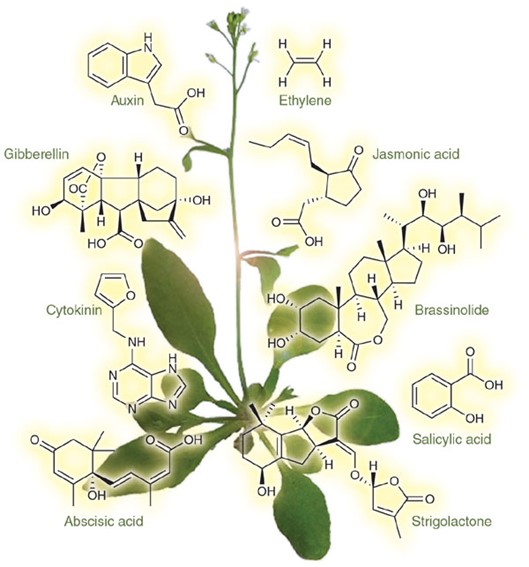
Brassinosteroids (BRs) are plant-specific steroid hormones that play essential roles in a wide range of developmental and physiological processes in plant life, including vascular differentiation, photomorphogenesis, male fertility, flowering senescence, and plant architecture. BRs are also known to regulate abiotic and biotic stress responses. BRs have been detected in almost every part of the plant, like in roots, shoots, buds, leaves, pollen, flower, seeds, fruits. More than 70 BRs have been identified in the plant. The extremely low concentrations of BRs and big differences in the polarity of individual members within the brassinosteroid hormone family can be a problem when detecting and quantifying their levels in plants. To address this problem, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is employed to determine BRs and has been become the most effective BR quantification method. Many efforts have been made to improve this analytical approach, such as optimizing the BR isolation and purification procedure.
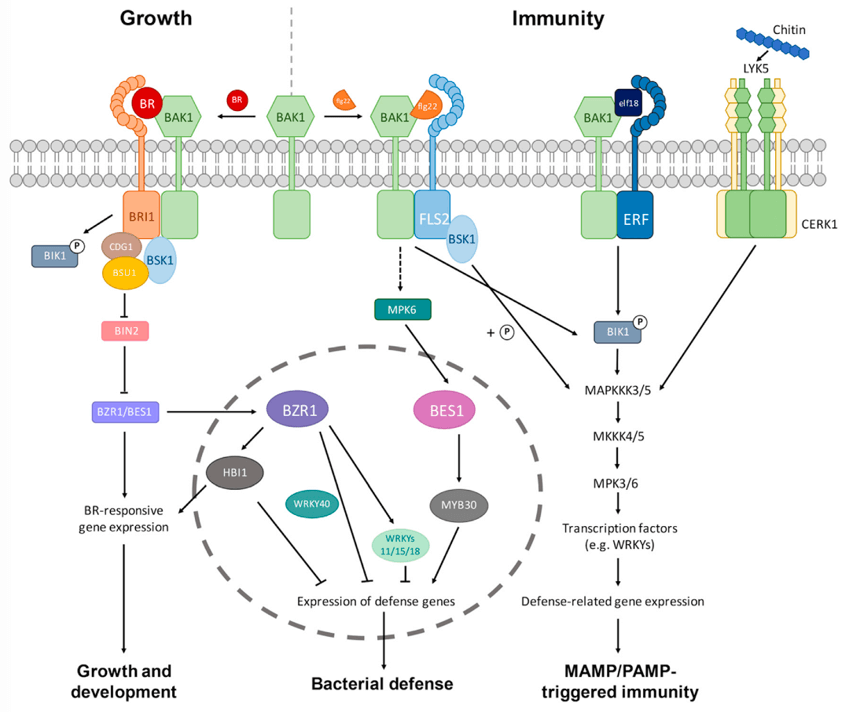 Figure 1. Brassinosteroid (BR) interaction with the innate immunity pathways in plants (Yu et al., 2018).
Figure 1. Brassinosteroid (BR) interaction with the innate immunity pathways in plants (Yu et al., 2018).
Applications of BR Analysis
- Elucidate the regulation of BR biosynthesis and BR perception
- Clarify the metabolism of BR hormone family
- Understand BR signal transduction
- Reveal mechanisms of receptor kinase activation
- Enhance crop quality for human utility
Advantages of Our BR Analysis Service
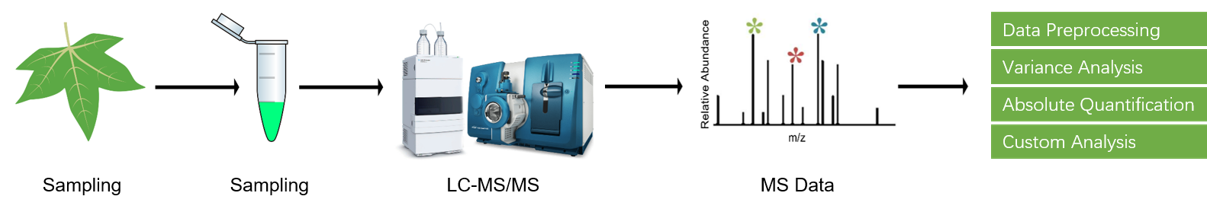
Service Workflow
Our team of experts has been dedicated to overcoming the major problems involved in the determination of BRs in complex plant matrices. Our newly developed sample preprocessing method ensures safety, environmental protection, effectiveness, and recovery rates consistently exceeding 85%, as well as maximized homogeneity between samples. LC-MS/MS in multiple-reaction monitoring (MRM) is employed for data acquisition.
Quantification methods: external reference method or isotope-labeled internal standard method
Mode: MRM, capable of simultaneously detecting more than 1000 MRM ion pairs
Precision: ≤10-9 g
Positive/Negative polarity switching time: ≤20 ms, allowing for the acquisition of Q1/Q3 MRM transition mass spectra in both ionization modes from a single LC-MS/MS run.
Analysis content:
- Standard curve creation
- Raw data preprocessing
- Absolute quantification of BL, CS, 6-DeoxoCS
- Differential metabolites screening
- Optimal analyses such as KEGG pathway analysis and hierarchical clustering
List of Detectable BRs at Creative Proteomics
| Detectable BRs | CAS | Quantification Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Brassinolide (BL) | 72962-43-7 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| Castasterone (CS) | 80736-41-0 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| 6-deoxocastasterone (6-DeoxoCS) | 87833-54-3 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
Sample Requirements
1. Fresh plant tissues from leaf, flower, stem, root, or fruit: >2 g. Provide young plant tissues for best results. Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after collection, and then transferred to -80°C for storage.
2. Plant seeds: >2 g.
At least 3 biological replicates.
Deliverables
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of liquid chromatography and MS
- MS raw data files and MS data quality checks
- BL, CS and 6-DeoxoCS quantification data
- Custom data analysis report
Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive BR analyses for precise determination of hormones within the brassinosteroid hormone family, including brassinolide (BL), castasterone (CS), 6-deoxocastasterone (6-DeoxoCS), powered by state-of-the-art mass spectrometry coupled with liquid chromatography (LC). We are committed to clarifying the roles and functions of BRs in plant developmental and physiological processes.
References
- Oklestkova J, Tarkowská D, Eyer L, et al. Immunoaffinity chromatography combined with tandem mass spectrometry: A new tool for the selective capture and analysis of brassinosteroid plant hormones. Talanta, 2017, 170: 432-440.
- Tang W, Deng Z, Wang Z Y. Proteomics shed light on the brassinosteroid signaling mechanisms. Current opinion in plant biology, 2010, 13(1): 27-33.
- Deng Z, Zhang X, Tang W, et al. A proteomics study of brassinosteroid response in Arabidopsis. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2007, 6(12): 2058-2071.
- Yu M H, Zhao Z Z, He J X. Brassinosteroid signaling in plant–microbe interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(12): 4091.