Cytokinin (CTK) Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryOverview
Cytokinins are N6-substituted adenine derivatives that have been implicated in numerous aspects of plant growth and development, including cell seed germination, de-etiolation, apical dominance, chloroplast differentiation, sink/source relationships, nutrient uptake, flower and fruit development, leaf senescence, and response to biotic and abiotic factors. The most common cytokinins have isoprenoid side chains, but there are also adenine derivatives with aromatic substituents, as well as synthetic cytokinins derived from diphenylurea (DPU). The structure and conformation of side chains are vital to the activity of cytokinins. For example, trans-zeatin is one of the most abundant cytokinins present in higher plants that displays a high activity in bioassays, but the cis-isomer displays a significantly lower activity. Determination of the distribution and content of the various cytokinins in a given plant tissue provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the action of cytokinins.
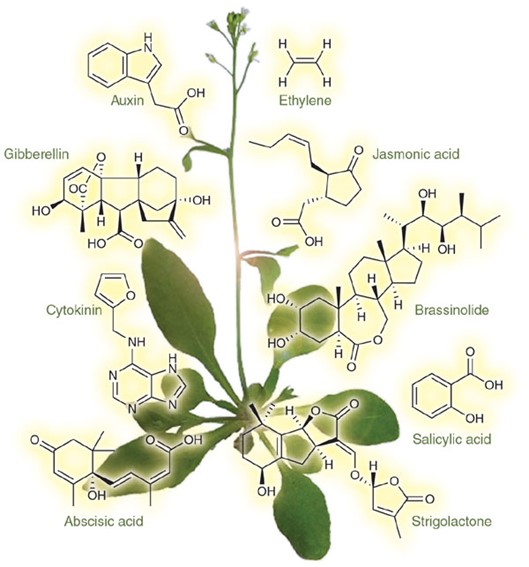
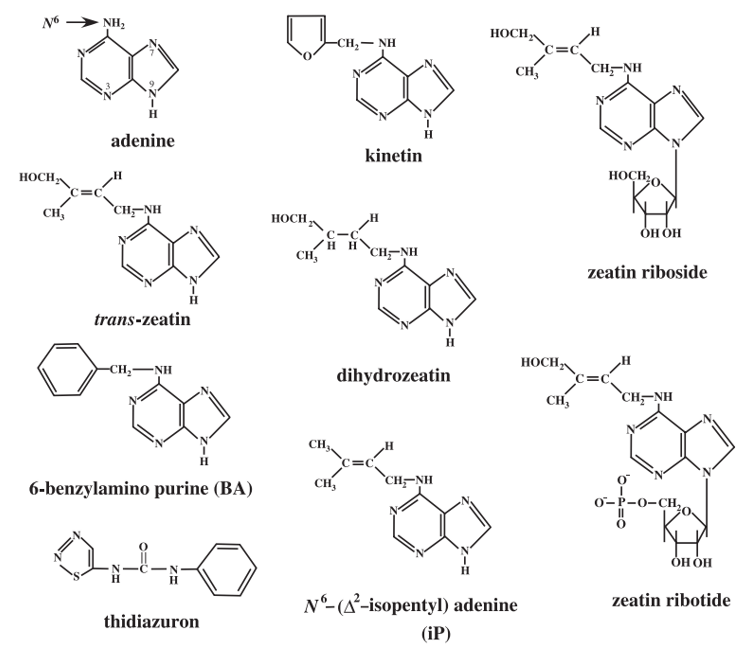 Figure 1. Structures of cytokinins (Kieber et al., 2014).
Figure 1. Structures of cytokinins (Kieber et al., 2014).
Applications of Cytokinin Analysis
- Reveal the involvement of CTKs in plant growth and development
- Elucidate the mechanism of action and molecular biological effects of CTKs
- Ensure food safety
- Crop improvement and management
Advantages of Our Cytokinin Analysis Service
Service Workflow
Creative Proteomics has optimized sample preprocessing methods to ensure efficiency and ultrahigh recovery rates consistently exceeding 85%. Mass spectrometry combined with our optimized sample preprocessing methods and other instrumentation offers precise detection down to ultra-trace levels.
 Figure 2. Cytokinins analysis service workflow.
Figure 2. Cytokinins analysis service workflow.
Quantification methods: external reference method or isotope-labeled internal standard method
Mode: MRM, capable of simultaneously detecting more than 1000 MRM ion pairs
Precision: ≤10-9 g
Positive/Negative polarity switching time: ≤20 ms, allowing for the acquisition of Q1/Q3 MRM transition mass spectra in both ionization modes from a single LC-MS/MS run.
Analysis content:
- Standard curve creation
- Raw data preprocessing
- Absolute quantitation of cytokinins
- Differential metabolites screening
- Optimal analyses such as KEGG pathway analysis and hierarchical clustering
List of Detectable Cytokinins at Creative Proteomics
| Detectable CTKs | CAS | Quantification Methods |
|---|---|---|
| N6-(Δ2-isopentenyl)-adenine (IP) | 2365-40-4 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| IPA (isopentenyladenosine) | 7724-76-7 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| Benzylaminopurine (6-BA) | 1214-39-7 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| Kinetin (KT) | 525-79-1 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| trans-zeatin ribotide (tZR) | 6025-53-2 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| (trans-zeatin) tZ | 1637-39-4 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
Sample Requirements
1. Fresh plant tissues: >1 g or > 0.2 mL. Provide young plant tissues for best results. Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after collection, and then transferred to -80°C for storage.
2. Plant seeds.
At least 3 biological replicates.
Deliverables
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- MS raw data files and MS data quality checks
- CTK quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Creative Proteomics provides high-throughput detection and quantitation of cytokinins based on state-of-the-art LC-MS platforms in a fast and sensitive manner. Our service offers maximized recovery rates and accurate profiling of cytokinins, as well as tailored statistical analysis and bioinformatics analysis to achieve reliable cytokinins analysis results.
References
- Kieber J J, Schaller G E. Cytokinins. The Arabidopsis Book/American Society of Plant Biologists, 2014, 12.
- Haberer G, Kieber J J. Cytokinins. New insights into a classic phytohormone. Plant Physiology, 2002, 128(2): 354-362.
- Ma Q H. Genetic engineering of cytokinins and their application to agriculture. Critical reviews in biotechnology, 2008, 28(3): 213-232.