Auxin Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryOverview
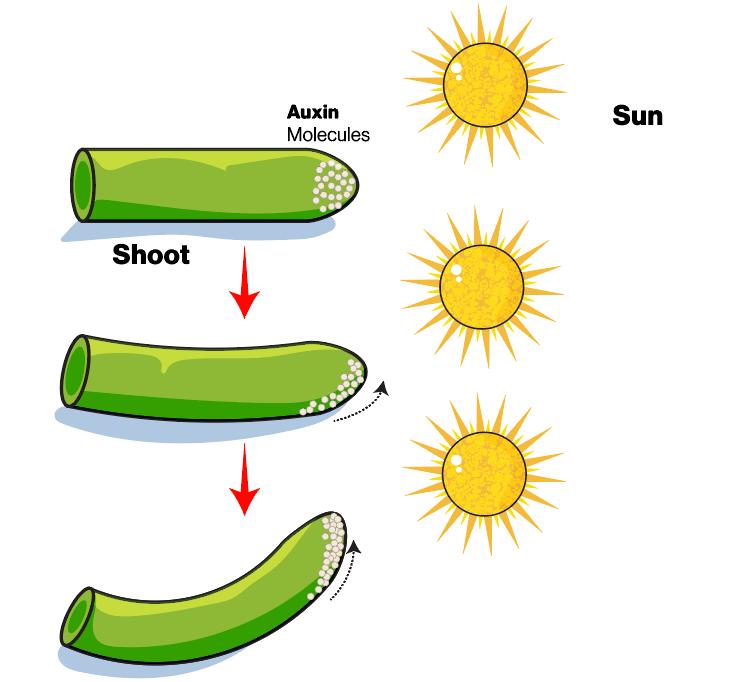
Auxins are a class of plant hormones found in shoot and root tips, promoting cell division, stem and root growth. Auxins play important roles in plant body development, indicated by their stimulation of shoot elongation and root branching, promotion of fruit development, as well as regulation of seedling orientation. Besides, epidermis-localized auxins trigger leaf and flower initiation. Auxins and their synthetic cousins have been applied to boost plant growth and kill weeds due to their vital roles in plant development. However, it is not well understood how endogenous auxin influences plant growth and development. Phytohormone analysis is challenging due to its trace concentration and the complexity of plant extracts. Fortunately, the advent of analytical techniques, ultra-fast liquid chromatography (LC) coupled with high-sensitivity tandem MS (LC-MS/MS), can solve some of the problems associated with plant hormones analysis. Optimized extraction and purification steps can also increase the sensitivity of the analytical method. MS-based methods are high-throughput and particularly sensitive for analyzing plant samples.
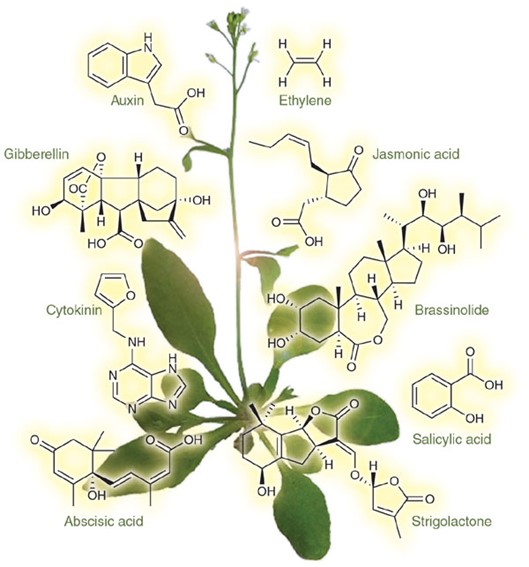
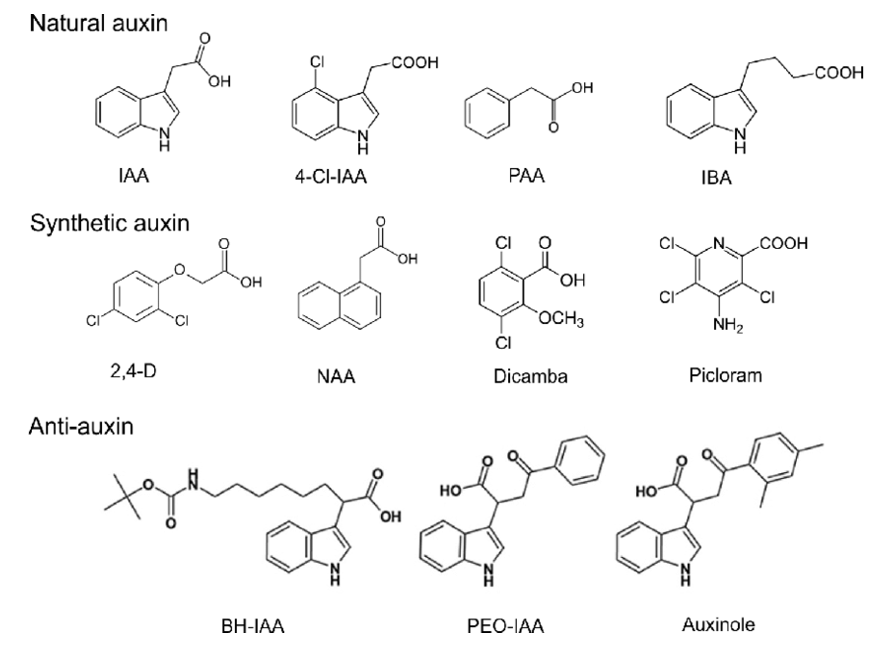 Figure 1. Chemical structures of natural and synthetic auxins, and of anti-auxins (Dhurvas 2015).
Figure 1. Chemical structures of natural and synthetic auxins, and of anti-auxins (Dhurvas 2015).
Applications of Auxin Analysis
- Improve understanding of auxin metabolism
- Ensure food safety
- Reveal mechanisms of plant growth and development
- Crop improvement
Advantages of Our Auxin Analysis Service
Service Workflow
Our newly developed sample preprocessing method provides safety, environmental protection, rapidness, effectiveness, and recovery rates consistently exceeding 85%. Sample preprocessing at Creative Proteomics complies with the in-house standard operation procedures (SOP), ensuring maximized homogeneity between samples.
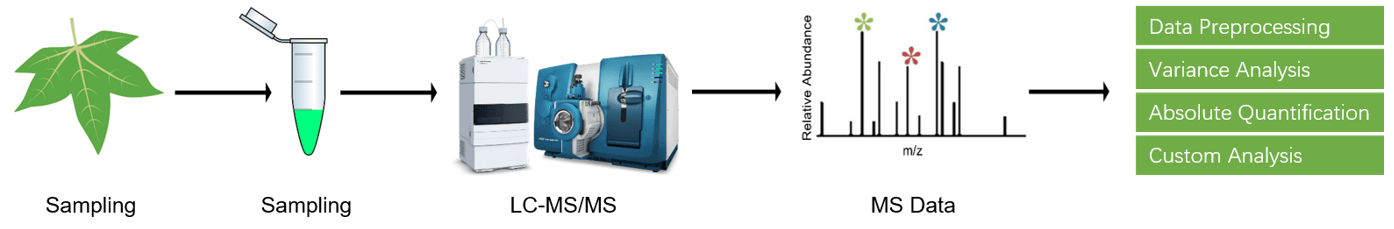 Figure 2. Auxin analysis service workflow.
Figure 2. Auxin analysis service workflow.
Quantification methods: external reference method or isotope-labeled internal standard method
Mode: MRM, capable of simultaneously detecting more than 1000 MRM ion pairs
Precision: ≤10-9 g
Positive/Negative polarity switching time: ≤20ms, allowing for the acquisition of Q1/Q3 MRM transition mass spectra in both ionization modes from a single LC-MS/MS run.
Analysis content:
- Standard curve creation
- Raw data preprocessing
- Absolute quantification of auxins
- Differential metabolite screening
- Optimal analyses such as KEGG pathway analysis and hierarchical clustering
List of Detectable Auxins at Creative Proteomics
| Detectable Auxins | CAS | Quantification Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Indole-3-acetic acid(IAA) | 87-51-4 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| Indole-3-butyric acid(IBA) | 133-32-4 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| Indole-3-acetic acid methyl ester(ME-IAA) | 1912-33-0 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| indole-3-carboxylic acid (ICA) | 771-50-6 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
| 1-Naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) | 86-87-3 | External reference method / isotope-labeled internal standard method |
Sample Requirements
1. Fresh plant tissues from leaf, flower, stem, root or fruit: >1 g. Please provide young plant tissues, if possible. Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen right after collection, and then transferred to -80°C for storage.
2. Plant seeds.
At least 3 biological replicates.
Deliverables:
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of liquid chromatography and MS
- MS raw data files and MS data quality checks
- Metabolites quantification data
- Overall auxin analysis report
Mass spectrometry-based profiling of plant hormones enables quantitative analyses of plant hormones in a faster, more convenient, and more sensitive manner. With decades of experience in mass spectrometry services, Creative Proteomics has a proven track record supporting diverse plant hormones detection and quantification. We can meet your specific project requirements, from sampling to bioinformatics.
References
- Hu W, Fagundez S, Katin-Grazzini L, et al. Endogenous auxin and its manipulation influence in vitro shoot organogenesis of citrus epicotyl explants.Horticulture research, 2017, 4(1): 1-6.
- Pěnčík A, Casanova-Sáez R, Pilařová V, et al. Ultra-rapid auxin metabolite profiling for high-throughput mutant screening in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(10): 2569-2579.
- Dhurvas Chandrasekaran D. High-resolution NMR structure and functional studies of the oligomerization domain of PsIAA4, an auxin-inducible transcriptional repressor from pea (Pisum sativum). 2015.DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.27146.36809.