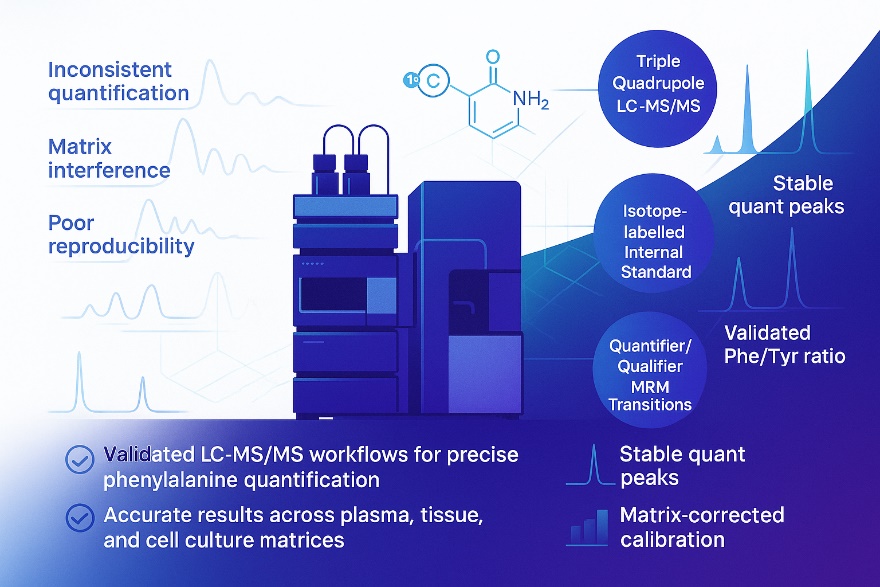
What Is Phenylalanine—and Why Measure It?
Phenylalanine (Phe) is an essential aromatic amino acid that enters metabolism through diet and feeds multiple pathways: it converts to tyrosine, contributes to catecholamine and thyroid hormone biosynthesis via downstream networks, and reflects amino-acid availability, protein turnover, and nitrogen balance. In experimental systems, shifts in Phe often accompany nutrient perturbation, microbiome–host interactions, and metabolic remodeling in cells, tissues, and biofluids.
Why analyze Phe with LC-MS/MS:
- Track pathway dynamics via Phe ↔ Tyr and related aromatic amino-acid networks
- Evaluate nutrient restriction/supplementation and media/formulation consistency
- Quantify changes linked to energy and signaling (e.g., mTOR, hepatic metabolism)
- Integrate with amino-acid panels or 13C isotope tracing for flux insights
- Obtain matrix-specific, low-LLOQ measurements suitable for plasma/serum, CSF, urine, tissues, and cell culture media
Creative Proteomics provides high-specificity LC-MS/MS phenylalanine quantification to support rigorous, decision-ready research.
Phenylalanine Analysis Services by Creative Proteomics
Choose from flexible, research-focused service packages—from single-analyte Phe measurement to dual-analyte ratios, amino-acid panels and stable-isotope tracing. All services are for research use only.
Related Analytes for Phenylalanine LC-MS/MS
To support broader pathway interpretation, several related amino acids can be co-quantified with phenylalanine (Phe) in the same LC-MS/MS workflow. These targets provide context on aromatic amino-acid metabolism, nitrogen balance, and overall metabolic status.
| Analyte |
Typical Purpose |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) |
Enables Phe/Tyr ratio for pathway analysis and neurochemistry studies |
| Tryptophan (Trp) |
Completes the aromatic amino acid network; supports neurotransmitter biosynthesis research |
| Valine · Leucine · Isoleucine (BCAAs) |
Indicators of nutrient status and energy metabolism |
| Glutamine · Glutamate |
Reflect nitrogen metabolism and anaplerotic flux in the TCA cycle |
These analytes can be seamlessly integrated into a custom amino acid panel or added individually to meet your experimental goals.
→ View Full Analyte List in our Amino Acid Panel.
Why Choose Our Phenylalanine Analysis Service?
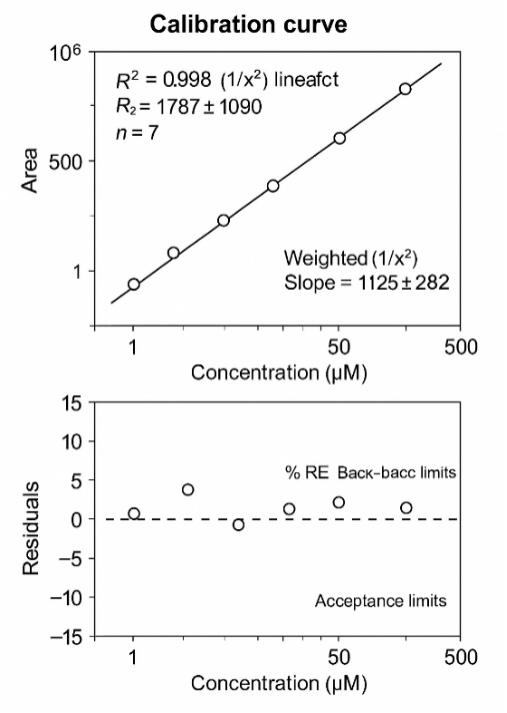
- Sensitivity: LLOQ typically ≤0.5–2.0 µM in plasma/serum(matrix-dependent).
- Linearity: dynamic range about 0.5–500 µM, R² ≥0.995.
- Precision: ≤10% intra-batch RSD; ≤15% inter-batch RSD(QC levels)。
- Accuracy/Recovery: 85–115% with isotope-labelled internal standards.
- Matrix effect (corrected): within ±15% after IS/matrix matching.
- Carryover: <0.1× LLOQ verified with post-high blanks.
- Phe/Tyr ratio robustness: propagated CV typically ≤5–8% in dual assays.
- Isotope tracing repeatability: major isotopologue CV ≤10–15%.
- Throughput: approx. 60–120 samples/day/instrument(method/panel dependent)
Phenylalanine LC‑MS/MS Method and Analytical Performance
Platform: Triple-quadrupole LC-MS/MS (MRM); HILIC or reversed-phase workflows by matrix
Internal Standards: isotope-labelled Phe (preferred) or validated analogue
Preparation: protein precipitation ± derivatization (if required); low-temperature handling to minimize conversion
Calibration & QC: matrix-matched calibration; multi-level QC (L/M/H) per batch
Typical performance (insert your validated numbers)
- Linearity: broad dynamic range for physiological/experimental levels
- LLOQ: sub-µM to low-µM (matrix-dependent)
- Precision: intra/inter-batch RSD within acceptance criteria
- Recovery & matrix effects: assessed and corrected (IS and/or matrix matching)
Phenylalanine Analysis Workflow: Step by Step
Sample Requirements for Phenylalanine Testing
| Matrix |
Minimum volume / mass |
Container |
Pre-analytical handling |
Storage & shipping |
Notes |
| Plasma / Serum |
≥ 80 µL (ideal 100 µL) |
EDTA or heparin tube |
Centrifuge promptly (≤30 min); keep on ice; avoid hemolysis |
Store −80 °C; ship on dry ice |
Record anticoagulant; limit freeze–thaw (≤3×) |
| CSF |
≥ 60 µL |
Sterile, low-bind tube |
Handle cold; minimize dwell time; no additives |
Store −80 °C; ship on dry ice |
Avoid repeated freeze–thaw |
| Urine |
≥ 250 µL |
Plain polypropylene |
Mix well; note specific gravity; aliquot if needed |
Store ≤−20 °C (short) or −80 °C; ship cold/dry ice |
Dilution factors must be recorded |
| Tissue homogenate |
≥ 25 mg eq. |
Pre-chilled, low-bind tube |
Pre-cool tools; rapid quench (e.g., cold MeOH); keep on ice |
Store −80 °C; ship on dry ice |
Provide wet weight and buffer composition |
| Cell supernatant / Media |
≥ 250 µL |
Sterile polypropylene |
Quench metabolism (cooling/organic); clarify by spin |
Store −80 °C; ship on dry ice |
Note time-point, cell density, treatment |
General tips: aliquot to avoid re-freeze; label with sample ID, matrix, collection time, and treatment; include a sample manifest with matrix, volume, and any dilution.
What You Receive: Deliverables from Our Phenylalanine Analysis
- Project overview, sample inventory, method summary
- Quantification table: Phe (units specified); optional Tyr and Phe/Tyr ratio
- Representative chromatograms/spectra and QC metrics (linearity, precision, recovery, matrix effects)
- Isotope tracing (optional): isotopologue distributions and corrected abundances
- File formats: PDF report + raw/processed data (CSV/Excel) upon request
Applications of Phenylalanine Analysis in Research and Industry
High Levels of Oxidative Stress Early after HSCT Are Associated with Later Adverse Outcomes
Cook, E., Langenberg, L., Luebbering, N., Ibrahimova, A., Sabulski, A., Lake, K. E., ... & Davies, S. M.
Transplantation and Cellular Therapy
Year: 2024
MS-CETSA Functional Proteomics Uncovers New DNA-Repair Programs Leading to Gemcitabine Resistance
Nordlund, P., Liang, Y. Y., Khalid, K., Van Le, H., Teo, H. M., Raitelaitis, M., ... & Prabhu, N.
Research Square
Year: 2024
Teriflunomide/Leflunomide Synergize with Chemotherapeutics by Decreasing Mitochondrial Fragmentation via DRP1 in SCLC
Mirzapoiazova, T., Tseng, L., Mambetsariev, B., Li, H., Lou, C. H., Pozhitkov, A., ... & Salgia, R.
iScience
Year: 2024