Proline Analysis Service
Submit Your Inquiry- Service Details
- Case Study
What is Proline?
Proline (Pro or P) is one of the 20 standard amino acids found in proteins. Unlike other amino acids, proline has a unique structural feature – its side chain forms a cyclic structure, which introduces rigidity to the protein chain. This structural peculiarity makes proline an essential component of proteins involved in maintaining protein conformation and stability, such as collagen.
Proline metabolism involves the synthesis and breakdown of proline within organisms. It is essential for various biological processes, including osmotic stress responses in plants and microorganisms. Additionally, proline can act as a signaling molecule, influencing responses to environmental stress and development.
What Can Proline Analysis Offer?
Comprehending Stress Reactions: Analyzing proline plays a pivotal role in uncovering how organisms react to diverse stress factors, rendering it indispensable for environmental and agricultural investigations.
Identification of Biomarkers: Proline levels have the potential to act as valuable indicators for various diseases and health conditions, aiding in their early detection and ongoing monitoring.
Exploring Nutrition: The evaluation of proline content in dietary sources is essential for nutritional inquiries and the creation of proline-enriched food products.
Gaining Metabolomics Insights: The analysis of proline is a crucial component of metabolomics research, assisting scientists in delving into metabolic pathways and their associated implications.
Proline Analysis Services by Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics, a leader in the field of biological analysis, offers a comprehensive suite of proline analysis services to cater to the diverse needs of researchers and industries.
Proline Quantification
At Creative Proteomics, we specialize in the precise quantification of proline levels, a fundamental component of our proline analysis services. Leveraging state-of-the-art mass spectrometry techniques, we offer accurate proline quantification across a wide range of sample types. These samples may include biological tissues, cell cultures, urine, and plasma, among others.
Our proline quantification relies on high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) systems. This cutting-edge technology not only ensures accuracy but also enhances sensitivity in proline quantification. This precision is of paramount importance, whether you're engaged in basic research or clinical applications where accurate proline level measurement is a critical requirement.
Proline Isotope Labeling
Stable isotope labeling is a powerful tool that allows for metabolic tracing studies. With this technique, researchers can track the utilization and turnover of proline within biological systems. Our proline isotope labeling services provide invaluable insights into proline kinetics and metabolic pathways.
Proline Metabolite Profiling
This comprehensive service involves the identification and quantification of proline-related metabolites, offering a holistic view of proline metabolism. Our proline metabolite profiling not only elucidates the intricate metabolic pathways involving proline but also uncovers potential biomarkers and signaling molecules associated with proline metabolism.
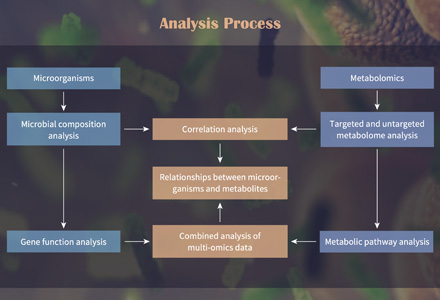
List of Detectable Proline, Derivatives and Metabolites
| Proline | Hydroxyproline | Pyrroline-5-carboxylate | Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase |
| Proline dehydrogenase | 1-Pyrroline-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone | Proline betaine | Trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline |
| 1-Pyrroline | Pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase | Proline racemase | Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase |
| Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase | Proline dihydratase | L-pyrroline-2-carboxylate reductase | Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase |
| Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase | L-pyrroline-4-hydroxy-2-carboxylate | L-proline betaine | Proline betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase |
Proline Analytical Techniques
Triple Quadrupole LC-MS/MS Systems (e.g., Agilent 6495): These high-resolution instruments ensure accurate and sensitive proline quantification in a wide range of sample types, such as biological tissues, cell cultures, urine, and plasma.
Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS, e.g., Thermo Fisher Delta V): For proline isotope labeling studies, we employ IRMS technology to trace proline utilization and metabolic pathways.
Metabolomics Mass Spectrometers (e.g., Waters Xevo G2-XS QTOF): Our metabolite profiling includes the identification and quantification of proline-related metabolites, offering a holistic view of proline metabolism.
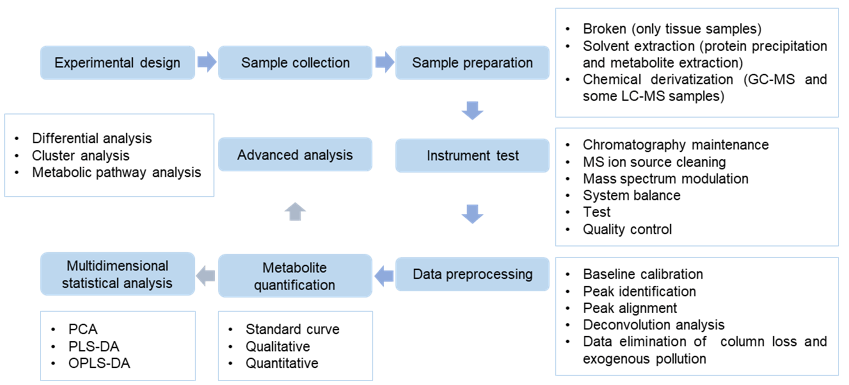 Proline analysis service workflow.
Proline analysis service workflow.
Sample Requirements for Proline Assay
| Sample Type | Sample Volume |
|---|---|
| Biological Tissues | 100 mg (approx.) |
| Cell Cultures | 1 mL |
| Urine | 1 mL |
| Plasma | 0.5 mL |
Case: Targeted Metabolomics Method for Investigating Proline Metabolism in HaCaT Human Keratinocytes
Background
Cell metabolomics is a field aimed at understanding cellular biochemistry, functions, and response mechanisms by characterizing small molecular weight compounds. It offers unique insights into metabolic phenomena in cells and finds applications in various areas, such as toxicology, pharmacology, cancer research, and biopharmaceutical production. The use of cultured cells in metabolomics studies provides greater control over external variables and eliminates ethical concerns associated with human or animal subjects.
Samples
In this study, HaCaT human keratinocytes were used as the cellular model. These cells were cultured in DMEM cell culture medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum and Penicillin/Streptomycin. The study involved treating the cells with porcine prolidase to investigate metabolic changes.
Technical Methods
Reagents: Analyte standards (L-proline, L-arginine, L-glutamic acid) and an internal standard (L-proline-d3) were used, along with LC-MS grade solvents and deionized water.
Preparation of Standard Solutions: Stock and working solutions of analytes and the internal standard were prepared. Calibration standards were created by mixing working solutions with the internal standard.
Cell Culture: HaCaT cells were cultured and treated with porcine prolidase to induce metabolic changes.
Quenching and Extraction: Metabolite extraction was performed using ice-cold methanol. The cell lysates were then transferred for LC-MS analysis, and metabolite concentrations were normalized to total protein content.
Instrumentation and Conditions: The study used an HPLC system with a Luna HILIC column and a Q-TOF mass spectrometer with electrospray ionization. Mobile phases consisted of ammonium formate and acetonitrile.
Method Validation: The developed method was rigorously validated. This included assessing linearity, carry-over, precision, recovery, accuracy, matrix effects, and stability.
Stability Testing: Autosampler stability was assessed for standard solutions and cell lysates after specific storage durations.
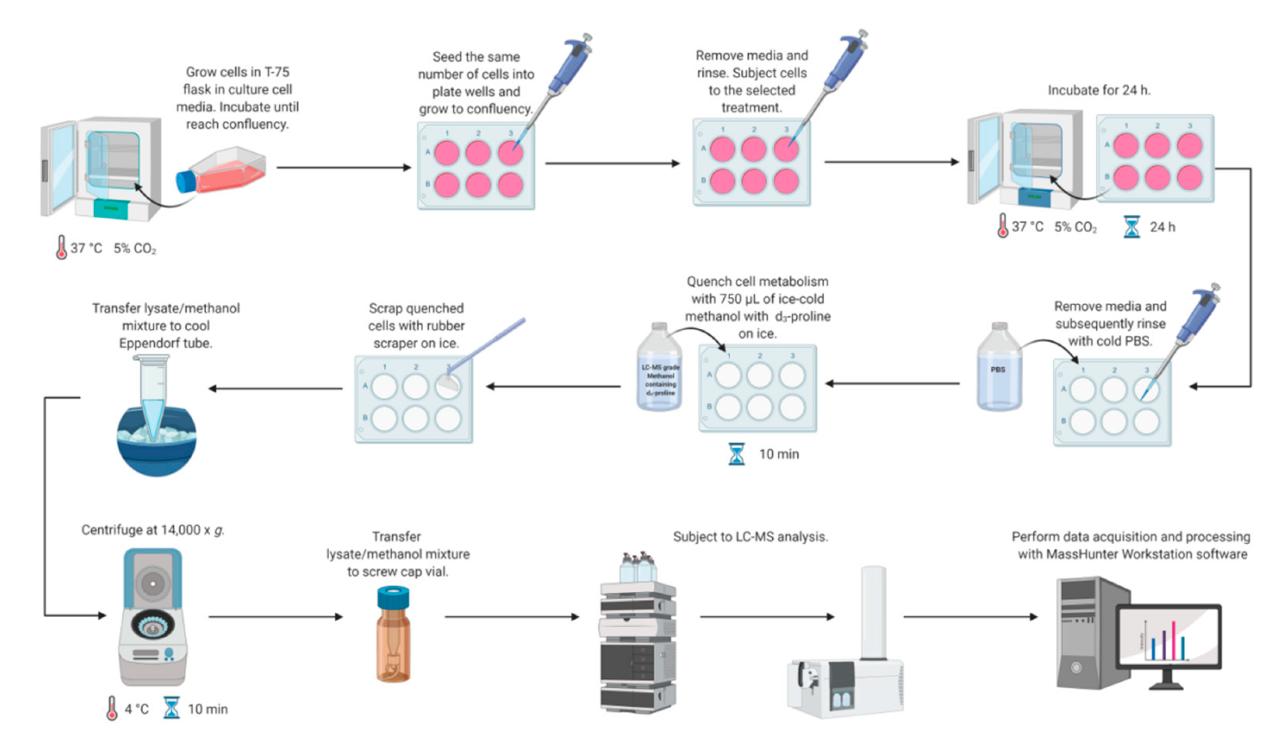 Workflow for LC-MS-based methodology for study proline metabolism in mammalian cell cultures.
Workflow for LC-MS-based methodology for study proline metabolism in mammalian cell cultures.
Results
The developed method proved effective for monitoring intracellular proline concentrations in HaCaT cells. When porcine prolidase was present, intracellular proline, glutamic acid, and arginine concentrations significantly increased. The study provided valuable insights into metabolic changes related to the promotion of wound healing in these cells.
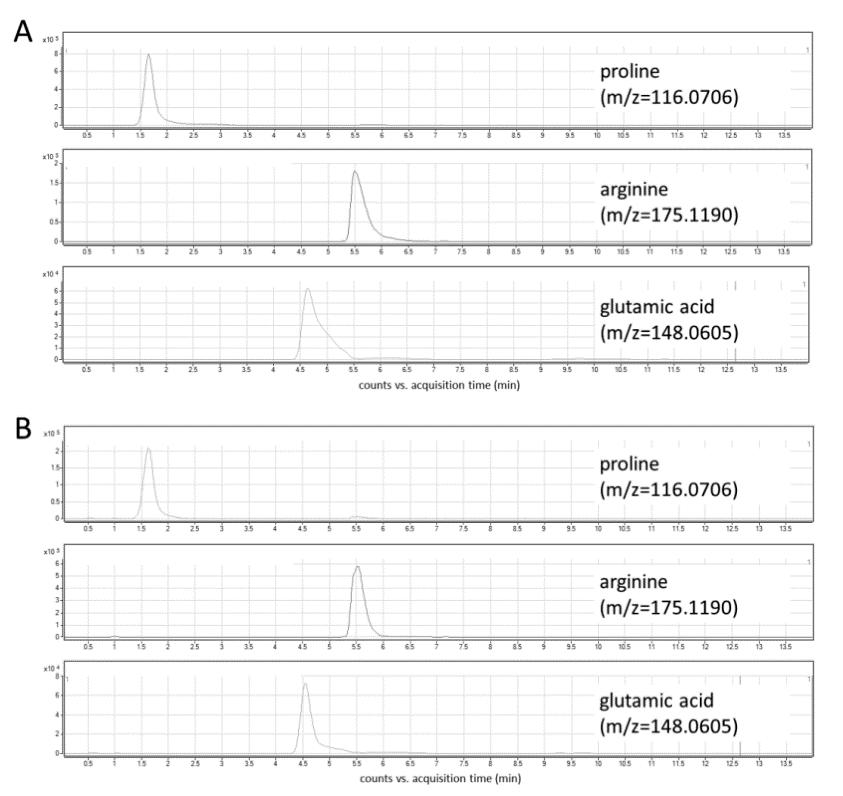 Extracted ion chromatograms of target metabolites
Extracted ion chromatograms of target metabolites
Reference
- Klupczynska, Agnieszka, et al. "Development of an LC-MS Targeted Metabolomics Methodology to Study Proline Metabolism in Mammalian Cell Cultures." Molecules 25.20 (2020): 4639.