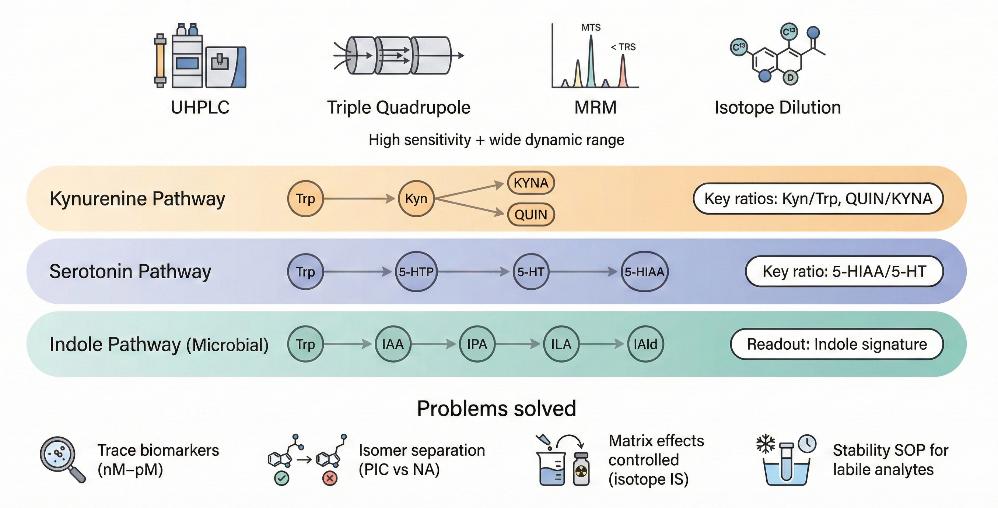
Targeted Quantification for Pathway Flux and Mechanistic Readouts
Tryptophan (Trp) metabolism is a critical regulator of physiology, extending far beyond protein synthesis. The flux of Tryptophan through the Kynurenine, Serotonin, and Indole pathways is a central driver in three major research areas:
- Immuno-Oncology: Upregulation of IDO1/TDO2 enzymes depletes Trp and produces immunosuppressive Kynurenine, facilitating tumor immune evasion.
- Neuroscience: The delicate balance between neuroprotective (e.g., Kynurenic Acid) and neurotoxic (e.g., Quinolinic Acid) metabolites is a hallmark of neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.
- Gut-Brain Axis: Microbiota-derived Indoles and gut-produced Serotonin are key modulators of intestinal barrier integrity and host immunity.
The analytical solution quantifying tryptophan alone is insufficient to reveal these mechanisms. Researchers need precise product-to-substrate ratios (e.g., Kyn/Trp) and the detection of unstable, trace-level intermediates.
Creative Proteomics overcomes the sensitivity and specificity limitations of conventional ELISA or HPLC methods. We provide a targeted LC-MS/MS workflow that delivers absolute quantification and strict isomer separation for the complete metabolic pathway, helping you capture key pathway signals.
Service Portfolio: Tailored Metabolic Panels
We recognize that different research fields require different analytical focuses. We offer flexible panel configurations to match your specific study goals:
Immuno-Oncology Panel (IDO/TDO Focus)
- Target: Assessment of immune checkpoint activity and tumor metabolism.
- Primary Readout: The Kynurenine-to-Tryptophan Ratio (Kyn/Trp), a widely used readout for IDO1/TDO2 activity in many study designs.
Neuro-Transmission & Circadian Panel
- Target: CNS disorders, mood regulation, sleep studies, and blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity.
- Primary Readout: The QUIN/KYNA ratio (Neurotoxic index) and 5-HIAA/5-HT (Serotonin turnover rates).
Microbiome-Gut Axis Panel (Indoles Focus)
- Target: Host-microbe interaction, intestinal inflammation (IBD), and gut barrier function.
- Primary Readout: Indole metabolite signatures (microbial-associated pathway activity).
Complete Analyte List for Tryptophan Metabolism
| Metabolic Branch |
Analyte Name |
Abbreviation |
Biological Significance |
| Precursor |
L-Tryptophan |
Trp |
Substrate for IDO, TDO, and TPH enzymes. |
Kynurenine Pathway
(Major Route: Immunity & Neuro) |
L-Kynurenine |
Kyn |
Key immunosuppressive metabolite; AhR ligand. |
| Kynurenic Acid |
KYNA |
Neuroprotective; NMDA receptor antagonist. |
| Anthranilic Acid |
AA |
Biomarker for inflammation; precursor to Acetyl-CoA. |
| 3-Hydroxykynurenine |
3-HK |
Generates reactive oxygen species (ROS); neurotoxic. |
| 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid |
3-HAA |
Immune regulator; suppresses T-cell response. |
| Xanthurenic Acid |
XA |
Indicator of Vitamin B6 deficiency. |
| Quinolinic Acid |
QUIN |
Potent Neurotoxin; NMDA receptor agonist. |
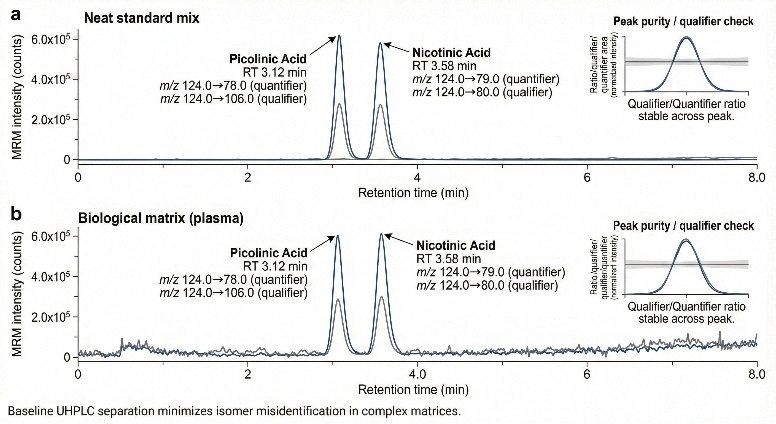
| Picolinic Acid |
PIC |
Macrophage activation marker; neuroprotective. |
| Nicotinic Acid |
NA |
Vitamin B3; end-product for NAD+ biosynthesis. |
Serotonin Pathway
(Mood, Sleep & Gut) |
5-Hydroxytryptophan |
5-HTP |
Direct precursor to Serotonin. |
| Serotonin |
5-HT |
Neurotransmitter; regulates mood and gut motility. |
| 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid |
5-HIAA |
Major urinary metabolite of Serotonin. |
| N-Acetylserotonin |
NAS |
Precursor to Melatonin; BDNF agonist. |
| Melatonin |
MT |
Regulates circadian rhythm; potent antioxidant. |
Indole Pathway
(Microbial Origin) |
Indole-3-acetic acid |
IAA |
Auxin (plant hormone) homolog; supports gut barrier. |
| Indole-3-propionic acid |
IPA |
Potent antioxidant; exclusively microbial origin. |
| Indole-3-lactic acid |
ILA |
Modulates immune response via AhR activation. |
| Indole-3-aldehyde |
IAld |
Regulates mucosal immunity (IL-22 production). |
Advantages for Targeted Tryptophan Metabolomics
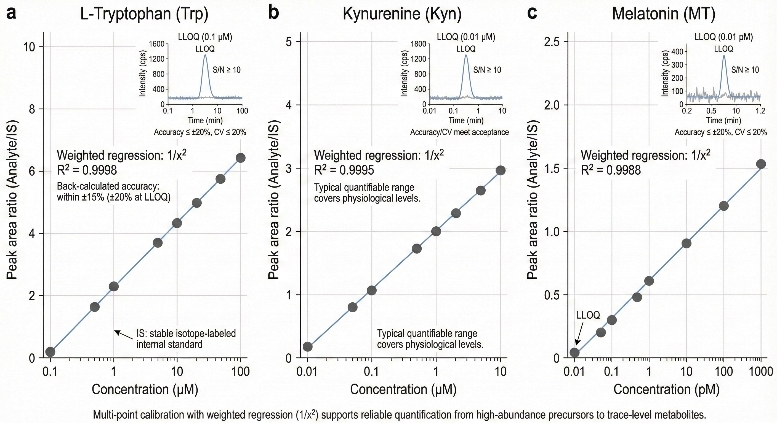
- Absolute Quantification via Isotope Dilution: We utilize specific stable isotope-labeled internal standards (e.g., d5-Trp, d4-Kyn) for critical analytes to correct for matrix effects. This ensures precise, absolute quantification (ng/mL or µM) in complex biofluids, independent of ion suppression.
- Strict Resolution of Isomers: Our optimized UHPLC methods fully resolve isobaric compounds with identical masses but distinct biological roles (e.g., Picolinic Acid vs. Nicotinic Acid), preventing the cross-identification errors common in standard screening assays.
- High Sensitivity for Trace Biomarkers: The platform achieves nM to pM sensitivity, enabling the reliable detection of low-abundance downstream metabolites (e.g., Melatonin, Quinolinic Acid) alongside high-concentration precursors in serum and brain tissue.
- Stability Protocols for Labile Analytes: To prevent the auto-oxidation of unstable intermediates like 3-HK and 3-HAA, we provide specialized collection protocols (including antioxidant stabilizers) to preserve sample integrity from collection through analysis.
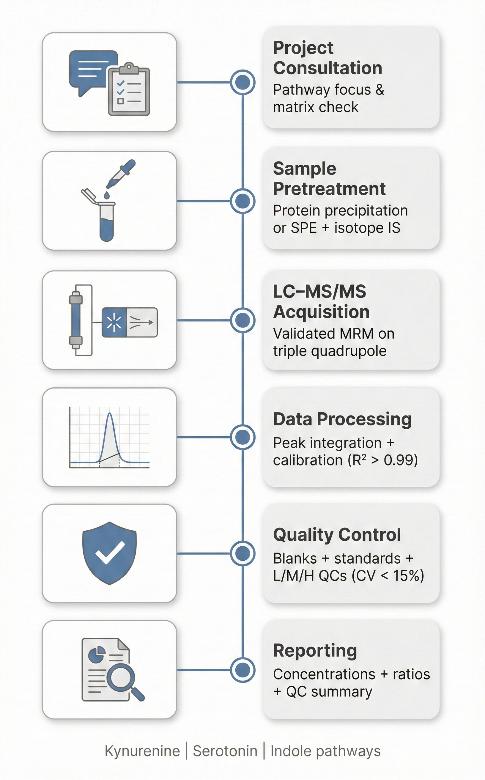
Service Workflow and Quality Control for Targeted Tryptophan Pathway Analysis
Analytical Platforms for Tryptophan Pathway Analysis
Chromatography: Agilent 1290 Infinity II UHPLC System
Reversed-phase C18 with sub-2 µm particle columns for high peak capacity and separation of 20+ metabolites in a single run
Mass Spectrometry: Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole LC/MS
- Mode: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM).
- Benefit: These systems offer the high sensitivity and wide dynamic range, allowing simultaneous quantification of high-abundance precursors and trace-level metabolites without detector saturation.
- Polarity: Rapid positive/negative ion switching to capture both basic (amines) and acidic (carboxylic acids) metabolites.
Sample Requirements & Collection SOP for Tryptophan Metabolism
| Sample Matrix |
Minimum Volume / Mass |
Container |
Storage & Shipping |
Special Notes (Critical) |
| Plasma / Serum |
100 µL (Min) / 200 µL (Rec) |
EDTA or Heparin tubes |
-80°C; Ship on Dry Ice |
Avoid hemolysis (RBCs contain enzymes that degrade Trp). |
| Urine |
500 µL |
Sterile screw-cap tube |
-80°C; Ship on Dry Ice |
Optional: Record 24h volume or request Creatinine normalization. |
| Tissue (Brain, Liver, etc.) |
50 - 100 mg |
Pre-weighed tube |
-80°C; Ship on Dry Ice |
Rinse with PBS to remove blood. Snap-freeze in liquid nitrogen immediately. |
| Feces / Stool |
100 - 200 mg |
Sterile tube |
-80°C; Ship on Dry Ice |
Essential for Indole/IPA quantification. |
| Cells |
5 × 106 cells |
Cell pellet |
-80°C; Ship on Dry Ice |
Wash twice with PBS to remove culture media (media contains high Trp). |
| CSF (Cerebrospinal Fluid) |
100 µL |
Sterile low-bind tube |
-80°C; Ship on Dry Ice |
Store in aliquots to avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
Stabilization Note: For studies targeting oxidative metabolites (3-HK, 3-HAA), we strongly recommend adding an antioxidant solution (e.g., 0.1% Ascorbic Acid + 0.05% EDTA) to plasma or tissue homogenates immediately after collection. Please contact our technical team for the detailed SOP.
Deliverables: Quantitative Data Package and QC Report
- Quantitative Data Matrix (Excel/CSV): Absolute concentrations for all targeted metabolites (e.g., µg/mL or pmol/mg tissue).
- Calculated Ratios: Key biological indices such as Kyn/Trp, Quin/KYNA, and 5-HIAA/5-HT are automatically calculated and included.
- QC Summary Report: A transparent summary of method performance, including Internal Standard recovery, LOD/LLOQ values for each analyte, and calibration linearity.
- Method Description: A detailed material and methods section suitable for publication in peer-reviewed journals.
- Raw Data Files: Available upon request for audit or re-analysis purposes.
Research Applications for Targeted Tryptophan Pathway Metabolomics
Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF‐1α
Pelletier, A., Nelius, E., Fan, Z., Khatchatourova, E., Alvarado‐Diaz, A., He, J., ... & Stockmann, C.
Journal: EMBO reports
Year: 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202256156
The activity of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in T cells tunes the gut microenvironment to sustain autoimmunity and neuroinflammation
Merchak, A. R., Cahill, H. J., Brown, L. C., Brown, R. M., Rivet-Noor, C., Beiter, R. M., ... & Gaultier, A.
Journal: PloS Biology
Year: 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002000
Dimethyl fumarate treatment restrains the antioxidative capacity of T cells to control autoimmunity
Liebmann, M., Korn, L., Janoschka, C., Albrecht, S., Lauks, S., Herrmann, A. M., ... & Klotz, L.
Journal: Brain
Year: 2021
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab307
The Brain Metabolome Is Modified by Obesity in a Sex-Dependent Manner
Norman, J. E., Milenkovic, D., Nuthikattu, S., & Villablanca, A. C.
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063475
Inflammation primes the kidney for recovery by activating AZIN1 A-to-I editing
Heruye, S., Myslinski, J., Zeng, C., Zollman, A., Makino, S., Nanamatsu, A., ... & Hato, T.
Journal: bioRxiv
Year: 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.09.566426