Glutamine Metabolism Analysis
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Glutamine?
Glutamine, an amino acid encoded by the genetic code, is categorized as a non-essential amino acid due to its synthesis within the body. It possesses a unique side chain containing an extra nitrogen atom, setting it apart from other amino acids. The conversion of glutamate by the enzyme glutamine synthetase primarily generates glutamine.
Beyond its involvement in protein synthesis, glutamine plays vital roles in numerous metabolic processes. It serves as a precursor for nucleotide synthesis, contributing to the formation of DNA and RNA. Additionally, glutamine acts as a building block for specific neurotransmitters, facilitating intercellular communication. Another crucial function of glutamine is its participation in the synthesis of glutathione, an antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage. Moreover, glutamine acts as a nitrogen donor in the urea cycle, aiding in the removal of toxic ammonia from the body and helps maintain the delicate acid-base balance.
Glutamine Metabolism Pathway
The glutamine metabolism pathway involves a series of intricate biochemical reactions that regulate the utilization and generation of glutamine in the body. Glutamine is primarily metabolized through two key processes: glutaminolysis and glutamine synthesis.
Glutaminolysis, or glutamine catabolism, refers to the breakdown of glutamine into glutamate and ammonia. This process mainly occurs in the mitochondria and serves as a significant energy source and supplier of metabolic intermediates. Glutaminolysis plays a crucial role in rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, which heavily rely on glutamine for sustained growth and proliferation.
On the other hand, glutamine synthesis, or glutamine anabolism, involves the conversion of glutamate into glutamine. This process is primarily mediated by the enzyme glutamine synthetase and occurs predominantly in the cytoplasm. Glutamine synthesis is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis, supporting nitrogen metabolism, and replenishing the intracellular pool of glutamine.
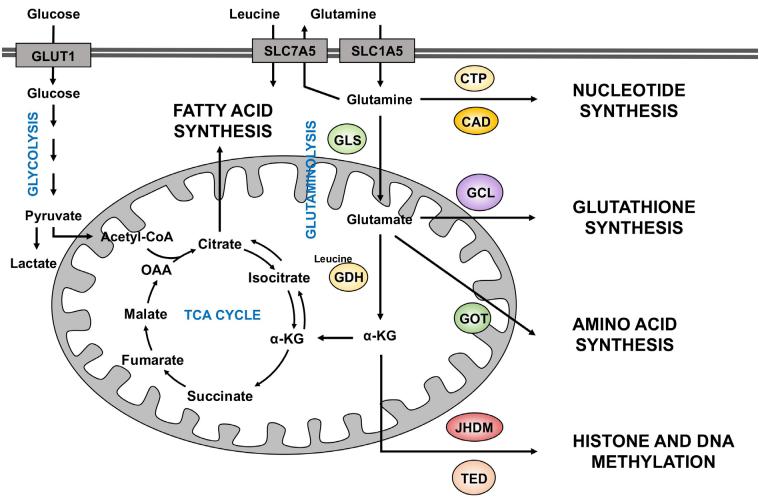 Different uses of glutamine in cancer cells (Nguyen et al., 2018)
Different uses of glutamine in cancer cells (Nguyen et al., 2018)
Glutamine and Metabolite Analysis in Creative Proteomics
Understanding the metabolism of glutamine is highly significant across multiple scientific domains. Glutamine analysis plays a crucial role in unraveling the intricate connections between glutamine and cellular metabolism. By investigating the metabolic destiny of glutamine, researchers can enhance their comprehension of the fundamental mechanisms governing cellular function and dysfunction.
Glutamine analysis enables the exploration of metabolic deviations that arise in various pathological states, including cancer, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. By studying alterations in glutamine metabolism, researchers can identify promising targets for therapeutic intervention and devise novel treatment approaches.
Creative Proteomics offers a range of services for glutamine and metabolite analysis, including:
Targeted Metabolomics
Creative Proteomics employs targeted metabolomics approaches to quantitatively measure glutamine and its related metabolites. This service enables the accurate assessment of specific metabolites of interest, providing detailed information about their concentrations and potential fluctuations in different biological samples. Targeted metabolomics allows researchers to explore the metabolic changes associated with specific pathways or cellular processes.
Untargeted Metabolomics
Creative Proteomics also offers untargeted metabolomics services, which involve a comprehensive profiling of metabolites within a given sample. This approach provides a holistic view of the metabolic landscape, allowing for the identification and quantification of a broad range of metabolites, including glutamine and its derivatives. Untargeted metabolomics facilitates the discovery of novel biomarkers and the exploration of metabolic alterations associated with various biological conditions.
Stable Isotope Labeling Experiments
We utilize stable isotope labeling techniques in combination with mass spectrometry to investigate the flux of glutamine and its related metabolites through different metabolic pathways. By introducing isotopically labeled substrates and tracking their incorporation into metabolic products, researchers can quantitatively assess metabolic fluxes and gain insights into the dynamic behavior of glutamine metabolism. Stable isotope labeling experiments provide valuable information about metabolic kinetics and pathway activities.
Metabolic Flux Analysis
We offer metabolic flux analysis to determine the rates and directions of metabolic reactions involving glutamine and other metabolites. This service utilizes computational modeling approaches combined with experimental data to quantify metabolic fluxes. By integrating stable isotope labeling data and metabolic network analysis, we can unravel the intricate interactions and flux distributions within metabolic pathways, shedding light on the regulation and coordination of glutamine metabolism.
Metabolite Identification and Annotation
Creative Proteomics provides metabolite identification and annotation services, utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometry and advanced metabolite databases. This enables the accurate identification and characterization of metabolites present in biological samples, including glutamine and its derivatives. Metabolite annotation allows researchers to assign putative functions and biochemical pathways to detected metabolites, facilitating the interpretation of metabolomics data.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
In addition to experimental services, we offer comprehensive data analysis and interpretation. The company's team of experts utilizes advanced bioinformatics tools and statistical analysis methods to process and analyze metabolomics data. This includes data normalization, statistical significance testing, pathway enrichment analysis, and visualization of results. Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive reports and interpretation of the obtained metabolomics data, assisting researchers in extracting meaningful insights from complex datasets.
Glutamine Analysis Platforms: Mass Spectrometry-Based Platforms
Creative Proteomics employs state-of-the-art mass spectrometry-based platforms for glutamine analysis. These platforms offer high sensitivity, selectivity, and accuracy in detecting and quantifying glutamine and its metabolites.
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): Creative Proteomics utilizes LC-MS systems such as the Thermo Scientific Q Exactive and the Agilent 6550 iFunnel Q-TOF for sensitive and accurate glutamine analysis.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): GC-MS is employed for the analysis of volatile compounds and stable isotope-labeled tracers in glutamine metabolism studies. GC-MS systems such as the Agilent 7890A GC coupled with the Agilent 5975C MSD are utilized for precise measurements of glutamine and related metabolites.
Sample Requirements for Glutamine Assay
For accurate glutamine and metabolite analysis, Creative Proteomics accepts various sample types, including:
- Cell Culture Samples: Cell lines or primary cells cultured under specific conditions can provide insights into glutamine metabolism in vitro.
- Tissue Samples: Tissue biopsies or organ samples allow the study of glutamine metabolism in the context of the whole organism.
- Biofluids: Biofluids such as blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid can be used to investigate glutamine metabolism non-invasively.
The recommended sample volume may vary depending on the specific analysis requirements. It is advisable to consult with the experts at Creative Proteomics to determine the appropriate sample size for a particular study.
Applications of Glutamine Analysis
Cancer Metabolism Research: Glutamine plays a crucial role in the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells. By analyzing glutamine metabolism, researchers can gain insights into the specific metabolic alterations that drive tumor growth and identify potential targets for cancer therapy.
Metabolic Disorders: Glutamine analysis can contribute to the understanding of metabolic disorders, such as obesity, diabetes, and liver diseases. By investigating the dysregulation of glutamine metabolism, researchers can unravel the metabolic imbalances associated with these conditions.
Neurodegenerative Disease Studies: Glutamine metabolism dysregulation has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Glutamine analysis can provide valuable information about the metabolic changes associated with these diseases and aid in the development of targeted therapeutic interventions.
Cellular Physiology and Bioenergetics: Glutamine analysis provides valuable insights into cellular physiology and bioenergetics. By studying the metabolism of glutamine and its related metabolites, researchers can unravel the mechanisms underlying energy production, nutrient utilization, and cellular homeostasis.
Drug Discovery and Development: Glutamine analysis plays a crucial role in drug discovery and development processes. By studying the effects of drugs on glutamine metabolism, researchers can assess their impact on cellular energy metabolism and identify potential side effects or drug-drug interactions. Glutamine analysis helps in the evaluation of drug efficacy, safety, and mechanism of action, facilitating the optimization of drug candidates and the development of targeted therapies.
If you would like to analyze other amino acids or learn more, please contact us. We look forward to working with you.
Reference
- Nguyen, Tra-Ly, and Raúl V. Durán. "Glutamine metabolism in cancer therapy." Cancer Drug Resist 1.3 (2018): 126-38.

