Lysine is far more than an essential amino acid. It sits at the crossroads of energy metabolism, inherited metabolic diseases, protein post-translational modifications (PTMs), and biopharmaceutical quality control. Because of this, many researchers are no longer satisfied with simply measuring “lysine concentration” – they need a lysine-centered view of metabolism and protein regulation.
At Creative Proteomics, we provide a dedicated lysine analysis service that covers
- Free lysine and lysine catabolism intermediates
- Lysine-based PTMs at the peptide / proteome level
- Lysine in targeted amino acid or metabolite panels
- Heavy lysine labeling and SILAC-related QC
Our flexible platform supports single-analyte quantification, lysine-focused panels, and integration into broader targeted metabolomics, tailored to your specific project.
Biological Role of Lysine and Its Analytical Relevance
Lysine participates in:
- Protein synthesis and structure – positively charged side chains that contribute to protein folding and interactions.
- Lysine degradation pathways – including saccharopine and pipecolate pathways, highly relevant in inherited metabolic diseases.
- Post-translational modifications – such as acetylation, lactylation, methylation, ubiquitination, and glycation on lysine residues.
- Biopharmaceuticals – lysine residues are frequent conjugation sites in antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) and important for C-terminal clipping in antibodies.
- Quantitative proteomics – heavy lysine is a key component in SILAC and related metabolic labeling strategies.
Because lysine appears in so many layers of biology, the "right" analytical strategy depends heavily on the research context. Our service is structured to capture those diverse needs.
Application Scenarios Covered by Our Lysine Analysis Service
Lysine Metabolism and Degradation Pathway (Lysine Catabolism Panel)
Lysine is degraded through distinct metabolic routes, and alterations in these pathways are closely linked to neurometabolic and inherited metabolic disorders. Our lysine metabolism assays are ideal for:
- Investigating lysine degradation (saccharopine / pipecolate pathways) in animal models or patient samples
- Identifying lysine catabolism–related biomarkers in plasma, CSF, urine or tissues
- Evaluating the impact of genetic variants or treatments on lysine metabolic flux
Our solution
We offer a targeted lysine catabolism panel that quantitatively measures free lysine and key degradation intermediates (such as saccharopine, aminoadipate-related species, pipecolate and other pathway markers) in a wide range of biological matrices. Results are delivered together with statistical summaries and pathway-oriented data visualization to support interpretation.
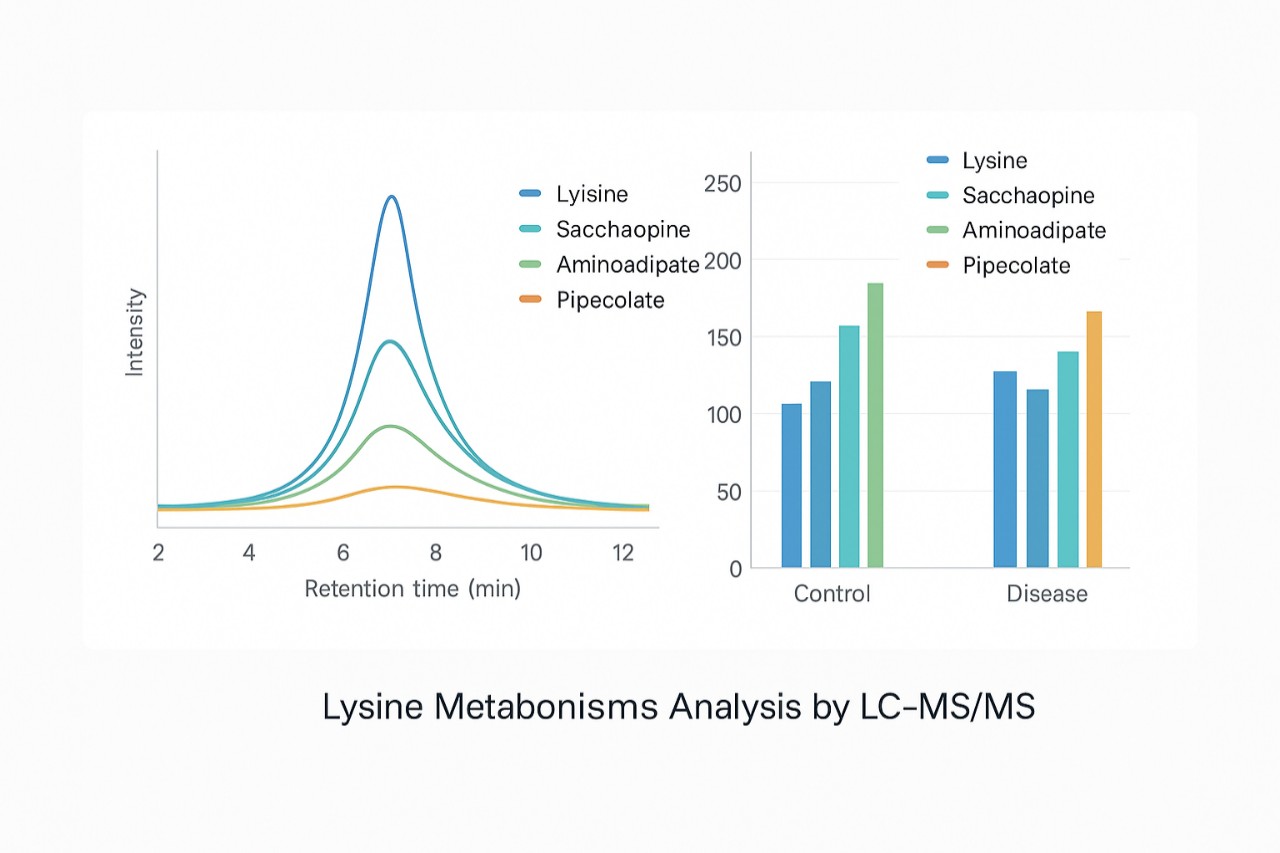 Representative LC–MS/MS chromatograms and group comparison for lysine and key catabolic intermediates in plasma.
Representative LC–MS/MS chromatograms and group comparison for lysine and key catabolic intermediates in plasma.
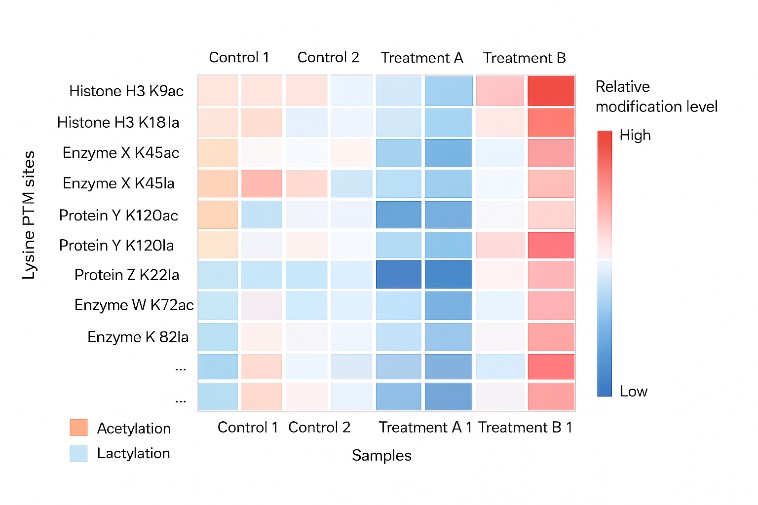
Lysine Acetylation, Lactylation and Other Lysine PTMs (Lysine PTM Proteomics)
Lysine residues are hotspots for post-translational modifications that modulate protein function, chromatin structure and cellular signaling. This application is suited for studies that aim to:
- Map lysine acetylation, lactylation and other acyl-lysine PTMs at the site and protein level
- Compare lysine PTM patterns between disease and control groups or under different treatments
- Connect lysine-based PTMs with metabolic rewiring, epigenetic regulation and signaling pathways
Our solution
Our Lysine PTM Proteomics workflow combines modification-specific peptide enrichment (e.g., anti–acetyl-lysine and other acyl-lysine antibodies when applicable) with high-resolution LC–MS/MS. We provide:
- Site-level identification of lysine modifications
- Quantitative comparison across conditions (label-free, TMT or SILAC)
- Functional annotation and pathway enrichment analysis to highlight key regulated proteins and networks
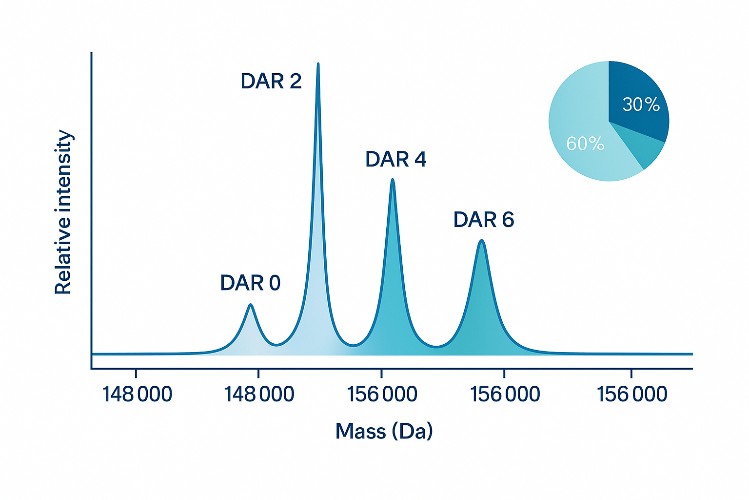
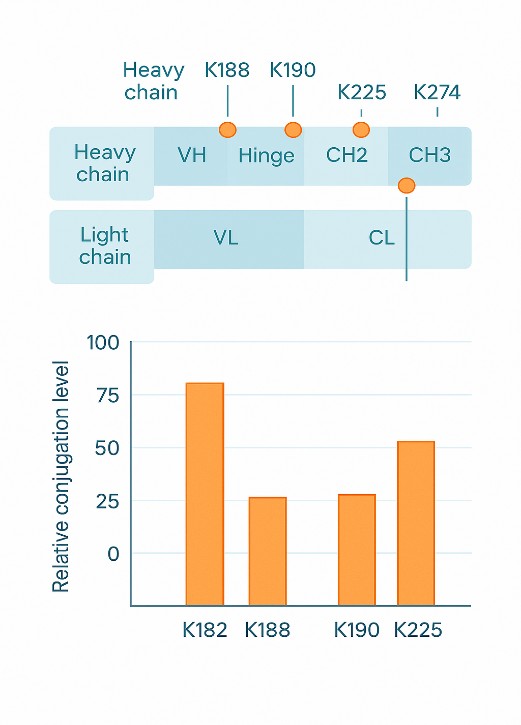
Lysine-Conjugated ADC and Biotherapeutic Characterization
Many antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) and other biotherapeutics rely on lysine residues as conjugation sites. Accurate characterization of these lysine-related attributes is critical for product quality. Typical applications include:
- Determining drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) distributions for lysine-conjugated ADCs
- Locating and quantifying lysine conjugation sites on monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins
- Monitoring C-terminal lysine variants and other lysine-related critical quality attributes
Our solution
For biotherapeutic projects we provide:
- Intact mass analysis to assess DAR distribution and global modification patterns
- Peptide mapping workflows to identify lysine conjugation sites and C-terminal lysine clipping
- Targeted monitoring of lysine-related attributes across process development, comparability and stability studies
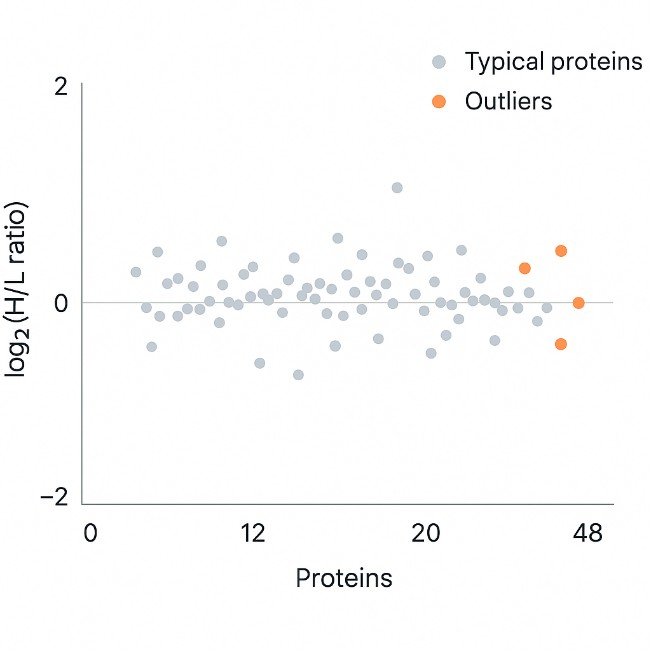
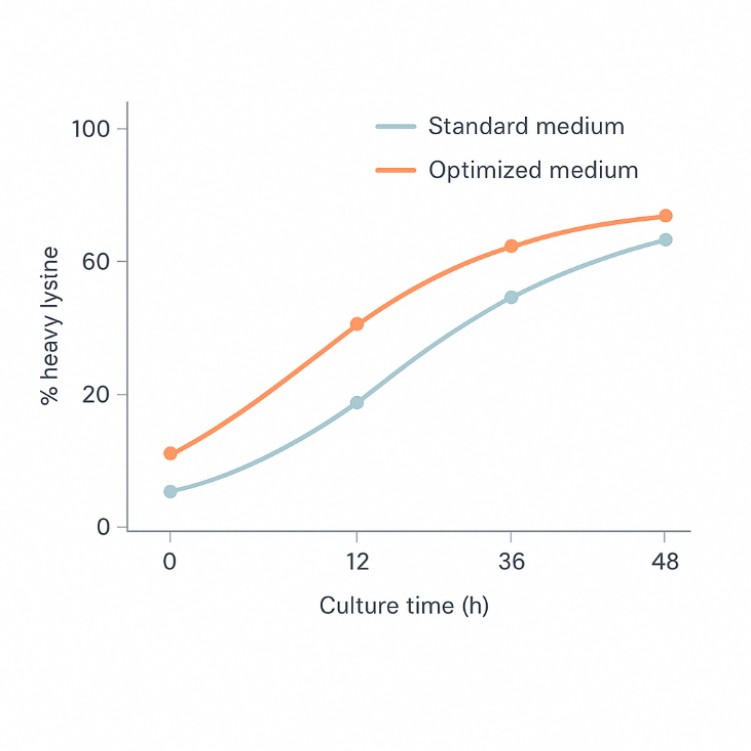
SILAC Heavy Lysine Labeling and Quantitative Proteomics QC
Stable isotope labeling with heavy lysine is widely used in quantitative proteomics and PTM studies. Reliable quantification depends on high and well-characterized labeling efficiency. Our service supports projects that aim to:
- Measure heavy and light lysine incorporation in SILAC-labeled cells or media
- Confirm that labeling efficiency is sufficient for accurate relative quantitation
- Optimize culture time and medium composition for metabolic labeling strategies
Our solution
We use targeted LC–MS/MS to quantify heavy and light lysine forms, calculate labeling efficiency and detect potential issues such as incomplete incorporation. Based on the data, we provide practical recommendations to refine your SILAC or heavy lysine labeling protocol before large-scale experiments.
In many studies, lysine is one of several amino acids or metabolites of interest, and needs to be measured consistently across samples, matrices and time points. This application is ideal for:
- Comprehensive amino acid profiling in plasma, CSF, tissues or cell culture systems
- Targeted metabolomics projects where lysine is included alongside other metabolites
- Longitudinal or multi-matrix studies requiring standardized amino acid panels
Our solution
Lysine can be incorporated into:
- Ready-to-use amino acid panels covering multiple proteinogenic amino acids
- Custom targeted metabolomics panels tailored to your specific analyte list
- Harmonized workflows across different sample types, enabling consistent comparison within multi-matrix and time-course designs
Recommended Lysine Panels and Target Analytes
Small-Molecule Lysine and Related Metabolites
Our targeted LC–MS/MS workflows can be configured as single-analyte assays or focused panels covering lysine and its key pathway intermediates.
| Panel type |
Representative analytes* |
Notes |
| Lysine (single analyte) |
Free lysine |
Stand-alone lysine quantification in any matrix |
| Lysine Catabolism Panel |
Free lysine; saccharopine; aminoadipate-related species; pipecolate; other intermediates |
Focused on lysine degradation pathways |
| Custom metabolite sub-panel |
Any subset of lysine and its pathway metabolites |
Tailored to user-defined analyte lists |
* Additional lysine-related intermediates can be included on request, depending on availability of standards and method feasibility.
Lysine-Based Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs)
For proteomics and PTM-oriented projects, we focus on lysine-containing peptides carrying specific modifications.
| Panel type |
Target class |
Representative targets / examples* |
| Lysine Acetylation Panel |
Acetyl-lysine on peptides/proteins |
Site-specific acetyl-lysine on histones, metabolic enzymes and other proteins |
| Lysine Lactylation Panel |
Lactyl-lysine on peptides/proteins |
Site-specific lactyl-lysine on nuclear and cytosolic proteins |
| Other Lysine Acylation Panel |
Other acyl-lysine residues (where suitable enrichment is available) |
Selected crotonyl-lysine, succinyl-lysine or related acyl-lysine PTMs |
| Selected Glycation Panel |
Glycation-related lysine modifications |
Selected advanced glycation end-product (AGE)–type lysine adducts in defined workflows |
* Exact coverage depends on antibody/enrichment reagents and project design; details are confirmed during method setup.
All PTM panels can be run with label-free, TMT or SILAC quantification, using high-resolution LC–MS/MS for peptide identification and site localization.
Lysine in Broader Amino Acid and Targeted Metabolomics Panels
Lysine can also be measured as part of broader amino acid or custom metabolite panels.
| Panel type |
Role of lysine |
Typical configuration |
| Standard amino acid panel |
One of multiple proteinogenic amino acids |
Fixed panel covering a broad set of amino acids |
| Custom targeted metabolomics panel |
Included as one metabolite in a custom list |
User-defined metabolite set, with lysine optionally included |
| SILAC / heavy lysine QC panel |
Marker of labeling efficiency |
Heavy/light lysine transitions for labeling QC |
In all cases, lysine can be added, removed or combined with other analytes according to your study design. If you already have a list of specific metabolites or protein targets, our team can configure a customized panel and advise on feasibility, expected sensitivity and sample requirements.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics for Lysine Analysis?
- Lysine-centered design
From inherited metabolic diseases to lysine acetylation or lysine-linked ADCs, we build the method around your lysine-related biological question, not the other way around.
- Multiple analytical modes on one platform
Targeted LC–MS/MS for small-molecule lysine metabolites, high-resolution MS for PTMs and biotherapeutics, with optional data-dependent or data-independent acquisition.
- Flexible panels & customization
Choose from ready-to-use lysine catabolism panels, lysine PTM workflows, amino acid panels, or fully custom analyte lists.
- End-to-end support
From study design and sample preparation to bioinformatics, pathway analysis, and result interpretation.
- Applicable to diverse samples
Biofluids, tissues, cells, recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), ADCs, culture media, and more.
Analytical Platforms & Methodology
We use robust LC–MS/MS and high-resolution MS platforms tailored to the specific type of lysine analysis.
Core instruments
- Triple quadrupole LC–MS/MS (UHPLC–QqQ): For highly sensitive, targeted quantification of free lysine and lysine pathway metabolites in complex matrices.
- High-resolution LC–MS/MS (Orbitrap / Q-TOF): For in-depth lysine PTM profiling, peptide mapping and biotherapeutic (mAb/ADC) characterization.
Method Performance Parameters
The values below summarize typical ranges from our validated amino acid, lysine metabolite and PTM workflows. Exact numbers will depend on the analyte, matrix and final assay configuration agreed for your study.
| Parameter |
Typical value / range |
Notes |
| LC mode |
UHPLC, sub-2 µm C18 or HILIC columns, up to ~1200 bar |
Fast gradients and good resolution for lysine and related analytes. |
| Acquisition mode (metabolites) |
ESI, positive mode, MRM (QqQ) |
Targeted transitions for lysine and key catabolic intermediates. |
| Acquisition mode (PTMs) |
DDA/DIA on HRMS |
High-resolution MS/MS for site-level lysine PTM identification. |
| LOD (metabolites) |
Typically low ng/mL or low-nM range |
Sufficient for physiological and pathological levels in biofluids. |
| LOQ (metabolites) |
Typically ≈0.3–10 ng/mL |
Project-specific validation available on request. |
| Linearity |
At least 3–4 orders of magnitude, R² ≥ 0.99 |
Multi-point calibration for quantitative assays. |
| Precision (intra- / inter-day) |
Typically < 10% RSD, often 3–8% |
Based on QC sample performance in lysine-focused methods. |
| Typical run time |
~10–20 min per injection |
Can be shortened or extended depending on panel complexity. |
If your study has special requirements (e.g., very low abundance matrices, GLP-oriented validation), our scientists can adjust and validate the method accordingly.
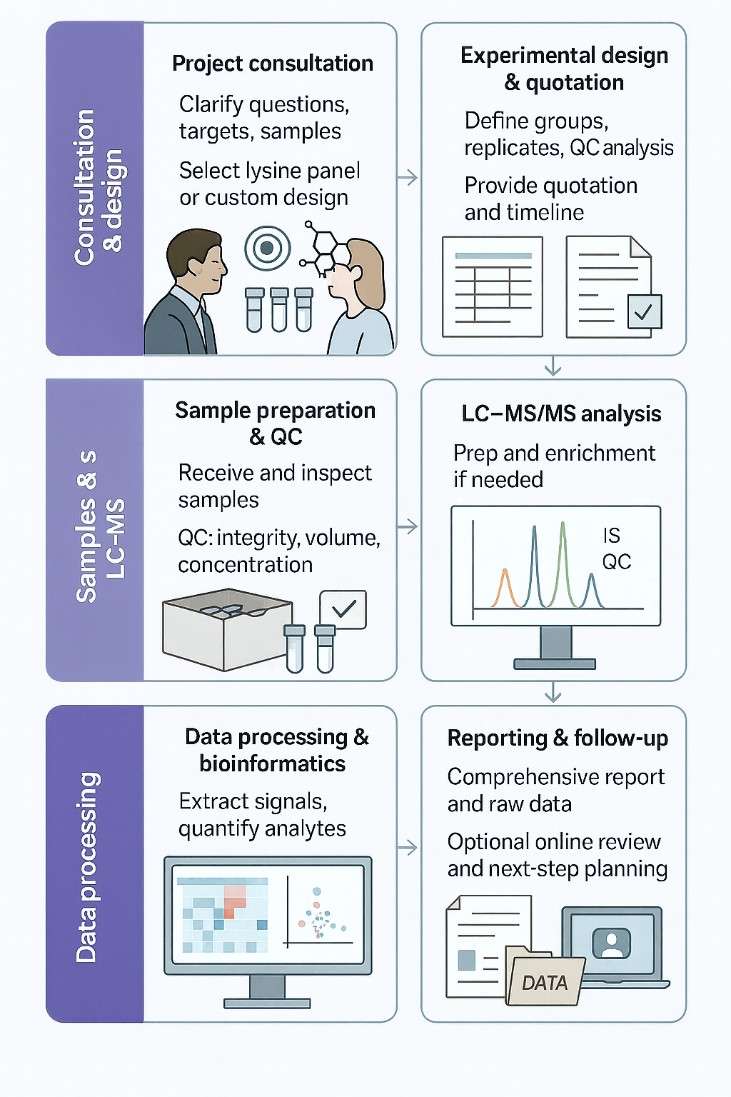
From Sample to Report: Workflow of Lysine Analysis Service
1. Project consultation
Clarify scientific questions, target analytes or PTMs, and sample types. Select the appropriate lysine-focused panel or design a custom solution.
2. Experimental design & quotation
Define group numbers, replicates, QC strategy, and data analysis plan. Provide a detailed quotation and project timeline.
3. Sample preparation & QC
Receive and inspect samples upon arrival. Perform pre-analysis QC (e.g., integrity, volume, concentration).
4. LC–MS/MS analysis
Execute sample preparation, enrichment (if needed), and LC–MS/MS runs. Monitor instrument performance with internal standards and QC samples.
5. Data processing & bioinformatics
Extract and process signals for all analytes / modified peptides. Perform quantitation, statistics, and pathway or functional analysis where requested.
Sample Types & Recommended Amounts
We accept a wide range of sample types. The table below is an example guideline; please contact us for precise requirements for your specific project.
| Sample Type |
Recommended Amount (Typical) |
Notes |
| Plasma / Serum |
≥ 100–200 µL |
Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles |
| Urine |
≥ 500 µL |
Collect midstream, record collection time |
| CSF (where applicable) |
≥ 100 µL |
Low-volume workflows available |
| Tissue (animal or human) |
≥ 20–50 mg |
Snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, stored at −80°C |
| Cultured cells |
≥ 1×10⁶–5×10⁶ cells |
Washed and snap-frozen or extracted |
| Culture supernatant / media |
≥ 500 µL |
Record culture conditions and time points |
| mAbs / ADCs / recombinant proteins |
≥ 50–100 µg |
Concentration and formulation information needed |
If your sample type is not listed (e.g., fermentation broth, organoids, special matrices), our technical support team can advise on collection and storage.
Data Outputs and Reporting
Data files
Raw MS data (vendor formats; mzML on request)
Processed result tables with:
- Peak areas / intensities
- Absolute or relative concentrations (if calibrated)
- Quality control summary
PTM / Proteomics Outputs (if applicable)
- Lists of identified proteins and peptides
- Site-specific lysine modifications with localization scores
- Quantitative comparisons between conditions
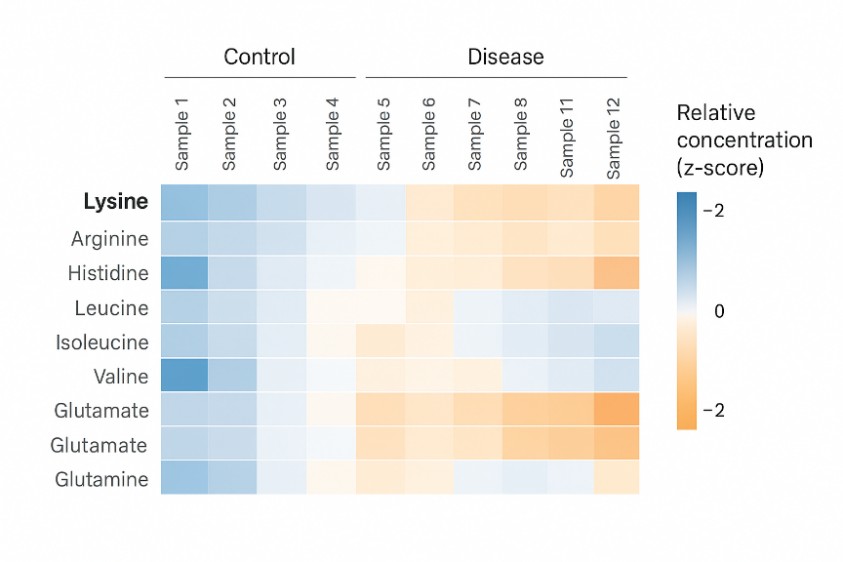
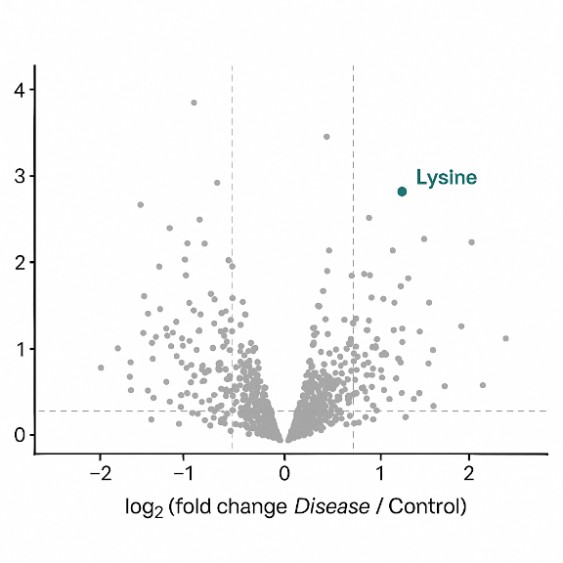
Bioinformatics & Visualization (on request)
- Heatmaps, volcano plots and clustering
- Pathway and GO enrichment analysis
- Lysine-related pathway diagrams
Technical Report
- Overview of experimental workflow
- Key LC–MS/MS parameters
- Data processing and statistical methods
- Interpretation of main findings and conclusions
Water-soluble saponins accumulate in drought-stressed switchgrass and reduce bioethanol production
Chipkar, S., Smith, K., et al.
Journal: Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts
Year: 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-022-02213-y
Elevated SLC7A2 expression is associated with an abnormal neuroinflammatory response and nitrosative stress in Huntington's disease
Gaudet, I. D., Xu, H., Gordon, E., Cannestro, G. A., Lu, M. L., & Wei, J.
Journal: Journal of Neuroinflammation
Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-024-03038-2
Macrophage-Associated Lipin-1 Promotes β-Oxidation in Response to Proresolving Stimuli
Schilke, R. M., Blackburn, C. M., Rao, S., Krzywanski, D. M., Finck, B. N., & Woolard, M. D.
Journal: ImmunoHorizons
Year: 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/immunohorizons.2000047
Lipin-1 regulates lipid catabolism in pro-resolving macrophages
Schilke, R. M., Blackburn, C. M., Rao, S., Krzywanski, D. M., Finck, B. N., & Woolard, M. D.
Journal: bioRxiv
Year: 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.03.121293

 Representative LC–MS/MS chromatograms and group comparison for lysine and key catabolic intermediates in plasma.
Representative LC–MS/MS chromatograms and group comparison for lysine and key catabolic intermediates in plasma.