What Is Valine—and Why Measure It?
Valine is an essential branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) that supports protein synthesis, nitrogen balance, and energy production—especially in muscle and rapidly dividing cells. Because Val concentrations shift with diet, training, metabolic stress, and drug exposure, quantitative LC-MS/MS provides the reproducible readouts needed to compare conditions, map pathway changes, and link phenotype to mechanism. Co-measurement with leucine/isoleucine and context markers (alanine, glutamine/glutamate) strengthens interpretation of BCAA utilization and central-carbon metabolism across plasma/serum, CSF, urine, tissues, and cell systems.
Valine Analysis Services by Creative Proteomics
At Creative Proteomics, we offer a comprehensive suite of LC‑MS/MS services centered on valine quantification, designed for scientists aiming to decipher BCAA metabolism and related pathways.
- Valine absolute quantification in plasma, serum, CSF, urine, tissue lysates, and cell culture systems
- BCAA panel analysis: Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine co-quantified to evaluate metabolic status
- Optional analyte extensions: Alanine (transamination), Glutamine/Glutamate (nitrogen turnover), Phenylalanine/Tyrosine (aromatic amino-acid pathways)
- Custom ratio outputs: BCAA ratios, optional Phe/Tyr ratio when co-measured
- Flux tracing capability: 13C/15N-labeled Valine with full isotopologue readout for pathway flux studies
Why Choose Our Valine Analysis Service?
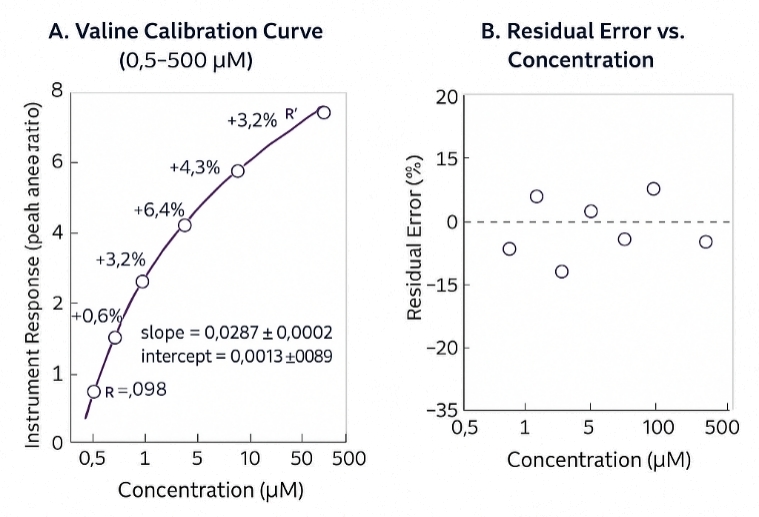
- Broad Dynamic Range – Quantitative range validated over 0.5–500 µM with excellent linearity
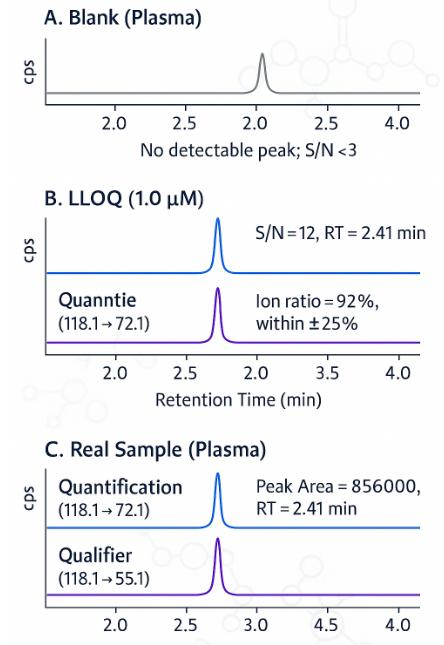
- High Sensitivity – Matrix-specific LLOQ as low as 0.5 µM, with S/N ≥10 at lowest level
- Strong Linearity – Weighted (1/x²) regression with R² ≥ 0.995 across all batches
- Precise & Reproducible – Intra-batch %RSD ≤ 10%, inter-batch ≤ 15% at QC levels
- Accurate Quantification – Back-calculated %RE within ±10% for calibrators and controls
- Selectivity Assured – Dual MRM transitions with ion-ratio deviation <25% and strict RT matching
- No Carryover – Verified in post-high blanks, signal <0.1× LLOQ
- Panel-Compatible – Co-analysis with BCAAs (Leu/Ile) or amino acids (Glu, Gln, Ala, Phe, Tyr) without compromising performance
- Flexible Throughput – Runtime per sample <8 minutes, adaptable for targeted studies or screening
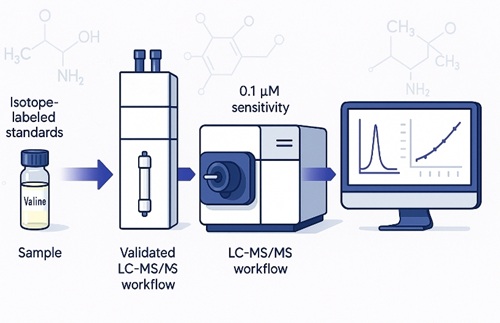
Valine LC‑MS/MS Method and Analytical Performance
Platform: Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC + 6495C Triple Quadrupole LC-MS/MS (MRM)
Chromatography: HILIC (amide) or reversed-phase (by matrix)
Internal Standard: isotope-labelled Val (preferred) or validated analogue
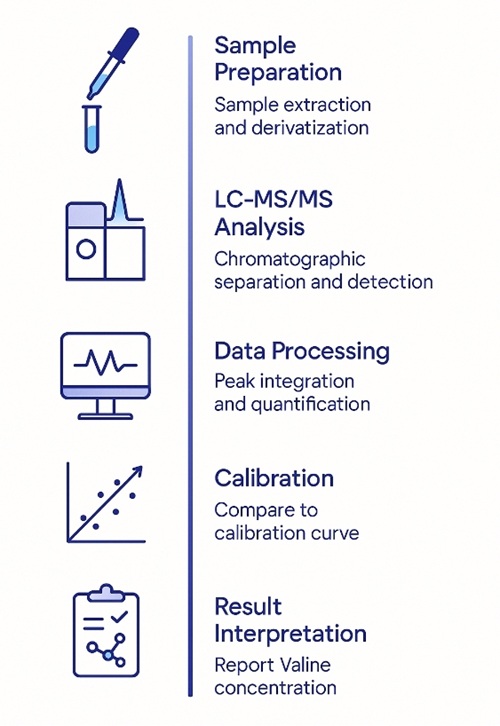
Preparation: cold protein precipitation ± derivatization (if justified by matrix/sensitivity); low-temperature handling to minimize conversion
Acquisition: ESI(+) MRM; example transitions Val m/z 118.1→72.1 (quant) and 118.1→55.1 (qual); IS matched transitions
Processing: MassHunter or an equivalently validated pipeline (ion-ratio check, RT window, peak integration review)
Valine Quantification Workflow: From Sample to Report
Sample Requirements for Valine Testing
| Matrix |
Minimum amount |
Container |
Pre-analytical handling |
Storage & shipping |
Notes / Normalization |
| Plasma / Serum |
≥ 80 µL (ideal 100 µL) |
Low-bind PP microtube; EDTA or heparin for plasma |
Keep on ice; prompt centrifugation; avoid hemolysis |
−80 °C; ship on dry ice |
Record anticoagulant; limit freeze–thaw (≤3) |
| CSF |
≥ 60 µL |
Sterile, low-bind tube |
Handle cold; minimize dwell time |
−80 °C; dry ice |
No additives |
| Urine |
≥ 250 µL |
PP tube |
Mix gently; note dilution or SG if applicable |
≤ −20 °C (short) or −80 °C; cold ship |
Optional normalization: creatinine / osmolality |
| Tissue homogenate |
≥ 25 mg eq. |
Pre-chilled, low-bind tube |
Rapid quench/extraction under cold conditions |
−80 °C; dry ice |
Provide wet weight & buffer details |
| Cell lysate / pellet |
≥ 50 µL lysate or ≥ 0.5–1×10⁶ cells |
Low-bind tube |
Work cold; clarify as needed |
−80 °C; dry ice |
Report protein concentration or cell count |
| Cell culture supernatant / media |
≥ 250 µL |
Sterile PP tube |
Quench promptly; remove debris by spin |
−80 °C; dry ice |
Note timepoint, cell density, treatment |
General tips: aliquot to avoid repeat freeze–thaw; include a manifest (sample ID, matrix, volume/mass, collection time, treatment, dilution/normalization plan).
What You Receive: Deliverables from Our Valine Analysis
- Concentration tables (SI units): Valine results per sample/matrix with sample IDs and any dilution factors.
- Calibration summary: Fit model (e.g., 1/x²), range, R², and back-calculated accuracy.
- QC overview: Precision/accuracy at L/M/H levels with pass/fail notes.
- Representative MRM chromatograms: Quantifier/qualifier traces with RT window and ion-ratio check.
- Data files: PDF report plus CSV/Excel; raw files available on request.
- If co-measured: BCAA ratios or study-specific indices included.
Applications of Valine Analysis in Research and Industry
Untargeted metabolomics reveal sex-specific and non-specific redox-modulating metabolites in kidneys following binge drinking
Rafferty, D., de Carvalho, L. M., Sutter, M., Heneghan, K., Nelson, V., Leitner, M., ... & Puthanveetil, P.
Redox Experimental Medicine
Year: 2023
Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF-1α
Pelletier, A., Nelius, E., Fan, Z., Khatchatourova, E., Alvarado-Diaz, A., He, J., ... & Stockmann, C.
EMBO Reports
Year: 2023
Exogenous lipase administration alters gut microbiota composition and ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in APP/PS1 mice
Menden, A., Hall, D., Hahn-Townsend, C., Broedlow, C. A., Joshi, U., Pearson, A., ... & Ait-Ghezala, G.
Scientific Reports
Year: 2022
The activity of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in T cells tunes the gut microenvironment to sustain autoimmunity and neuroinflammation
Merchak, A. R., Cahill, H. J., Brown, L. C., Brown, R. M., Rivet-Noor, C., Beiter, R. M., ... & Gaultier, A.
PLOS Biology
Year: 2023
Multiomics of a rice population identifies genes and genomic regions that bestow low glycemic index and high protein content
Badoni, S., Pasion-Uy, E. A., Kor, S., Kim, S. R., Tiozon Jr, R. N., Misra, G., ... & Sreenivasulu, N.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)
Year: 2024