Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate?
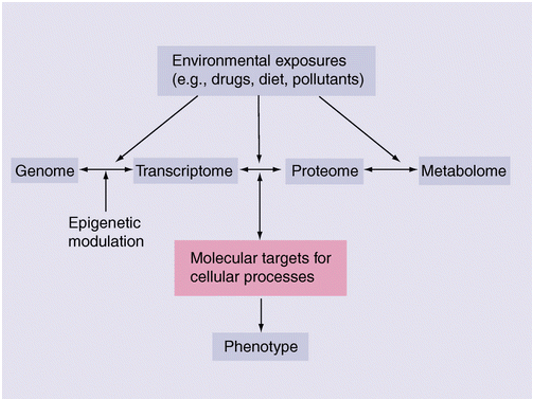
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is an important metabolic intermediate in the glycolytic pathway. It is a phosphorylated form of dihydroxyacetone, a simple carbohydrate that can be found in many living organisms. DHAP is produced during the breakdown of glucose and can be further converted to either glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate or used in the biosynthesis of glycerolipids.
Analyzing DHAP levels is crucial for understanding the metabolic state of cells, tissues, and organisms. The analysis of DHAP can provide valuable information about energy production and utilization, as well as lipid metabolism.
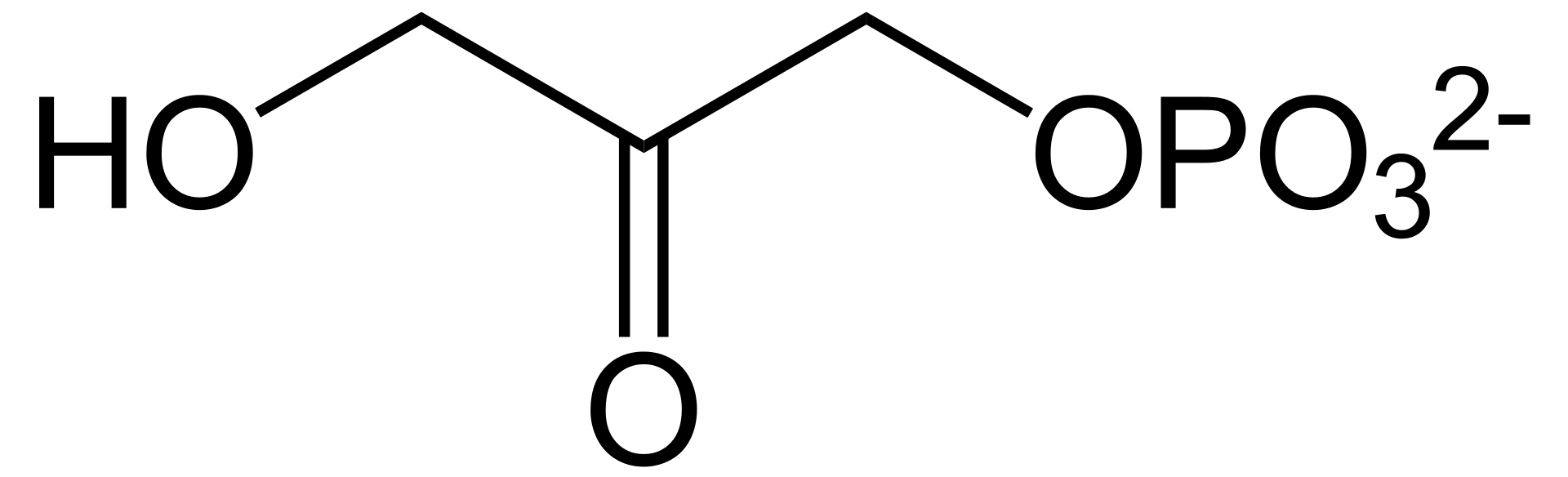 Molecular structure of dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Molecular structure of dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate Analysis Technology Platform in Creative Proteomics
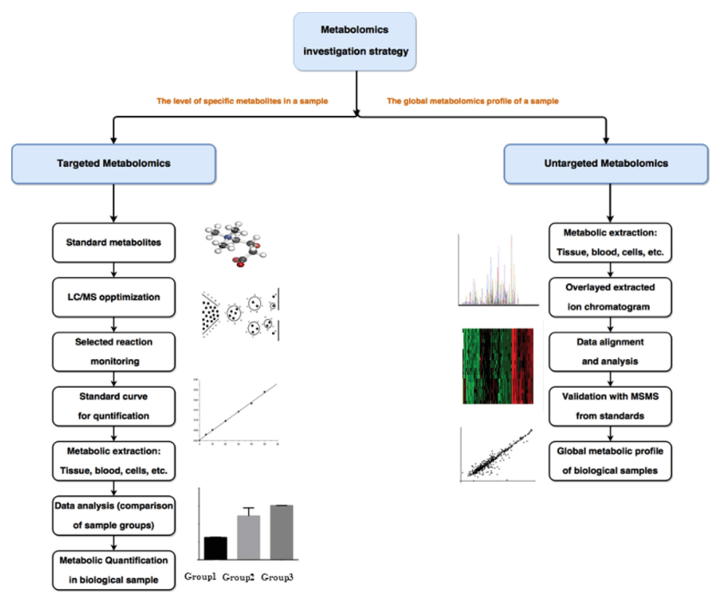
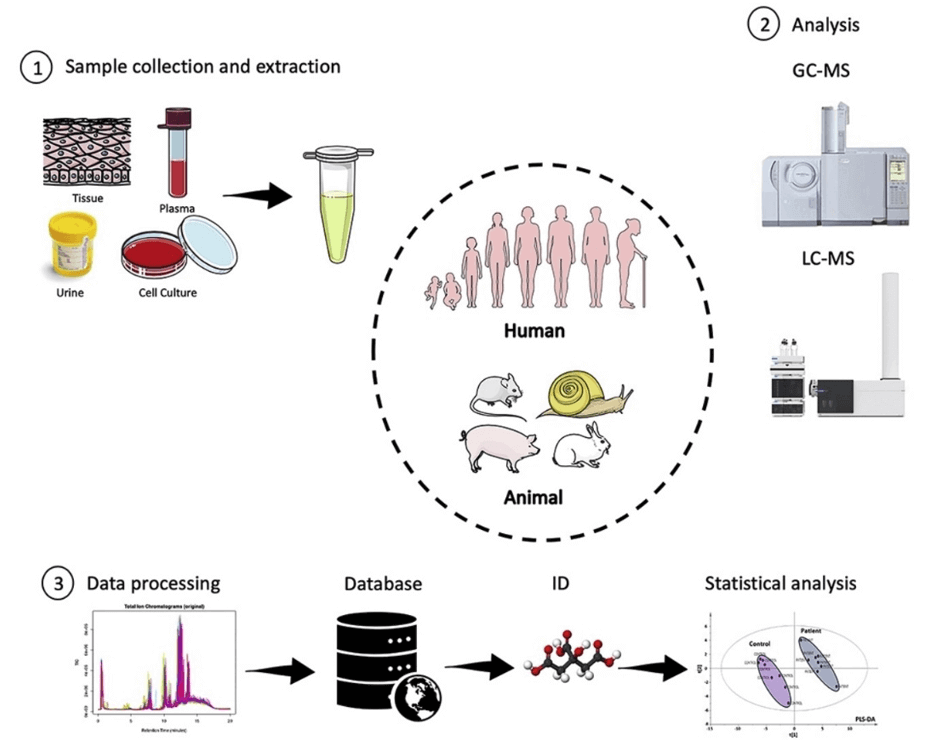
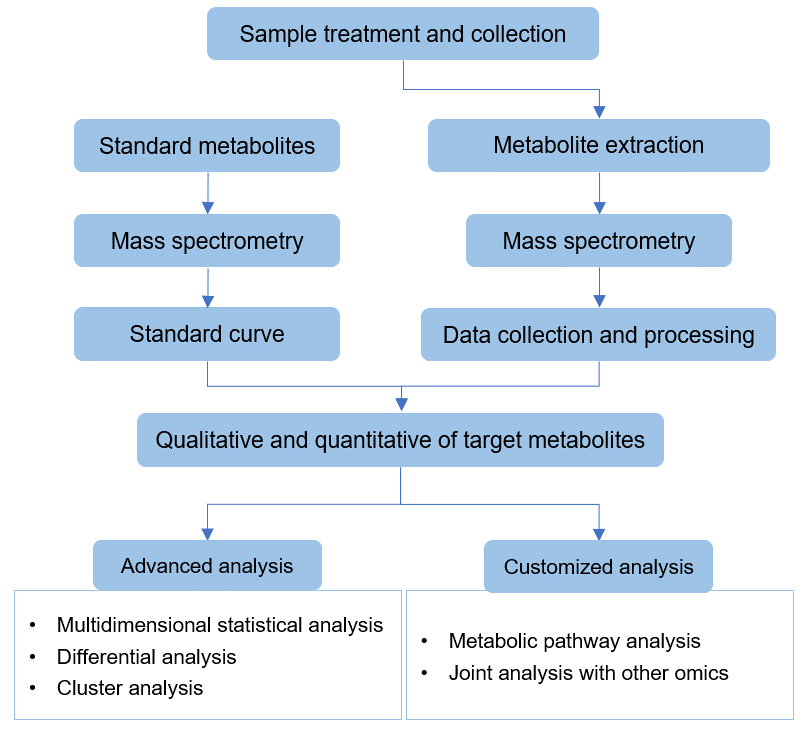
The DHAP analysis technology platform at Creative Proteomics is based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). This platform allows for the sensitive and accurate detection of DHAP in various sample types, including cells, tissues, and biofluids. The LC-MS method offers several advantages over other analytical methods, including high sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity. It also allows for the simultaneous analysis of multiple metabolites in a single sample, making it a powerful tool for metabolomics research.
Technical Route of Targeted Metabolomics of Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
Applications of Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate Analysis
Glycolysis studies: DHAP is a key intermediate in glycolysis and its analysis can provide valuable information on the metabolic state of cells. By measuring DHAP levels, the activity of glycolytic enzymes can be assessed and potential targets for drug development can be identified.
Studies of lipid metabolism: DHAP is a precursor for the biosynthesis of glycerolipids, which are important components of cell membranes and energy storage molecules. Analysis of DHAP levels can provide insight into the regulation of lipid metabolism and identify potential targets for the treatment of metabolic disorders.
Various disease mechanism studies: DHAP levels have been shown to be altered in diabetes, obesity and cancer. By measuring DHAP levels in samples, it is possible to assess disease progression and aid in disease diagnosis and treatment development.
Feedback to Customers
Creative Proteomics will provide you with detailed technical reports, including
- Experimental steps
- Related mass spectrometry parameters
- Part of the mass spectrum picture
- Raw data
- Metabolic molecular identification results
Creative Proteomics offers several approaches to metabolomics studies, delivers precise and detailed data and analysis report. We can also customize the methods or establish new methods together with our collaborators, so they are fit-for-purpose and meet your specific needs. If you have any questions or specific requirements, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Kim M J, Lee M Y, Shon J C, et al. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics analyses of blackberries – Understanding postharvest red drupelet disorder. Food Chemistry, 2019, 300:125169.
- Pawlak M, Klupczynska A, Kokot Z J, et al. Extending Metabolomic Studies of Apis mellifera Venom: LC-MS-Based Targeted Analysis of Organic Acids. Toxins, 2019, 12(1):14.
- Wang X, Zhao X, Zhao J, et al. Serum metabolite signatures of epithelial ovarian cancer based on targeted metabolomics. Clinica Chimica Acta, 2021, 518: 59-69.