Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryGlucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is the main regulatory enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway. g6PD catalyzes the oxidation of glucose 6-phosphate to gluconolactone 6-phosphate, while its reduction equivalent product is stored as NADPH for biosynthesis and maintenance of the intracellular reduced state.
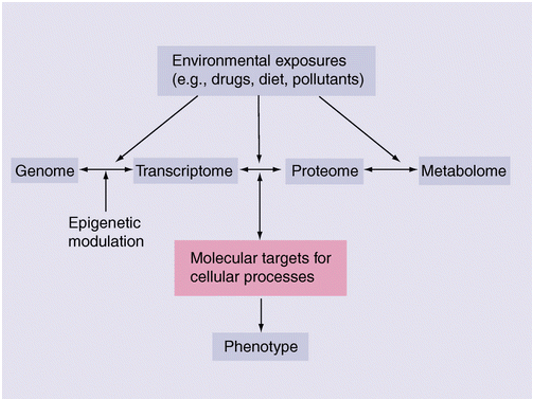
G6PD deficiency is the most common inherited cellular enzyme disease in humans, and previous studies have focused on hemolysis and anemia. In recent years, the importance of G6PD at the cellular level and in development and disease progression has received increasing attention. Reduced G6PD activity and disruption of intracellular redox homeostasis will lead to dysregulation of cell growth and signaling, abnormal embryonic development, susceptibility to viruses and promotion of degenerative diseases.
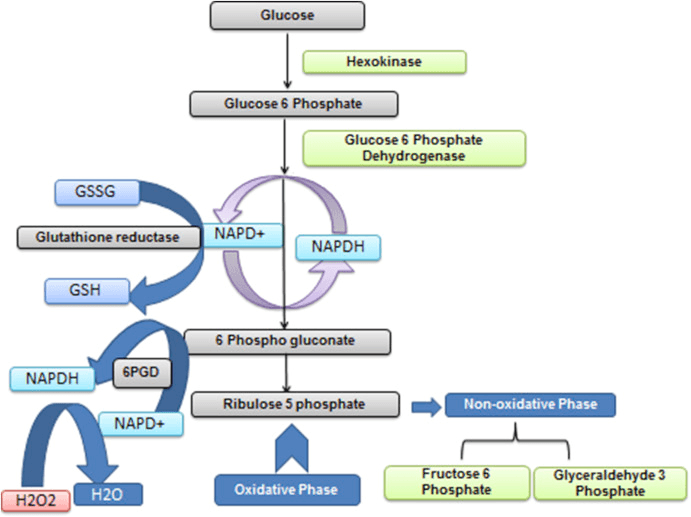 Schematic representation of the involvement of G6PD in energy harnessing and as an antioxidant (Tiwari et al., 2017)
Schematic representation of the involvement of G6PD in energy harnessing and as an antioxidant (Tiwari et al., 2017)
Plants are in a wide variety of environments and G6PD activity is involved in many physiological and biochemical processes within plant cells and in tolerance to different environmental stresses. During plant growth and development, the pentose phosphate pathway is a ubiquitous pathway for sugar catabolism, but with different proportions in different tissues. It provides a variety of raw materials for other biosynthesis in addition to energy.
By regulating the metabolic flux of the pentose phosphate pathway, G6PD provides NADPH for fatty acid synthesis in oilseed crops, which promotes increased oil content, ribose 5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis in certain metabolically active tissues, and erythrose 4-phosphate for aromatic amino acid synthesis. In addition, the ribulose-5-phosphate generated by this pathway can be converted to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate to participate in photosynthesis and increase the accumulation of glycoconjugates. It is by promoting the production of these substances that G6PD promotes cell growth and regulates growth and development.
The NADPH catalyzed by G6PD can be directly dehydrogenated by the action of NADPH oxidase on the plasma membrane to scavenge reactive oxygen species, or through the interaction of a series of intracellular antioxidant enzymes to scavenge reactive oxygen species and eliminate cellular hazards.
Creative Proteomics has established reliable MALDI-TOF MS and LC-MS assay that enables the determination of G6PD content, helping researchers to accelerate the progress of their projects.
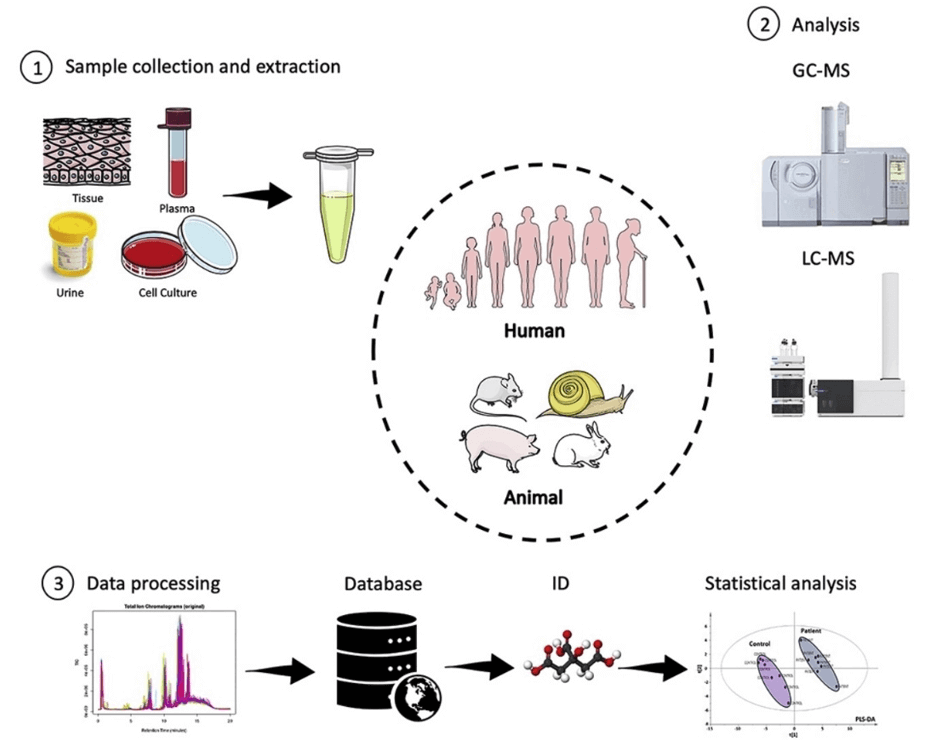
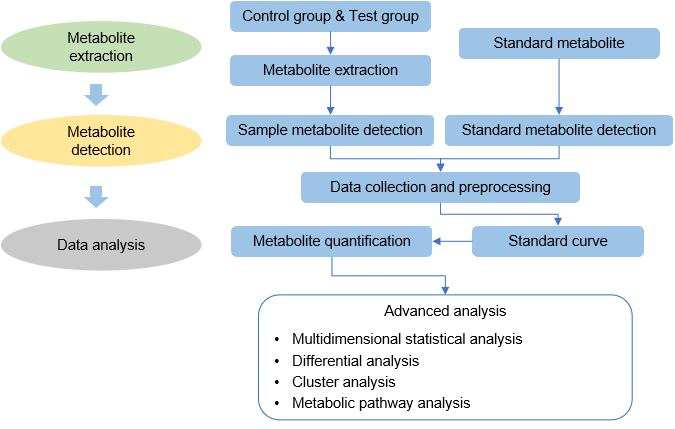
Technical Route of Targeted Metabolomics of Glucose-6-phosphate
Sample Requirements
- Tissues (animal / plant): ≥ 100 mg/sample
- Cells or bacteria > 107, supernatant > 2 mL
- Blood / Serum / Plasma ≥ 200 μL/sample
- Urine ≥ 100 µL
For other sample types, please consult technical support.
It is recommended that select more than 3 materials with the same condition for each sample and prepare 6 biological replicates for each group.
Deliverables
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of mass spectrometry
- Chromatography and mass spectrometry raw data
- Chromatogram and mass spectrum
- Hexanoic acid quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Turnaround Time: 1-4 weeks
Creative Proteomics offers several approaches to provide glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase analysis service and deliver precise and detailed data and analysis report. If you want to detect other metabolites but have not found them, you can tell us through the inquiry form, and our technicians will communicate with you.
Reference
- Tiwari, M. (2017). Glucose 6 phosphatase dehydrogenase (G6PD) and neurodegenerative disorders: Mapping diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. Genes & diseases, 4(4), 196-203.