Why Analyze the Pantothenate & CoA Metabolic Pathway and Biosynthesis?
Pantothenate (vitamin B5) is the precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), a central cofactor that carries acyl groups in hundreds of biochemical reactions. The pantothenate & CoA metabolic pathway converts pantothenate through a series of phosphorylated intermediates into CoA, linking carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabolism.
When this pantothenate & CoA biosynthesis pathway is perturbed, cells rapidly adjust energy production, fatty acid synthesis, and even epigenetic regulation through changes in acetyl-CoA and other acyl-CoA species. Subtle shifts in pathway intermediates can therefore signal:
- metabolic stress or nutrient imbalance
- drug target engagement in microbes and parasites
- functional changes in immune cells and tumors
Targeted quantitative analysis of the pantothenate & CoA metabolic pathway provides pathway-level information that goes far beyond single-metabolite readouts. Our service is designed to capture these changes with high sensitivity and reproducibility, so you can connect experimental interventions to clear biochemical mechanisms.
Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Targeted Metabolomics Solutions
Standard pantothenate & CoA biosynthesis targeted assay: Ready-to-use LC–MS/MS method covering the core pantothenate & CoA biosynthesis pathway.
Custom panel design and expansion: Tailored panel setup or extension, including combination with other targeted metabolomics panels (e.g. central carbon metabolism, amino acids, organic acids, lipids).
Pathway visualization and biological interpretation: Mapping quantitative changes onto the pantothenate & CoA metabolic pathway, with expert comments on affected steps and potential mechanisms.
Integration into broader metabolomics and multi-omics projects: Incorporation of pantothenate & CoA biosynthesis data into larger metabolomics studies or multi-omics workflows.
Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Metabolite Panel and Pathway Coverage
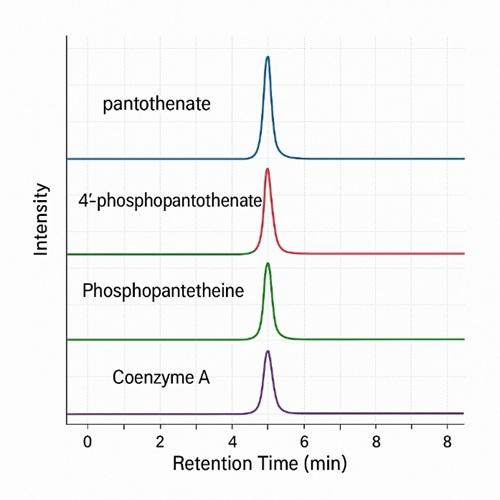
Our pantothenate & CoA biosynthesis targeted metabolomics panel focuses on key intermediates along the vitamin B5–to–CoA route. Representative analytes include, but are not limited to, the following metabolites:
Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Pathway Metabolites
| Metabolite |
Role in Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis |
| Pantothenate (Vitamin B5) |
Precursor for CoA biosynthesis, essential for energy metabolism and acyl transfer reactions. |
| Pantoic acid |
Intermediate in pantothenate biosynthesis. Involved in the conversion of pantoate to pantothenate. |
| β-Alanine |
Combines with pantoate to form pantothenate, crucial in amino acid and energy metabolism. |
| 4'-Phosphopantothenate |
First phosphorylated intermediate in the biosynthesis of CoA. Essential for further CoA production. |
| 4'-Phosphopantothenoyl-L-cysteine |
Cysteine conjugate intermediate, connecting pantothenate to CoA in the biosynthetic pathway. |
| Phosphopantetheine |
Central intermediate linking pantothenate to CoA, required for CoA activation. |
| Dephospho-CoA |
Key intermediate in CoA biosynthesis, necessary for enzymatic reactions in metabolic pathways. |
| Coenzyme A (CoA) |
Final active cofactor in the biosynthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones. |
Acyl-CoA Species and Related Metabolites
| Metabolite |
Role in Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis |
| Acetyl-CoA |
The most common acyl-CoA, central to the TCA cycle, fatty acid synthesis, and protein acetylation. |
| Malonyl-CoA |
Precursor for fatty acid synthesis, involved in lipid metabolism and regulation of mitochondrial function. |
| Palmitoyl-CoA |
Intermediate in fatty acid metabolism and mitochondrial function. Used in acylation reactions. |
| Butyryl-CoA |
Involved in fatty acid metabolism, particularly in the catabolism of branched-chain fatty acids. |
Upstream Precursors and Related Intermediates
| Metabolite |
Role in Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis |
| Pantoate |
The precursor for pantothenate, essential in the first step of CoA biosynthesis. |
| Dehydropantoate |
Intermediate in the conversion of pantoate to pantothenate, part of the initial biosynthetic steps. |
Optional Custom Metabolites
Additional metabolites can be added to the panel based on your research needs:
- CoA derivatives (e.g., Acyl-CoA esters) involved in lipid and amino acid metabolism.
- Other cofactor-related metabolites such as CoQ10, NAD+, NADH, and FAD, for more comprehensive metabolic pathway analysis.
Why Choose Our Pantothenate & CoA Targeted Metabolomics
- Pathway-focused targeted LC–MS/MS
Optimized MRM methods for pantothenate (vitamin B5), CoA and key biosynthetic intermediates, with typical run times of 10–20 minutes per sample for efficient batch analysis.
- High sensitivity and wide dynamic range
LLOQ typically in the low-nanomolar range for most pantothenate & CoA biosynthesis intermediates, with 3–4 orders of magnitude linear dynamic range (R² ≥ 0.99).
- Excellent precision and reproducibility
Intra-batch QC CVs typically < 10%, inter-batch CVs typically < 15%, supporting robust comparisons across groups and time points.
- Quantitative accuracy with isotope-labeled standards
Optional isotope-labeled internal standards and matrix-matched calibration curves, with typical analyte recoveries in the 80–120% range to enhance absolute quantification accuracy.
- Low missing-value rates in targeted data
Targeted acquisition and strict QC help keep missing-value rates below 5–10% in well-prepared sample sets, reducing the need for imputation.
Technical Parameters for Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis LC–MS/MS Analysis
We utilize a robust, validated LC–MS/MS setup tailored for quantitative analysis of pantothenate, CoA, and related biosynthetic intermediates.
Instrumentation Overview
| Component |
Model |
Function |
| HPLC System |
Agilent 1260 Infinity II |
High-performance liquid chromatography for efficient separation of polar metabolites. Stable gradient flow and reproducible retention times support high-throughput analysis. |
| Mass Spectrometer |
Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole |
Ultra-sensitive LC–MS/MS system optimized for MRM-based targeted metabolomics, capable of detecting analytes at low-nanomolar concentrations with wide dynamic range. |
Technical Specifications
| Parameter |
Typical Performance |
| LOD (Limit of Detection) |
Low nanomolar (nM) range for most analytes |
| LOQ (Limit of Quantification) |
Typically 1–5 nM, depending on matrix and analyte |
| Linear Dynamic Range |
3–4 orders of magnitude (e.g. 0.5–5,000 nM), R² ≥ 0.99 |
| Run Time per Sample |
10–20 minutes |
| Intra-batch Precision |
CV < 10% (based on QC replicates) |
| Inter-batch Precision |
CV < 15% (in controlled multi-batch runs) |
| Quantification Method |
External or matrix-matched calibration with internal standards |
| Calibration Levels |
Typically 6–8 levels per compound |
| Recovery Accuracy |
80–120% (when using isotope-labeled standards) |
Workflow for Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Analysis
Sample Requirements for Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Projects
| Sample type |
Recommended amount per sample |
Container & labeling |
Storage & stability |
Special notes |
| Plasma / Serum |
≥ 100–200 µL |
Pre-labelled low-bind microcentrifuge tubes |
Snap-freeze in liquid N₂; store at −80 °C; avoid >2 freeze–thaw cycles |
Collect using EDTA or heparin tubes; centrifuge promptly; separate plasma/serum within 1–2 h. |
| Whole Blood (by agreement) |
≥ 200–300 µL |
Pre-labelled cryovials |
Snap-freeze and store at −80 °C |
Requires prior consultation; anticoagulant type and protocol must be aligned with project goals. |
| Tissues (animal / plant) |
≥ 20–30 mg wet weight |
Pre-cooled cryovials or foil-wrapped tissue |
Snap-freeze immediately after collection; store at −80 °C |
Minimize ischemia time; avoid buffer immersion; record tissue type, location and treatment. |
| Cultured Cells |
≥ 1–5 × 10⁶ cells (pellet, washed) |
Pre-labelled low-bind tubes |
Snap-freeze cell pellets; store at −80 °C |
Wash quickly with ice-cold PBS or saline; remove supernatant completely before freezing. |
| Biofluids (urine, CSF, others) |
≥ 200–500 µL (depending on matrix) |
Pre-labelled microcentrifuge tubes |
Aliquot, snap-freeze, store at −80 °C |
Clarify whether samples are spot, timed, or pooled collections; note any preservatives used. |
| Microbial Cultures / Pellets |
Equivalent to ≥ 20 mg wet biomass |
Pre-labelled tubes or cryovials |
Snap-freeze and store at −80 °C |
Indicate medium, growth phase, OD and treatment; pellet and remove medium quickly on ice. |
| Extracts (by prior agreement) |
≥ 50–100 µL of pre-extracted metabolite solution |
LC–MS compatible tubes (e.g., PP or glass) |
Store at −80 °C, protected from light if applicable |
Provide full extraction solvent composition and protocol; avoid detergents and high salt. |
| General Shipping Instructions |
— |
— |
Ship on dry ice (minimum 5 kg) to maintain −80 °C conditions |
Include a detailed sample list (ID, matrix, treatment, time point); avoid shipment on weekends/holidays. |
Recommended Replicates
- Cell and microbial experiments: ≥ 6 biological replicates per group
- Animal studies: ≥ 8–10 biological replicates per group
- Human cohorts: as large as feasible; please contact us to discuss power and design
What You Receive from Our Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Analysis Service
- Processed LC–MS/MS data tables
Peak lists and quantitative result tables for pantothenate, CoA and covered intermediates (per sample, per group).
- QC performance summary
Brief report with calibration results, linear ranges, basic accuracy and precision (CV) metrics.
- Method and settings overview
Concise description of sample preparation, LC conditions, MRM settings and data-processing workflow.
- Raw data files (on request)
Vendor-format raw LC–MS/MS files and/or export formats agreed at project setup (research use only).
Applications of Pantothenate & CoA Biosynthesis Targeted Metabolomics
Quantifying forms and functions of intestinal bile acid pools in mice
Sudo, K., Delmas-Eliason, A., Soucy, S., Barrack, K. E., Liu, J., Balasubramanian, A., ... & Sundrud, M. S.
Journal: bioRxiv
Year: 2024
Thermotolerance capabilities, blood metabolomics, and mammary gland hemodynamics and transcriptomic profiles of slick-haired Holstein cattle during mid lactation in Puerto Rico
Contreras-Correa, Z. E., Sánchez-Rodríguez, H. L., Arick II, M. A., Muñiz-Colón, G., & Lemley, C. O.
Journal: Journal of Dairy Science
Year: 2024
Untargeted metabolomics reveal sex-specific and non-specific redox-modulating metabolites in kidneys following binge drinking
Rafferty, D., de Carvalho, L. M., Sutter, M., Heneghan, K., Nelson, V., Leitner, M., ... & Puthanveetil, P.
Journal: Redox Experimental Medicine
Year: 2023
Metabolites and Genes behind Cardiac Metabolic Remodeling in Mice with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Kambis, T. N., Shahshahan, H. R., & Mishra, P. K.
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year: 2022
Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF‐1α
Pelletier, A., Nelius, E., Fan, Z., Khatchatourova, E., Alvarado‐Diaz, A., He, J., ... & Stockmann, C.
Journal: EMBO Reports
Year: 2023
Enhance trial: effects of NAD3® on hallmarks of aging and clinical endpoints of health in middle aged adults: a subset analysis focused on blood cell NAD+ concentrations and lipid metabolism
Roberts, M. D., Osburn, S. C., Godwin, J. S., Ruple, B. A., La Monica, M. B., Raub, B., ... & Lopez, H. L.
Journal: Physiologia
Year: 2022