Why Analyze Nicotinate and Nicotinamide?
Nicotinate and nicotinamide are central building blocks for the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide pool. Through de novo synthesis from tryptophan and salvage pathways that recycle nicotinamide and nicotinamide riboside, cells maintain NAD and NADP levels to support glycolysis, the TCA cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid oxidation, and many other redox-dependent reactions.
When precursor levels are perturbed, you may see:
- Imbalanced NAD⁺/NADH or NADP⁺/NADPH ratios.
- Compensatory changes in de novo versus salvage pathways.
- Accumulation of downstream catabolites such as trigonelline or nicotinurate.
By profiling nicotinate, nicotinamide, and their derivatives alongside broader metabolomics data, you can:
- Clarify whether changes in NAD metabolism are driven by precursor limitation, pathway bottlenecks, or increased consumption.
- Link redox changes to nutrient status, cofactor metabolism, and one-carbon pathways.
- Support mechanism-of-action studies for compounds that modulate NAD biosynthesis or salvage.
What Our Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Analysis Service Includes
Our nicotinate and nicotinamide analysis is built as a targeted metabolomics panel that can stand alone or be integrated into wider cofactor and vitamin profiling.
Typical service modules include:
- Absolute quantification of nicotinate and nicotinamide in biofluids, tissues, cells, and other research samples.
- Extended panel of related metabolites, including key intermediates and catabolites for pathway interpretation.
- Custom panel design to add or remove analytes that are relevant to your model or intervention.
- Optional integration with NAD species (NAD⁺, NADH, NADP⁺, NADPH) and one-carbon metabolites via linked services.
- Data analysis and visualization, including group comparisons, ratios (for example nicotinate/nicotinamide), and basic pathway mapping.
Targeted Metabolite Panel: Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Pathway
| Metabolite Name |
Abbreviation |
Biological Role / Pathway Node |
Sample Compatibility |
| Nicotinate |
NA |
Precursor in Preiss–Handler pathway |
Plasma, tissue, urine |
| Nicotinamide |
NAM |
Salvage pathway substrate |
Plasma, serum, urine, cells |
| NAD⁺ |
NAD⁺ |
Central redox cofactor in catabolic metabolism |
Tissue, cells, plasma |
| NADP⁺ |
NADP⁺ |
Redox cofactor for biosynthetic and antioxidant processes |
Cells, tissues |
| Nicotinamide mononucleotide |
NMN |
Intermediate in NAD⁺ salvage synthesis |
Plasma, liver, cultured cells |
| Nicotinate mononucleotide |
NaMN |
Intermediate from nicotinate to NAD⁺ |
Cells, tissues |
| Nicotinamide riboside |
NR |
Alternative precursor for NAD⁺ formation |
Plasma, supplements |
| Trigonelline |
— |
Methylated nicotinate derivative; dietary exposure marker |
Urine, plasma |
| Nicotinurate |
— |
Degradation product of nicotinate |
Urine |
| N-methyl-nicotinamide |
MNA |
Nicotinamide degradation product |
Urine, plasma |
Advantages of Our Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Analysis Service
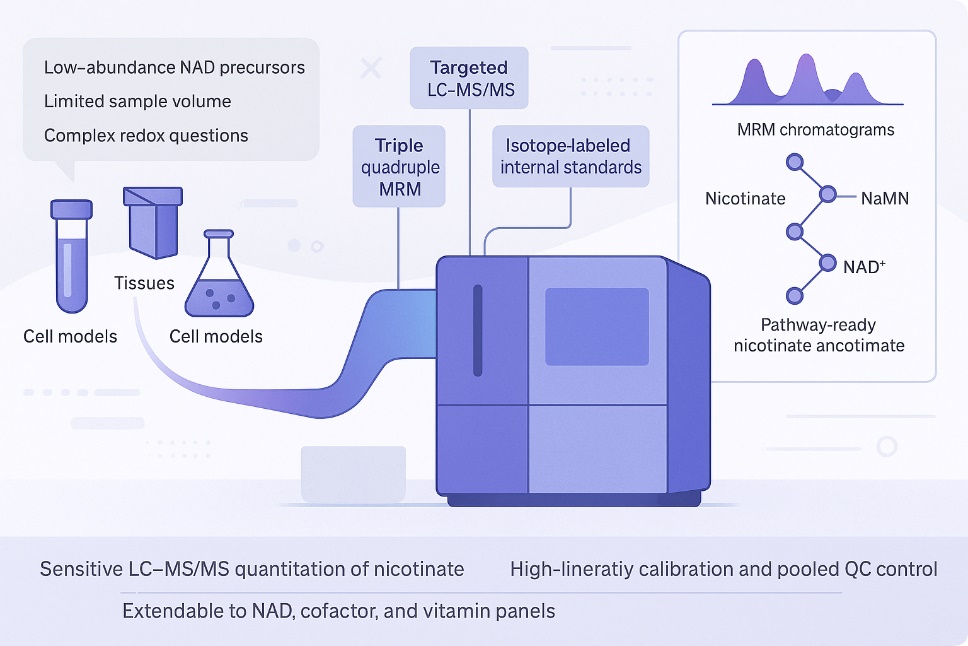
- Sensitive LC–MS/MS quantification: Targeted methods capture low-abundance nicotinate/nicotinamide in small-volume samples.
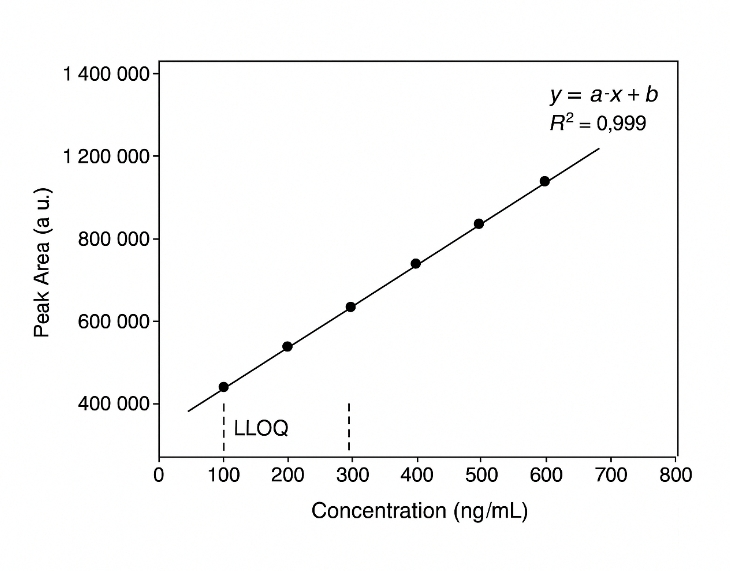
- High calibration linearity: Calibration curves are tuned for strong linearity, typically with R² ≥ 0.99 across working ranges.
- QC-anchored reproducibility: Isotope-labeled internal standards and pooled QCs help keep batch-to-batch drift under tight control.
- Easy extension to cofactor networks: The same platform can be expanded to include NAD species, vitamins, one-carbon or CoA-related metabolites when you need broader pathway coverage.
Analytical Platform for Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Analysis
Core Instruments
Our nicotinate and nicotinamide panel is run on targeted LC–MS/MS platforms commonly used in small-molecule metabolomics.
UHPLC systems: High-performance UHPLC with binary pumps and autosamplers for low-volume injections and stable gradients.
Triple quadrupole mass spectrometers (primary quantification)
Representative platforms used in targeted metabolomics, such as:
- Thermo Scientific TSQ series triple quadrupole systems.
- AB Sciex QTRAP or API series triple quadrupole instruments.
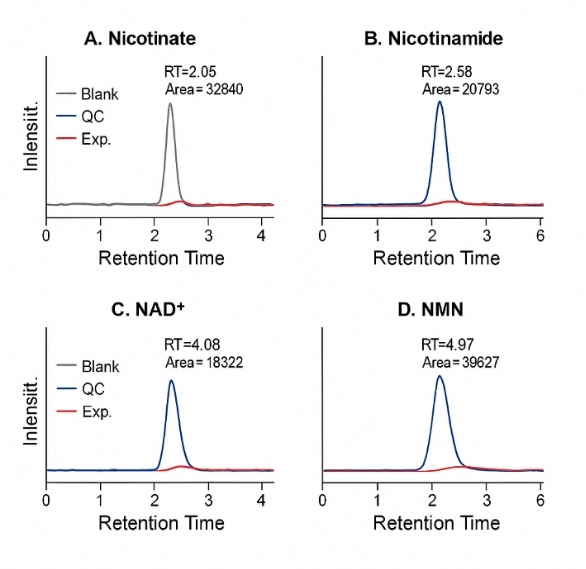
These are operated in electrospray ionization (ESI), typically in positive mode, using MRM for nicotinate, nicotinamide, and related metabolites.
High-resolution MS (method development and confirmation, when needed)
Orbitrap or TOF-based instruments (for example Thermo Q Exactive or similar HRMS systems) can be used to confirm identities and refine transitions before locking the routine LC–MS/MS method.
Method Performance Parameters
| Parameter |
Typical setup for nicotinate/nicotinamide panel |
| Chromatography mode |
UHPLC, reversed-phase or mixed-mode gradient |
| Column |
Short analytical column for polar pyridine metabolites |
| Mobile phases |
Aqueous buffer with volatile acid or salt; organic phase methanol or acetonitrile |
| Flow rate |
Sub-mL/min range to balance resolution, sensitivity, and throughput |
| Injection volume |
Low-µL range to maintain peak shape and reproducibility |
| Ionization |
Electrospray ionization (ESI), positive mode |
| Acquisition mode |
Triple quadrupole MRM with optimized precursor/product ion pairs |
| Linearity target |
Calibration curves tuned for strong linearity (R² typically ≥ 0.99) |
| Internal standards |
Isotope-labeled standards for nicotinamide/nicotinate where available |
| Batch quality control |
Regular pooled QC and calibration checks to monitor drift and stability |
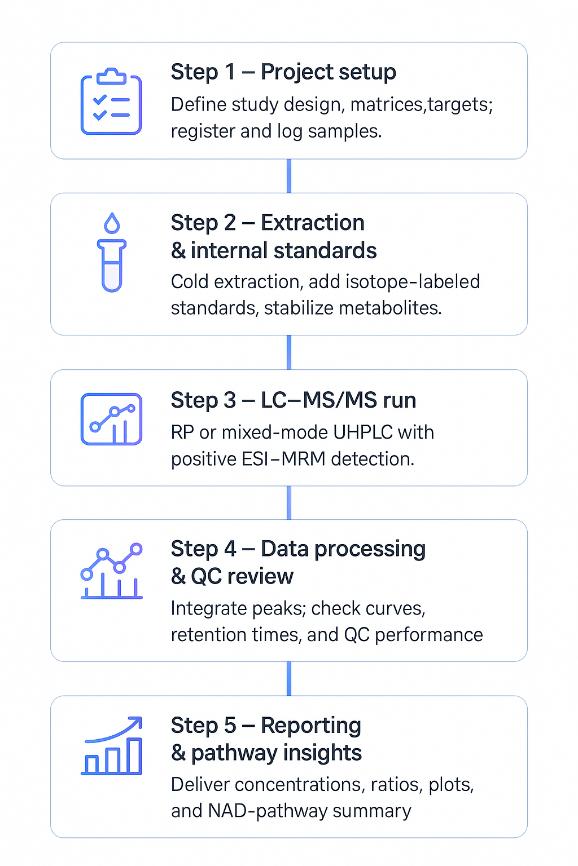
From Sample to Data: Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Analysis Workflow
Sample Requirements for Nicotinate and Nicotinamide LC–MS/MS Analysis
| Sample type |
Recommended amount |
Container |
Storage & transport notes |
| Blood / plasma / serum |
≥ 500 µL per sample |
Pre-labeled cryovial, anticoagulant as appropriate |
Keep frozen; ship on dry ice; avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles. |
| Urine |
≥ 1 mL per sample |
Screw-cap tube or cryovial |
Mix well before aliquoting; freeze promptly; send on dry ice. |
| Solid tissue |
~ 200 mg per sample |
Pre-cooled tube |
Snap-freeze after collection; keep at ultra-low temperature; ship on dry ice. |
| Cultured cells |
≥ 1 × 10⁷ cells per sample |
Tube compatible with rapid quenching |
Quench metabolism rapidly; store pellets frozen; transport on dry ice. |
| Feces or digesta |
~ 500 mg per sample |
Leak-proof tube |
Freeze as soon as possible; ship on dry ice to preserve metabolite stability. |
For other matrices such as culture media, formulated products, or specialized biological fluids, tailored requirements can be defined during project setup.
What You Receive: Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Analysis Deliverables
Method & run summary: PDF with sample list and groups, run order, and a short method description (prep outline, LC gradient, MS mode, key MRM transitions).
Raw LC–MS/MS files: Vendor-format raw data for standards, QCs, and all study samples.
Processed result tables: Editable spreadsheets (e.g., .xlsx) with peak areas and calculated concentrations for each analyte, linked to sample IDs.
Calibration & QC report: Brief report summarizing calibration curves, QC performance, and any excluded injections or notes.
Optional figures: Simple charts (bar/box plots, group comparisons) for key nicotinate/nicotinamide levels and ratios, if requested.
Research Applications of Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Profiling
Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF-1α
Pelletier, A., Nelius, E., Fan, Z., Khatchatourova, E., Alvarado-Diaz, A., He, J., ... & Stockmann, C.
Journal: EMBO Reports
Year: 2023
Enhance Trial: Effects of NAD3® on Hallmarks of Aging and Clinical Endpoints of Health in Middle Aged Adults: A Subset Analysis Focused on Blood Cell NAD+ Concentrations and Lipid Metabolism
Roberts, M. D., Osburn, S. C., Godwin, J. S., Ruple, B. A., La Monica, M. B., Raub, B., ... & Lopez, H. L.
Journal: Physiologia
Year: 2022
Inflammation primes the kidney for recovery by activating AZIN1 A-to-I editing
Heruye, S., Myslinski, J., Zeng, C., Zollman, A., Makino, S., Nanamatsu, A., ... & Hato, T.
Journal: bioRxiv
Year: 2023
Sarcosine Is Uniquely Modulated by Aging and Dietary Restriction in Rodents and Humans
Walters, R. O., Arias, E., Diaz, A., Burgos, E. S., Guan, F., Tiano, S., ... & Huffman, D. M.
Journal: Cell Reports
Year: 2018