Methyl Glucosinolate Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat are Methyl Glucosinolates?
Methyl glucosinolates (MGs) are a group of secondary metabolites found in various plant species, particularly in the family Brassicaceae (cruciferous vegetables). They are sulfur-containing compounds derived from amino acids, mainly methionine and phenylalanine, through a series of enzymatic reactions.
Structurally, methyl glucosinolates consist of a β-D-glucopyranose (glucose) moiety linked to a sulfonated oxime moiety, which is further connected to a variable side chain derived from the specific amino acid precursor. The side chain determines the specific type of MG and contributes to its biological activity.
MGs are typically stored in plant tissues, particularly in specialized cells called idioblasts, where they play a significant role in the plant's defense mechanisms against herbivores, pests, and microbial pathogens. When the plant is damaged or attacked, the enzyme myrosinase, present in separate compartments within the cells, comes into contact with MGs and catalyzes their breakdown.
The breakdown of MGs by myrosinase leads to the formation of several products, including isothiocyanates, nitriles, thiocyanates, and epithionitriles, depending on the specific conditions and the nature of the side chain. These breakdown products exhibit various biological activities, such as acting as deterrents against herbivores, participating in the plant's immune response, and influencing soil ecology.
Beyond their role in plant defense, MGs have attracted significant attention due to their potential health benefits for humans. Studies have suggested that MGs and their breakdown products may possess anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Cruciferous vegetables, rich sources of MGs, have been associated with reduced risks of certain types of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic illnesses.
The quantification and analysis of MGs in plants are crucial for understanding their roles in plant biology, as well as for breeding programs aiming to develop crops with enhanced nutritional and defensive properties. Various analytical techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and enzymatic assays, are employed to determine MG content in plant samples.
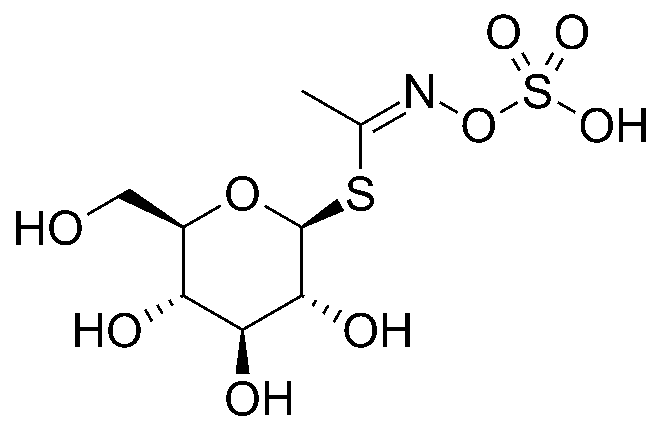 Structure of methyl glucosinolate
Structure of methyl glucosinolate
Methyl Glucosinolate Assay at Creative Proteomics
Detection platform:
LC-MS/MS: Waters ACQUITY UPLC, MS-SCIEX QTRAP 4500/5500/6500 and Waters Xevo TQ-S
GC-MS: Agilent 7890A-5975C, Agilent 7890B-5977A
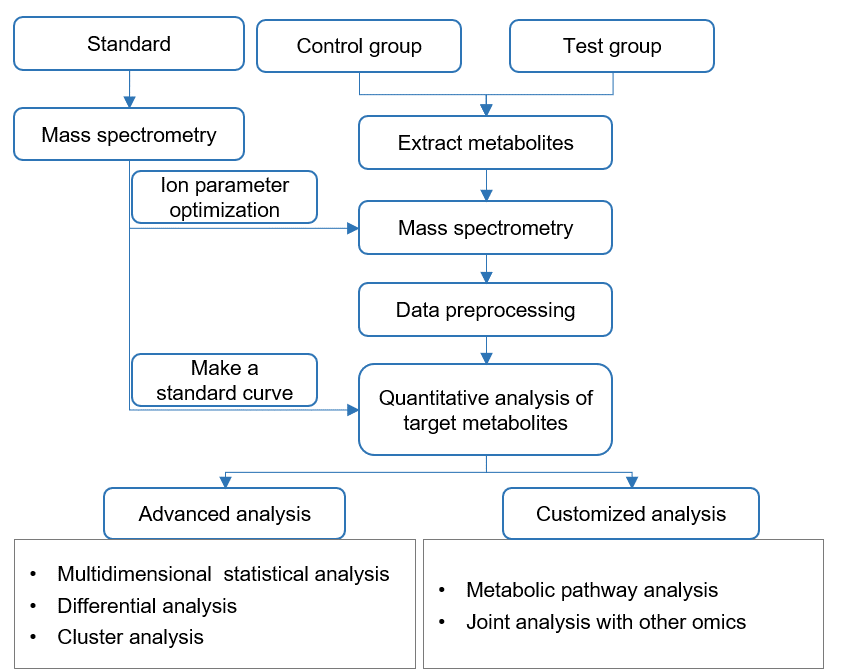
Workflow of methyl glucosinolate analysis:
- Sample preparation: Obtain plant tissue samples and prepare them by cleaning, freezing, drying, or grinding.
- Extraction of MGs: Extract MGs from the plant material using suitable solvents and optimize extraction conditions.
- Purification and concentration: Purify the extract to remove interfering substances and concentrate the MGs using techniques like solid-phase extraction or liquid-liquid extraction.
- HPLC-MS analysis:
Choose HPLC-MS for MG analysis, combining separation and detection.
Inject and separate the sample in the HPLC-MS system.
Detect MGs based on their properties and mass-to-charge ratio.
Identify MGs by comparing mass spectra with reference standards. - GC-MS analysis:
Opt for GC-MS for MG analysis, combining separation and detection.
Derivatize the MGs and inject the sample in the GC-MS system.
Separate and detect MGs based on their volatility and mass-to-charge ratio.
Identify MGs by comparing mass spectra with reference standards.
Suggestions for Sample Delivery
Sample requirements
- Plant tissue ≥ 300mg
- Plant seeds ≥ 200 mg
- Animal tissue ≥ 200mg
- Serum, plasma, urine and other body fluids ≥ 300ul
- Cell ≥ 1×107
- All samples were quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C, and shipped on dry ice. Please consult customer service staff for details of the sample delivery standards.
Sample packaging
Store in RNase-free 1.5 ml or 2 ml centrifuge tubes, and seal with parafilm. Larger tissue samples should be packaged in tin foil and clearly marked with the sample name and group, and placed in a sealed bag. If the tube contains organic solvent, it should be stored and sealed in a threaded cryotube.
Sample transportation
The samples are transported on dry ice. Please be sure to contact the company staff before sending the samples.
Number of repetitions (recommended)
- Plant samples ≥ 3 cases / group
- Clinical samples ≥ 30 cases / group
- Animal samples ≥ 10 cases / group
- Cell samples ≥ 6 cases / group
Feedback to Customers
Creative Proteomics will provide you with detailed technical reports, including
- Experimental steps
- Related mass spectrometry parameters
- Part of the mass spectrum picture
- Raw data
- Quantitative results of targeted metabolites





