Lutein Analysis Service
Submit Your Inquiry- Service Details
- Case Study
Introduction of Lutein
Lutein is a xanthophyll, a class of carotenoids, widely recognized for its vibrant yellow to orange pigmentation. This natural compound is found in numerous vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and corn, as well as in egg yolks. Lutein has gained substantial attention due to its role in promoting eye health and its antioxidant properties.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lutein is essential for assessing its presence, concentration, and purity in various samples. Creative Proteomics offers a range of cutting-edge techniques and instruments for in-depth lutein analysis.
Lutein Analysis Services by Creative Proteomics
Lutein Metabolite Identification: We excel in the identification of lutein metabolites in complex biological matrices. This involves the characterization of the chemical structures of the breakdown products or derivatives of lutein, allowing for a deeper understanding of its metabolism in different systems.
Metabolite Quantification: Our services include the quantification of lutein metabolites, providing precise concentration data. This quantification is essential for understanding the dynamics of lutein metabolism and its influence on health or specific biological processes.
Metabolomic Profiling: Creative Proteomics conducts comprehensive metabolomic profiling of samples, enabling the simultaneous analysis of a wide range of metabolites, including lutein and its derivatives. This approach is valuable for unraveling metabolic pathways and their interactions.
Metabolic Pathway Analysis: We offer in-depth analysis of lutein metabolic pathways. This involves the mapping of lutein metabolism within specific biological systems, helping researchers gain insights into how lutein is utilized or modified in different contexts.
Bioavailability Studies: Our services extend to assessing the bioavailability of lutein and its metabolites. This is crucial for understanding how effectively lutein is absorbed and utilized in the human body, especially in the context of dietary supplements and functional foods.
In Vitro and In Vivo Studies: Creative Proteomics is proficient in conducting both in vitro and in vivo metabolomics studies. This versatility allows us to investigate lutein metabolism in cell cultures, animal models, and human samples, offering a holistic view of its metabolic fate.
Customized Metabolomics: We understand that each research project may have unique objectives and sample types. Our team is experienced in tailoring metabolomics analysis to the specific needs of your study, ensuring that you obtain the most relevant and accurate data.
Lutein Analysis Analytical Techniques
Our lutein analysis services employ advanced mass spectrometry techniques to ensure accurate and comprehensive results. Some of the key instruments utilized in our analysis are:
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) - This technique offers a high level of sensitivity and specificity in the detection and quantification of lutein in diverse samples. Our arsenal includes models like the Thermo Fisher Scientific Q-Exactive series and the Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) - GC-MS stands as an effective method for the analysis of lutein. We rely on instruments such as the Agilent 7890B GC and the Thermo Fisher Scientific ISQ EC MS.
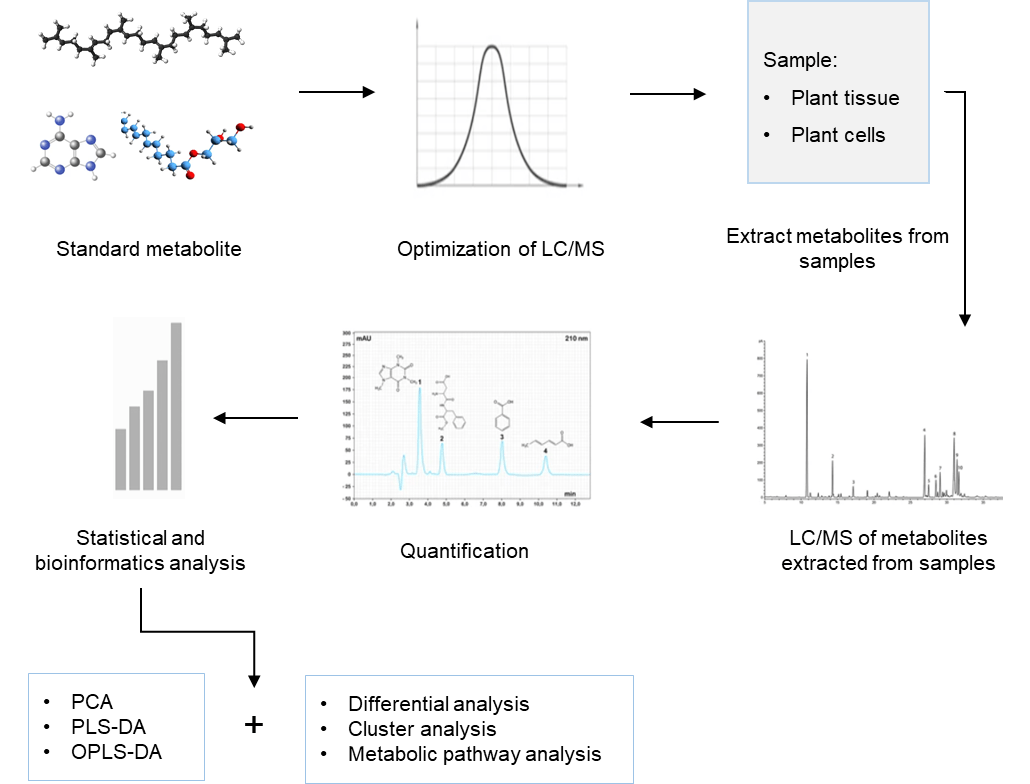 Workflow of lutein analysis
Workflow of lutein analysis
Sample Requirements for Lutein Analysis
| Sample Type | Minimum Quantity | Storage Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Plant Extracts | 1 gram | -20°C, protected from light |
| Food Products | 5 grams | -20°C, protected from light |
| Serum and Plasma | 100 μL | -80°C |
| Agricultural Products | Varies | Consult with our experts |
Case: Analysis of Lutein and Its Metabolites: In Vitro Photo-oxidation and In Vivo Biotransformation in a Murine Model
Background
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a significant cause of vision loss in the elderly, and dietary carotenoids, particularly lutein, have been associated with reduced risk. This study aims to investigate the biotransformation of lutein, including its degradation and formation of metabolites, both in vitro and in a murine model.
Samples
The study involved in vitro samples (liposome) and in vivo samples collected from male albino rats. In vivo samples included eyes, liver, plasma, and intestine.
Techniques
Analytical Conditions: The study optimized analytical conditions for enumerating lutein and its metabolites using HPLC and LC-MS (APCI) for both in vitro and in vivo samples.
In Vitro Photo-oxidation: Lutein was exposed to sunlight in an in vitro study, and the extent of degradation and formation of oxidized products were measured. Characteristic UV-visible spectra were used to support findings.
In Vivo Biotransformation in Eyes: Biotransformation of lutein in the eyes was studied in two groups of rats, one fed lutein via gavage and the other through dietary supplementation. Various lutein isomers, including 3'-oxolutein and meso-zeaxanthin, were identified in eye samples.
Biotransformation in Liver and Plasma: The liver and plasma samples were analyzed to identify lutein oxidative metabolites, including lutein diepoxide and zeaxanthin. The study suggested that diepoxides might be formed in the liver or mobilized from the intestine via plasma.
Biotransformation in Intestine: In the intestine, anhydrolutein was the primary compound identified.
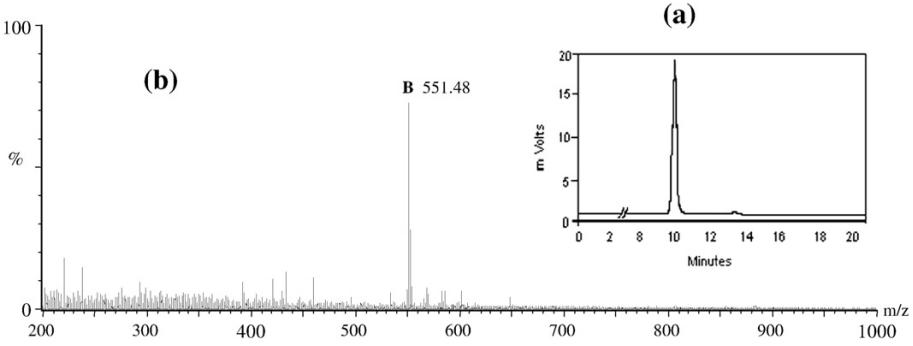 A typical HPLC profile and spectrum of (a) standard lutein and (b) its mass spectrum. HPLC and LC-MS conditions adopted are outlined under Materials and methods.
A typical HPLC profile and spectrum of (a) standard lutein and (b) its mass spectrum. HPLC and LC-MS conditions adopted are outlined under Materials and methods.
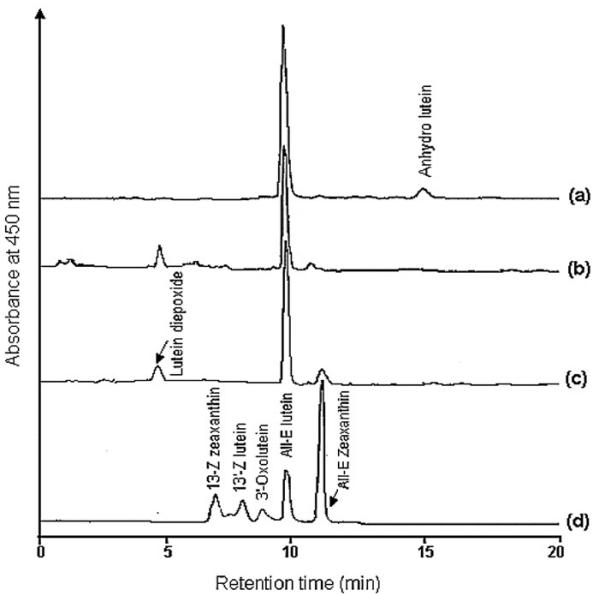 HPLC profiles of lutein and its metabolized/oxidized products eluted from (a) intestine, (b) plasma, (c) liver, and (d) eyes after feeding lutein to rats
HPLC profiles of lutein and its metabolized/oxidized products eluted from (a) intestine, (b) plasma, (c) liver, and (d) eyes after feeding lutein to rats
Results
The results indicate that lutein can undergo various transformations, including degradation and the formation of oxidized products, isomers, and metabolites both in vitro and in vivo. These findings provide insights into how lutein is metabolized and modified within the body, which can have implications for understanding its potential health benefits in preventing AMD.
Reference
- Lakshminarayana, Rangaswamy, et al. "Possible degradation/biotransformation of lutein in vitro and in vivo: isolation and structural elucidation of lutein metabolites by HPLC and LC-MS (atmospheric pressure chemical ionization)." Free Radical Biology and Medicine 45.7 (2008): 982-993.