Phytol Analysis Service
Submit Your Inquiry- Service Details
- Case Study
What is Phytol?
Phytol, chemically known as 3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol, is a long-chain alcohol closely associated with chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for capturing light energy during photosynthesis. It can be found in the lipid tail of the chlorophyll molecule and is released during the breakdown of chlorophyll.
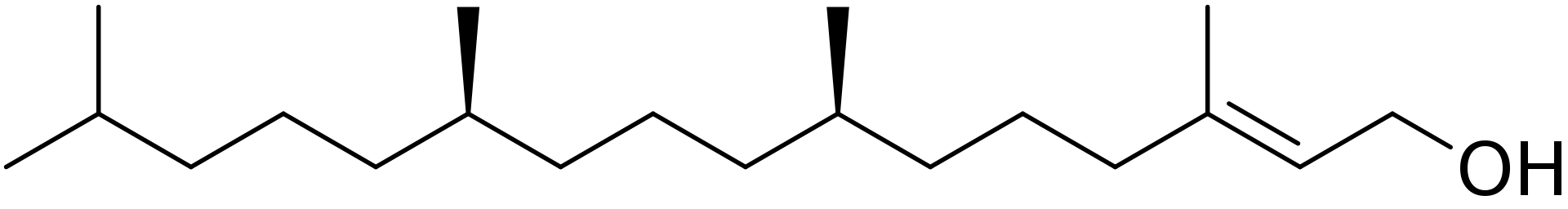 The molecular structure of phytol
The molecular structure of phytol
Creative Proteomics offers a comprehensive range of services for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of phytol. Qualitative analysis focuses on identifying the presence of phytol in a given sample. This can be crucial in research, where the confirmation of phytol's presence is a primary goal. It is also a prerequisite for quantitative analysis. Quantitative analysis aims to precisely measure the concentration of phytol in a sample. Accurate quantification is necessary in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and food science, where the exact amount of phytol can influence the product's quality and effectiveness.
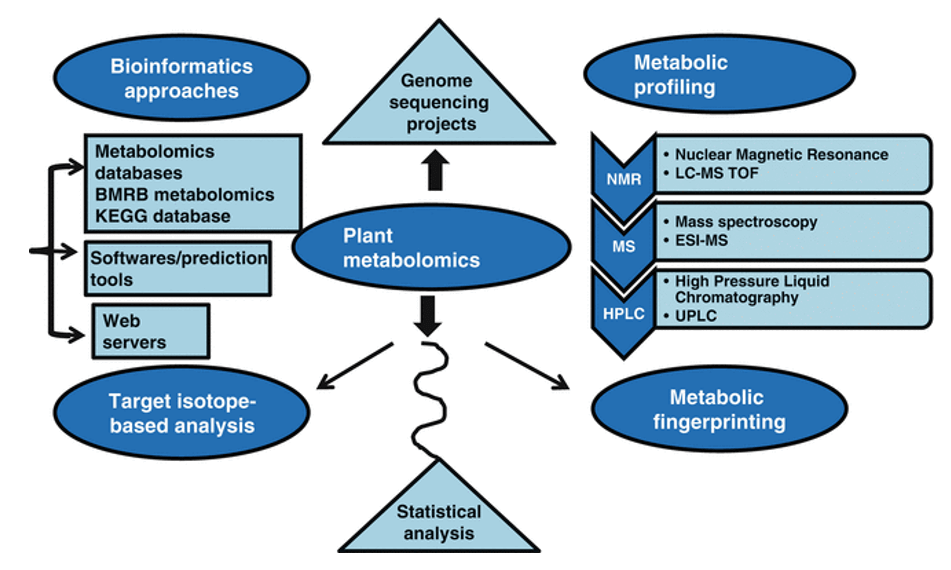
What We Offer
Qualitative Analysis
Our qualitative analysis services are the gateway to confirming the presence of phytol in your samples. This initial step is essential for researchers looking to validate hypotheses and explore the occurrence of phytol in various matrices. With our rigorous qualitative approach, we can unequivocally identify the presence of phytol in your samples.
Quantitative Analysis
For industries and research projects where precision matters, our quantitative analysis services step in. We go beyond mere identification and provide you with precise measurements of phytol concentrations in your samples. This data is vital for quality control, formulation adjustments, and scientific investigations where the exact quantity of phytol plays a pivotal role.
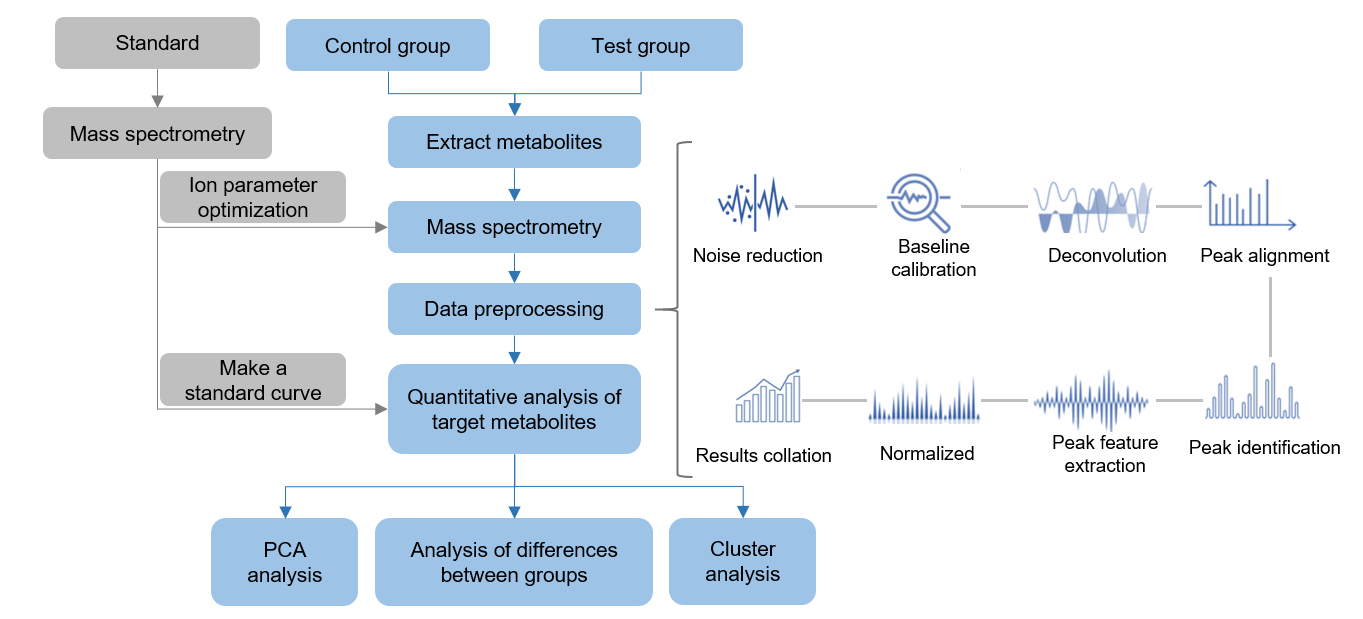 Workflow for phytol analysis
Workflow for phytol analysis
Diverse Sample Types
Creative Proteomics recognizes that phytol analysis is needed across a spectrum of sample types. Our services encompass a wide range, including:
- Plant Extracts: Covering various plant species.
- Algae Samples: From freshwater to marine algae species.
- Soil Samples: Extracted from phytol-rich environments.
- Dietary Supplements: Evaluating phytol content in supplements.
- Cosmetics: Analyzing products containing phytol.
- Biofuels: Ensuring biodiesel and other fuels meet phytol specifications.
- Pharmaceutical Samples: Testing pharmaceuticals with phytol content.
- Drug Intermediates: Assessing intermediate compounds in drug synthesis.
Our expertise transcends boundaries, enabling us to provide phytol analysis services for a multitude of applications.
Advanced Analytical Techniques
To deliver precise and dependable results, we employ state-of-the-art analytical techniques, primarily based on mass spectrometry:
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Our GC-MS analysis combines gas chromatography with mass spectrometry, utilizing the highly sensitive Agilent 7890A GC System coupled with the Agilent 5975C MSD. This technique ensures precision and resolution in the analysis of Phytol across diverse samples.
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): Our LC-MS analysis utilizes the Thermo Fisher Q Exactive series, a powerful tool for the analysis of complex samples. This technique provides accurate results, even in the presence of challenging matrices.
Customized Solutions
We understand that no two projects are the same. That's why we offer customization options for our phytol analysis services. We work closely with our clients to tailor our services to their unique requirements, ensuring that the data we provide is directly relevant to their objectives.
Sample Requirements for Phytol Analysis
| Sample Type | Sample Volume | Storage Temperature | Preparation Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Extracts | 1-2 mL | -20°C | Freeze samples immediately after collection. |
| Algae Samples | 5-10 g | -80°C | Freeze samples promptly. |
| Soil Samples | 50-100 g | -20°C | Ensure samples are well-sealed to prevent contamination. |
| Dietary Supplements | 2-5 g | Room temperature | Keep samples in original packaging. |
| Cosmetics | 1-2 g | Room temperature | Provide samples in their original containers. |
| Biofuels | 1-2 mL | -20°C | Store samples in airtight containers. |
| Medicinal Products | 1-2 g | Room temperature | Avoid exposure to light and moisture. |
| Drug Intermediates | 1-2 g | Room temperature | Submit samples in well-sealed containers. |
| Food Items | 2-5 g | -20°C | Keep samples in airtight packaging. |
| Water Samples | 50-100 mL | 4°C (refrigerated) | Collect samples in clean, sterile containers. |
| Crop Samples | 10-20 g | -20°C | Freeze samples promptly after collection. |
| Veterinary Medications | 1-2 g | Room temperature | Ensure samples are tightly sealed and labeled. |
Case: Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activities of Essential Oils from Celtis zenkeri Engl.
Background
Essential oils (EOs) are volatile compounds derived from plant metabolism and have garnered attention for their potential medicinal applications. Celtis zenkeri Engl., a plant from the Cannabaceae family, is traditionally used in Nigeria for various therapeutic purposes. This study aims to analyze the chemical composition and antioxidant properties of EOs extracted from the leaves and stem bark of Celtis zenkeri Engl., a previously unreported research endeavor.
Samples
The leaves and stem bark of Celtis zenkeri Engl. were collected in Nigeria, specifically in Ikire, Osun State. The plant was identified and authenticated, with voucher specimens deposited at the Forest Research Institute of Nigeria.
Technique Methods
Extraction of Essential Oils: The EOs were obtained from the plant material via hydrodistillation using a British Pharmacopoeia-compliant distillation unit.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Analysis: The chemical composition of the EOs was analyzed using GC-MS.
Antioxidant Assay: The antioxidant activity of the EOs was assessed by their ability to scavenge the DPPH+ radical using spectrophotometric measurements.
Results
- A total of 23 compounds were identified in the leaf EO, representing 99.9% composition, while nine compounds were found in the stem bark EO, accounting for 98.9% composition.
- Phytol was the major compound in both EOs, with the leaf EO containing 46.1% and the stem bark EO containing 27.0%.
- The EOs exhibited good radical scavenging activities due to the presence of chemical constituents, including phytol and α-caryophyllene.
- The antioxidant activity of the leaf EO was comparable to that of standard antioxidants like ascorbic acid and butylated hydroxyl anisole (BHA).
- The stem bark EO also displayed strong antioxidant activity and outperformed α-tocopherol, a known antioxidant.
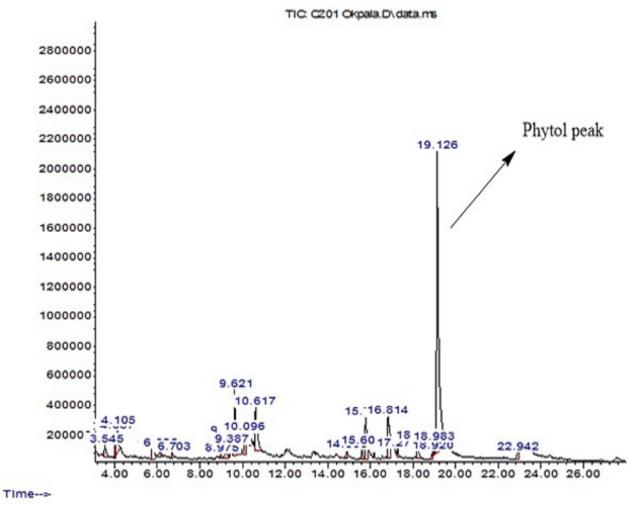 The GC-MS chromatogram of the leaf of C. zenkeri Engl. essential oil.
The GC-MS chromatogram of the leaf of C. zenkeri Engl. essential oil.
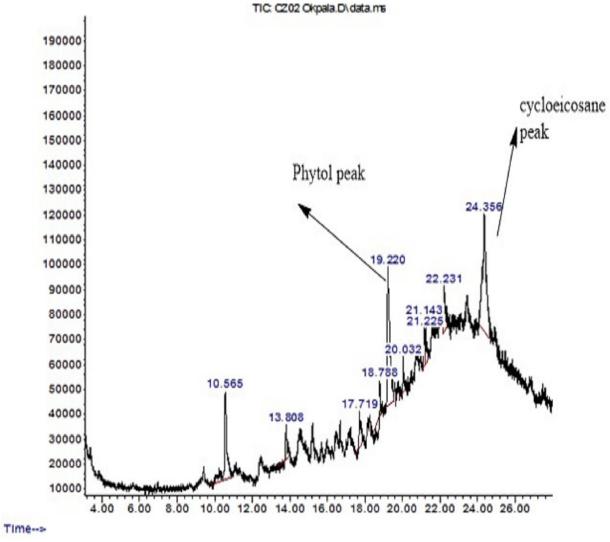 The GC-MS chromatogram of the stem bark of C. zenkeri Engl. essential oil.
The GC-MS chromatogram of the stem bark of C. zenkeri Engl. essential oil.
Reference
- Okpala, Ejike Onwudiegwu, Patricia Akpomedaye Onocha, and Muhammad Shaiq Ali. "Antioxidant activity of phytol dominated stem bark and leaf essential oils of Celtis zenkeri Engl." Trends in Phytochemical Research 6.2 (2022): 137-144.