Scopolamine Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Scopolamine and Scopolamine Metabolism?
Scopolamine is a tropane alkaloid derived from plants such as nightshade and honeysuckle. It has anticholinergic properties and functions as an antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
The metabolism of scopolamine undergoes various enzymatic processes in the body. One of its major metabolic pathways involves hydrolysis by esterases. Scopolamine is hydrolyzed into scopolamine and tropic acid primarily by the action of carboxylesterases. Scopolamine is further metabolized to tropine via scopolamine dehydrogenase. Tropic acid can undergo further conjugation reactions such as glucuronidation, which facilitates its excretion from the body. Another metabolic pathway of scopolamine involves cytochrome P450 enzymes, specifically the CYP3A subfamily. These enzymes oxidize scopolamine to form various metabolites, including norscopolamine and dihydroscopolamine. These metabolites may undergo further conjugation reactions, such as glucuronidation or sulfation, to facilitate their excretion from the body.
The metabolism of scopolamine is affected by a number of factors, such as age, liver function, and the presence of other drugs or substances that affect metabolic enzyme activity. Certain genetic variants in drug-metabolizing enzymes may also affect the metabolism of scopolamine by individuals.
Scopolamine has a short half-life, and its metabolites are excreted primarily through the kidneys. The exact metabolic outcome of scopolamine and its metabolites may vary depending on individual factors and the specific metabolic pathway involved. By performing a comprehensive scopolamine assay, researchers can gain valuable insight into its mechanistic studies, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and potential therapeutic applications.
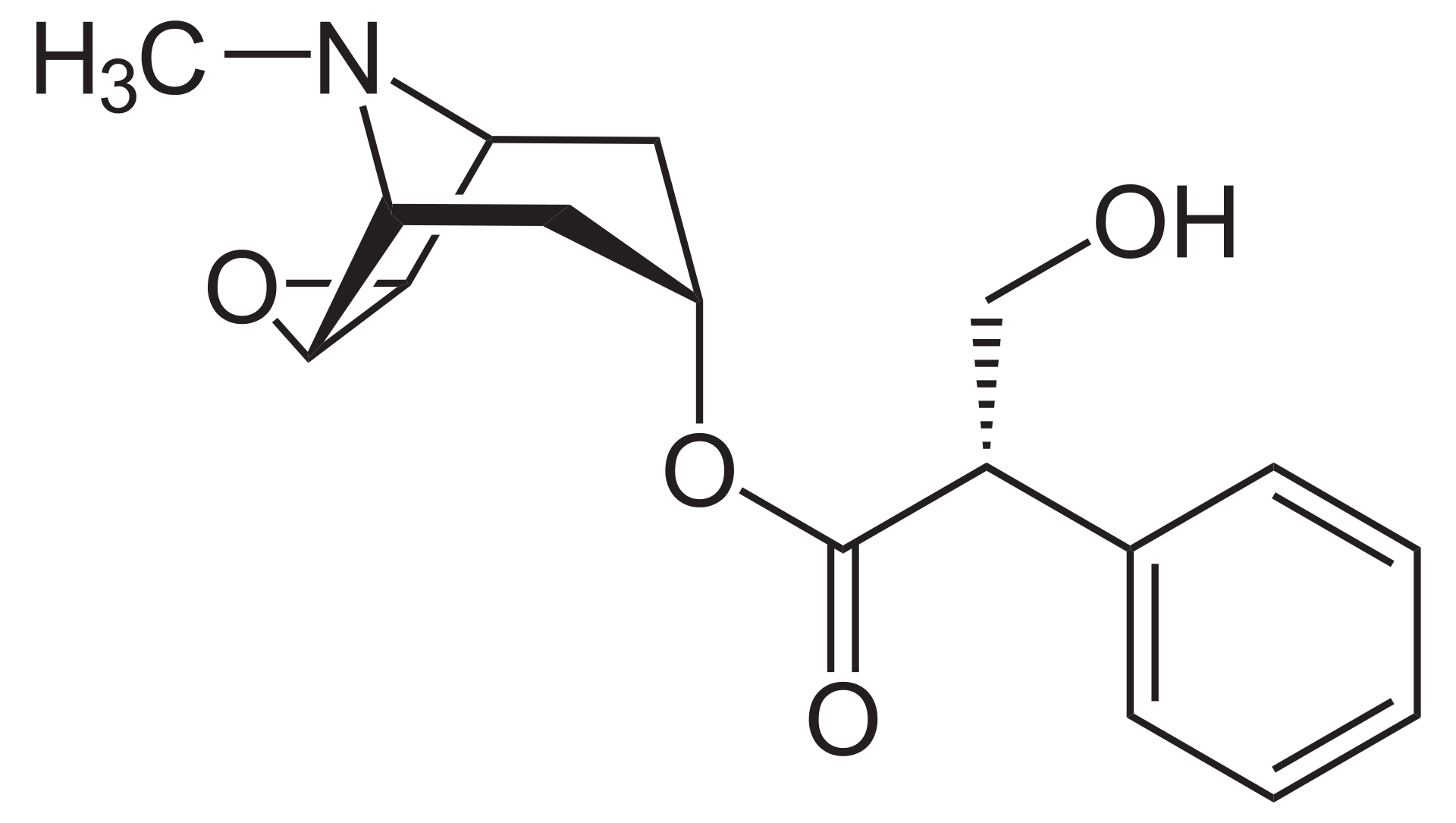 Molecular structure of scopolamine
Molecular structure of scopolamine
Scopolamine Assay at Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics employs Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) technology to analyze scopolamine and unravel its intricacies. LC-MS offers several advantages, including high sensitivity, selectivity, and the ability to simultaneously identify and quantify multiple compounds.
Equipment Utilized:
In scopolamine assays, Creative Proteomics utilizes cutting-edge LC-MS instruments such as the Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC system coupled with the Agilent 6545 Q-TOF mass spectrometer. This powerful combination enables accurate and reliable detection of scopolamine in various biological matrices.
Benefits of LC-MS:
- Sensitivity: Detects scopolamine at low concentrations
- Selectivity: Distinguishes scopolamine from other compounds present in the biological matrix
- Quantitative: Quantify the concentration of scopolamine in a given sample
- Metabolite identification: Identifies scopolamine metabolites, providing a comprehensive understanding of their metabolism and potential interactions in vivo.
Scopolamine Assay Process:
Sample preparation: Biological samples (e.g. blood, urine or tissue) are collected and processed to extract scopolamine and remove any interfering substances. Ensure sample purity for accurate analysis.
Chromatographic separation: The extracted scopolamine is subjected to liquid chromatography analysis to separate it from other compounds based on its physicochemical properties, improving the accuracy of detection and quantification.
Mass spectrometric analysis: The separated scopolamine is introduced into a mass spectrometer where it is ionized and fragmented. The resulting ions are detected and analyzed to determine the concentration and identity of scopolamine.
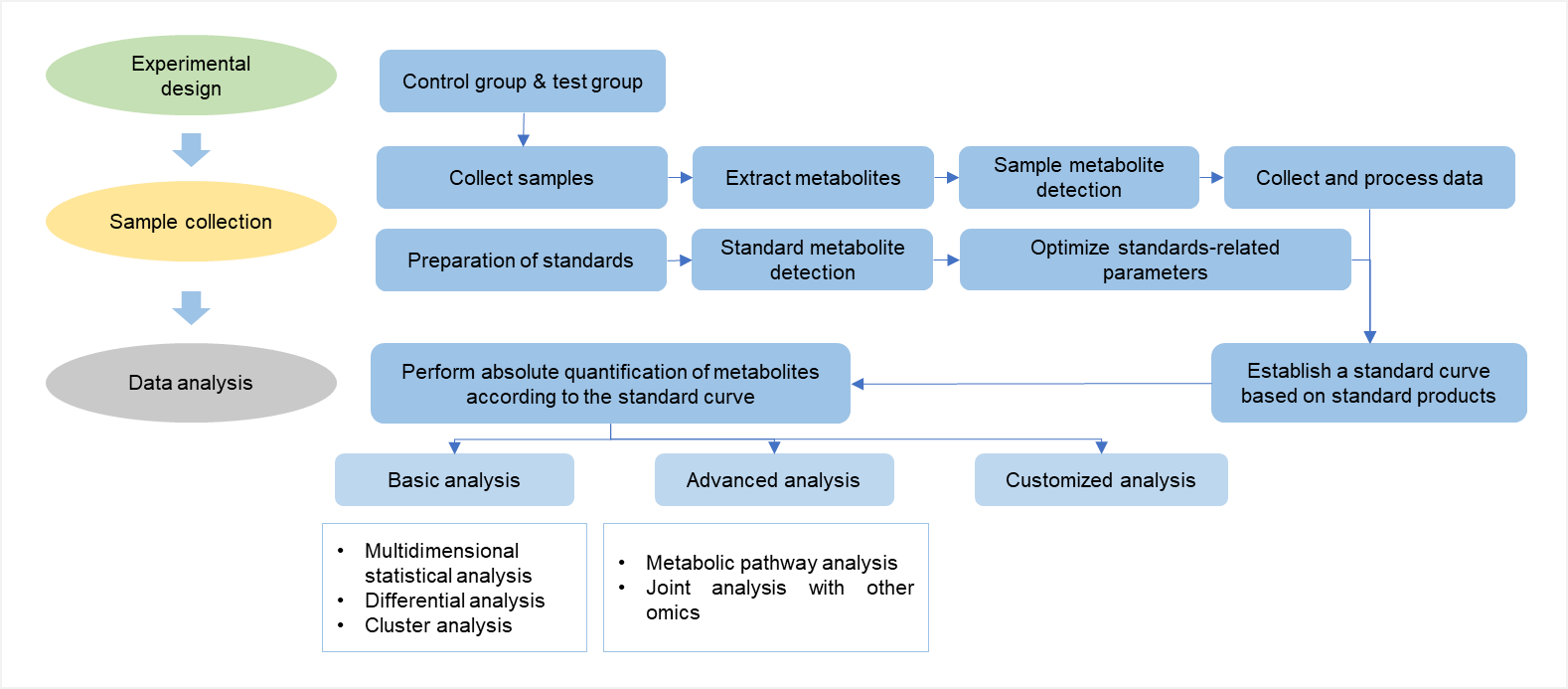
Platform
- LC-MS/MS
- GC-MS/MS
- NMR
Workflow of targeted metabolomics service of scopolamine
Targeted metabolomics is a study that identifies and quantitatively analyzes known metabolites in a sample. Its advantages are high specificity and accuracy. Therefore, this method has been widely used to analyze and compare multiple target metabolites in different physiological states.
Delivery standard
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- Raw data, chromatograms and mass spectra
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom analysis report





