Purine Metabolism Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Purine Metabolism and Why is it Important?
Purines are heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines make up the one group of nitrogenous bases by attaching to ribose 5-phosphate. Both adenine and guanine are derived from the nucleotide inosine monophosphate (IMP), which is the first compound in the pathway to have a completely formed purine ring system. In general, purine nucleotides can be synthesized by salvage pathway and de novo biosynthetic pathway (Figure 1). On the other hand, accumulation of purine nucleotides is detrimental to various cellular processes, in particular those involving DNA and RNA. Therefore, organisms possess distinct (deoxy)purine phosphohydrolases, that hydrolyse these purine derivatives removing them from the active NTP and dNTP pools. Additionally, purines are essential for the synthesis of proteins, other metabolites as well as for energy requiring reactions as well. It would not be surprising that the disorder of purine metabolism leads to various human diseases like gout and cancer. Therefore, understanding the purine metabolism contribute to gain new insights behind these pathologies. Researches at Creative Proteomics take advantage of highly quantitative methods with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of purine metabolism related metabolites levels in various samples. Furthermore, we provide reliable, rapid and cost-effective purine related service to speed up your research aims ranging from diseases diagnosis to gaining new insights in disease mechanism or treatment.
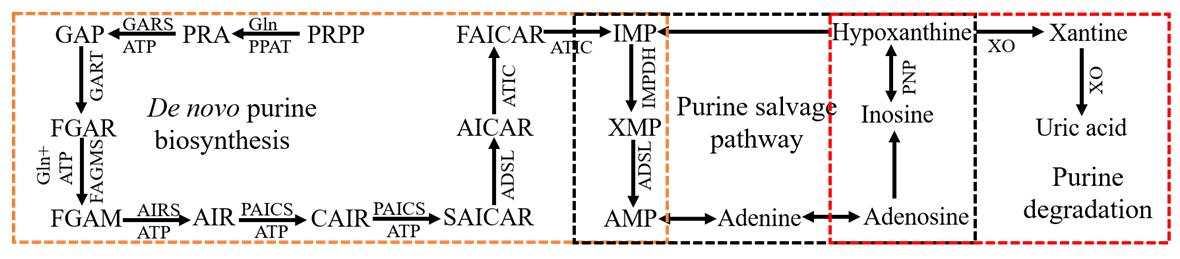 Figure 1. The overview of purine metabolism pathways
Figure 1. The overview of purine metabolism pathways
The Main Applications of Purine Metabolism Service
- Identifying novel biomarkers of diseases
- Improving diagnose diseases
- Accelerating development of novel drugs
- Gaining new mechanism of diseases
Advantages of Our Purine Metabolism Service
- Constantly optimized protocol and analytical software
- Professional experiment design
- Quick turnaround time
- High accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity
Service Workflow
Creative Proteomics provides alpha-linolenic acid metabolism analysis service in a reliable and effective manner, based on our cutting-edge high-performance liquid chromatography- mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS). The experimental procedures contain four main procedures: sample collection, metabolites extraction, HPLC-MS data analysis and bioinformatics analysis (Figure 2). Our service will be tailored to specific samples and needs for optimal results.
 Figure 2. The overall workflow of purine metabolism
Figure 2. The overall workflow of purine metabolism
List of Partial Detectable Purine Metabolism Related Metabolites at Creative Proteomics
| Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate | 5-phosphoribosylamine | Inosine 5'-monophosphate | N-formylglycinamide ribonucleotide | Uric acid |
| Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide | Xantine | Adenosine 5'-monophosphate | N-succinocarboxyamide-5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide | Inosine |
| Adenine | Adenosine | Hypoxanthine | aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide | Purine |
Sample Requirements
We can analyze a wide range of biological materials including but not limited to cells and solid tissues from animals. If you need transport your samples to us, please follow the following requirements for different types of sample:
- Blood/plasma: 500ul/sample
- Urine: 1ml/sample
- Tissue: 200mg/sample
- Cells: 1x107/sample
- Feces: 500mg/sample
Shipment condition: dry ice
Report Delivery
- Experimental protocols
- Instrumental factors of HPLC
- The raw data files of HPLC and the summary of HPLC data quality
- Bioinformatics analysis report
Based on advanced HPLC platforms for the determination of purine metabolism, professional bioinformatic analysis software and experienced technicians and scientists, Creative Proteomics provides customer-tailored purine metabolism analysis service with rapid experimental procedures and easy to read report, to accelerate your scientific research.
References
- An Songon, Kumar Ravindra, Sheets Erin D, et al. Reversible compartmentalization of de novo purine biosynthetic complexes in living cells. Science. 2008. 320:103-106.
- Yin Jie, Ren Wenkai, Huang Xingguo, et al. Potential Mechanisms Connecting Purine Metabolism and Cancer Therapy. Front Immunol. 2018.9:1697.