Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Cinnamic Acid?
Cinnamic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound, a phenolic acid formed by the deamination of phenylalanine. It is an aromatic compound found in various plants, including cinnamon, balsam, and sage. It is used as a flavoring agent in foods such as candy, baked goods, and chewing gum. In addition to its applications in the food industry, cinnamic acid has also been studied for its potential therapeutic properties. It is antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, and may also have anticancer properties.
Creative Proteomics is a leading provider of HPLC-MS services for cinnamic acid analysis, using state-of-the-art equipment and technology to provide accurate and reliable results for cinnamic acid analysis. Our platform includes positive and negative ionization modes, multiple reaction monitoring (MRM), and full scan modes to detect and quantify cinnamic acid in a variety of samples, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
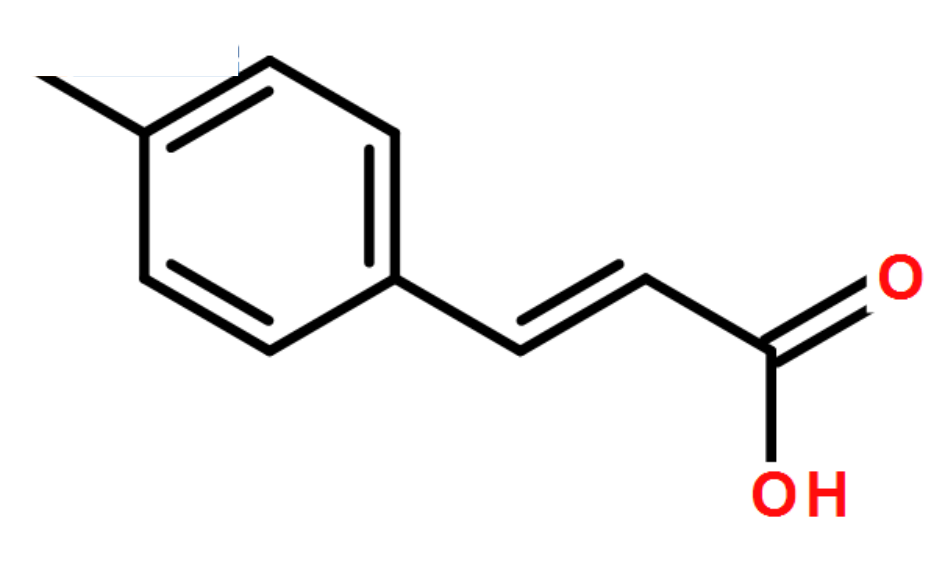 Figure 1. The chemical structure of natural and synthetic plant cinnamic acid and resistant plant cinnamic acid (Park 2020).
Figure 1. The chemical structure of natural and synthetic plant cinnamic acid and resistant plant cinnamic acid (Park 2020).
Detection Methods of Cinnamic Acid Analysis
To detect and quantify cinnamic acid in different samples, high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) is commonly used.
HPLC-MS is a widely used analytical method that involves separating the different components of a sample based on their chemical properties, followed by the detection and identification of cinnamic acid using mass spectrometry.
In HPLC-MS, a sample is first injected into an HPLC system, which separates the different components based on their interaction with the stationary phase. The separated components are then sent to a mass spectrometer, where they are ionized and separated according to their mass-to-charge ratios. The resulting mass spectrum can be used to identify and quantify cinnamic acid in the sample.
HPLC-MS is highly sensitive and selective for the detection of cinnamic acid at low concentrations and in complex matrices, such as food and biological samples, with accurate and reproducible results.
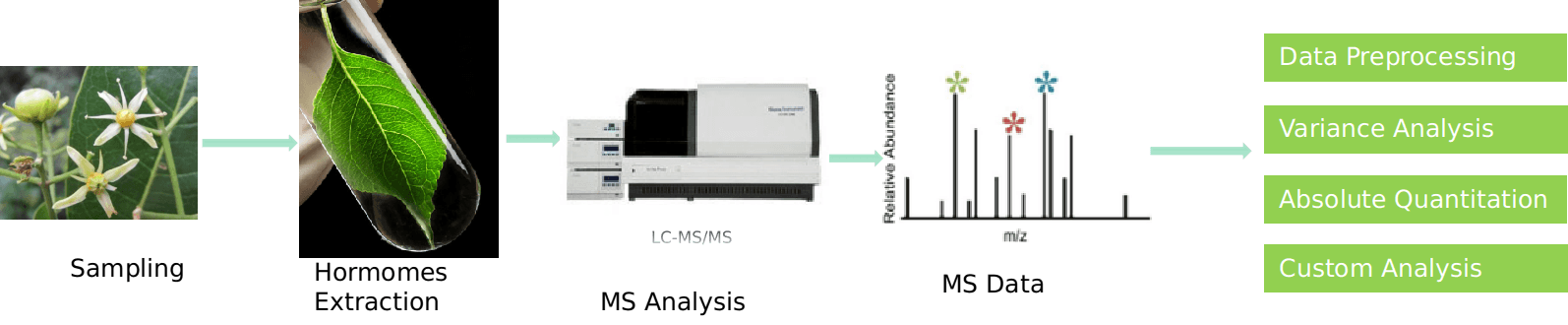 Figure 2. Cinnamic acid analysis service workflow.
Figure 2. Cinnamic acid analysis service workflow.
Mode: MRM
Precision: pmol
Linear: R2 > 0.99
Analysis content:
- Standard curve creation
- Raw data preprocessing
- Absolute quantitative and qualitative analysis of plant cinnamic acid
- Differential metabolite screening
Applications of Cinnamic Acid Analysis
Pharmacology: Identify and quantify the active ingredients of cinnamic acid and its derivatives in pharmaceuticals, helping to study the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of these compounds.
Food Science: Determining the amount of cinnamic acid in different food products, such as cinnamon, is critical to ensure compliance and quality control. In addition, it can also be used to study the bioavailability and metabolism of cinnamic acid in the human body.
Cosmetics Industry: Identify the botanical extracts they use in skin care products, measure the concentration of cinnamic acid in cosmetic formulations to ensure consistency of quality and efficacy.
Natural Product Chemistry: Identify the presence of cinnamic acid in various plant species and exploration of its biosynthetic and metabolic pathways. Screening of natural product extracts for the presence of cinnamic acid and its derivatives.
Advantages of Our Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service:
List of Cinnamic Acid Compounds We Can Detect
| Trans-cinnamic acid | Cis-cinnamic acid | p-Coumaric acid | Caffeic acid | Ferulic acid |
| Sinapic acid | Isoferulic acid | 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid | 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid |
Sample Requirements of Cinnamic Acid Assay
| Sample Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Types | Plant extracts, food products, beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceutical formulations, etc. |
| Sample Volume | Recommended volume: 5-10 mL for liquid samples, 1-5 g for solid samples |
| Sample Storage | Store samples in amber glass vials or airtight containers. Keep at -20°C for long-term storage. |
| Sample Transportation | Ship samples on dry ice to maintain stability. Avoid temperature fluctuations during transit. |
| Sample Preparation | Extraction method: Depending on sample type, use techniques such as maceration, solvent extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, etc. |
| Sample Homogeneity | Ensure homogeneity by thoroughly mixing or grinding the sample. |
| Sample Information | Provide accurate information about sample origin, composition, processing methods, and any relevant details. |
Delivery
- Experimental procedures
- The parameters of liquid chromatograph and mass spectrometer
- Extract mitochondria and purified protein samples
- Purity analysis report
- MS raw data files and MS data quality inspection
- Metabolite quantitative data
- Customized analysis report
References
- Lee, YS, Son, E, et al. Synergistic uric acid-lowering effects of the combination of chrysanthemum indicum linne flower and cinnamomum cassia (l.) j. persl bark extracts. Evid Based Compl Alt. 2017.
- Park, Y. H. , Kim, D. H. , et al. A 12-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial for evaluation of the efficacy and safety of dkb114 on reduction of uric acid in serum. Nutrients, (2020), 12(12), 3794.