Fumaric Acid Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Fumaric Acid?
The multifaceted nature of fumaric acid, also known as trans-butenedioic acid, cannot be overstated. Found naturally in a variety of fruits and vegetables, such as apples, oranges, tomatoes, and carrots, this acid's acidic taste is frequently added as a food additive to baked goods, fruit-flavored beverages, and candy during their production. Its importance, however, extends far beyond that of a mere flavoring agent, as it plays a crucial role in the citric acid cycle - a metabolic pathway that takes place in the mitochondria of cells - by first converting to malic acid, then to oxaloacetate, which serves as a critical intermediate in the cycle.
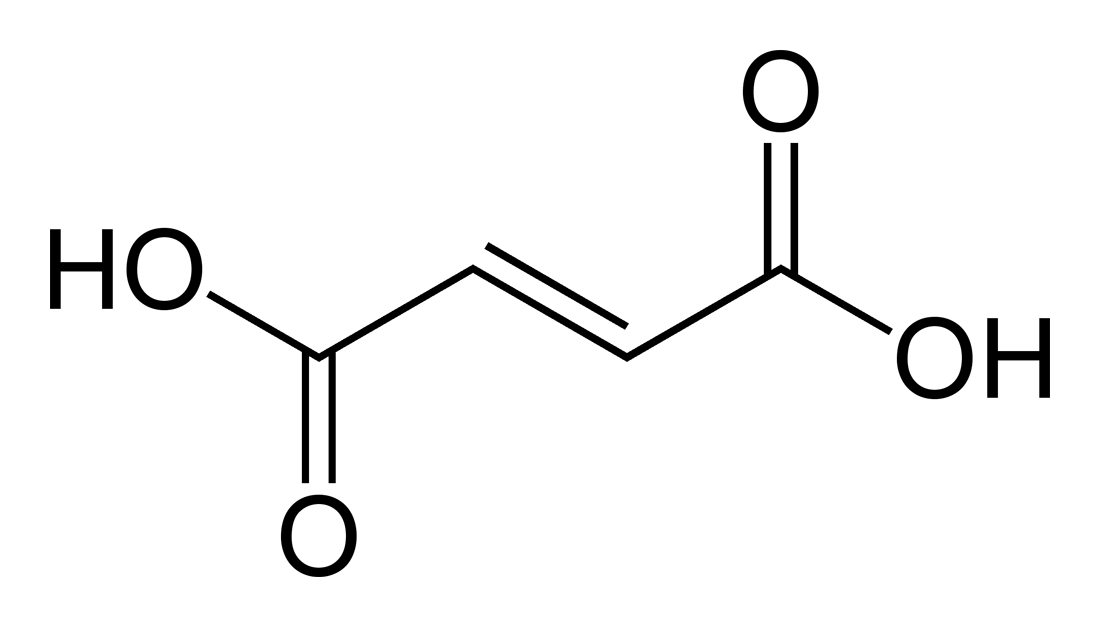 Molecular structure of fumaric acid
Molecular structure of fumaric acid
Beyond its involvement in the citric acid cycle, fumaric acid has been shown to be implicated in other biological processes. For instance, it has been demonstrated to be essential in regulating cellular oxidative stress and inflammation. Furthermore, certain drugs, such as fumaric acid esters, which are used in the treatment of psoriasis, include it as an active ingredient. These drugs function by regulating the immune system and reducing skin inflammation.
Fumaric acid is not only found in nature but is also produced artificially via the catalytic isomerization of maleic acid or the catalytic oxidation of benzene. Its synthetic production is of great importance, as it enables the production of the acid in large quantities for commercial use.
Why Analyze Fumaric Acid?
Research on fumaric acid can reveal its involvement in regulating cellular oxidative stress and inflammation, indicating its potential use in developing new treatments for diseases related to these processes. In particular, by analyzing fumaric acid in biological samples, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of its precise role and potential therapeutic benefits.
In the food industry, fumaric acid is a prevalent additive, and its presence and concentration in food must be precisely determined to meet regulatory and safety standards. Likewise, fumaric acid is widely used in the production of certain drugs, and ensuring its quality and purity is paramount to ensure its safe use in medicine.
Fumaric Acid Analysis Technology Platform at Creative Proteomics:
Creative Proteomics offers a state-of-the-art and all-encompassing technology platform for analyzing fumaric acid. Our platform harnesses the potential of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to deliver a comprehensive analysis of fumaric acid in an assortment of matrices, spanning from food to pharmaceuticals, to biological samples.
Our LC-MS technology is endowed with ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and high-resolution mass spectrometry, thereby ensuring the expeditious separation and detection of fumaric acid, even in the presence of complex matrices. The team of experts at Creative Proteomics boasts of extensive experience in sample preparation, method development, and data analysis, thus ensuring dependable and accurate results that transcend expectations.
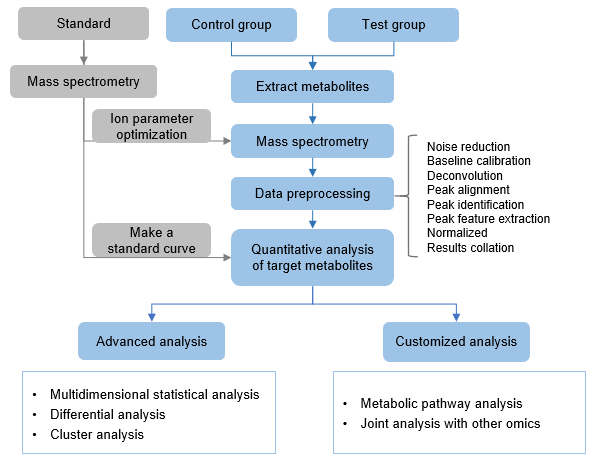
Applications of Fumaric Acid Analysis
Biomedical Research
Fumaric acid analysis plays a role in biomedical research, where it is studied for its potential therapeutic applications and metabolic pathways. Understanding fumaric acid metabolism and its interactions with cellular processes can contribute to the development of new treatments and therapies.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, fumaric acid has gained significant attention due to its therapeutic properties. It is used as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in the treatment of various diseases, including psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Reliable analysis methods are essential to determine the purity, stability, and concentration of fumaric acid in pharmaceutical formulations. Techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS) are commonly employed to characterize fumaric acid and ensure its quality and efficacy in drug formulations.
Food and Beverage Industry:
Fumaric acid is widely used in the food industry as an acidulant, flavor enhancer, and preservative. It is commonly found in beverages, bakery products, confectioneries, and dairy products. Accurate analysis of fumaric acid content is crucial to maintain consistent product quality and ensure compliance with food safety regulations. By employing analytical techniques such as chromatography or spectroscopy, the concentration of fumaric acid can be determined, enabling manufacturers to adjust formulations and monitor product quality.
Cosmetic Industry
Fumaric acid finds applications in the cosmetic industry, particularly in skincare and haircare products. It is known for its anti-aging, skin-lightening, and antioxidant properties. Accurate analysis of fumaric acid in cosmetic formulations is essential to ensure proper ingredient labeling and adherence to regulatory guidelines. Analytical methods such as gas chromatography (GC) or liquid chromatography (LC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) can be utilized to quantify fumaric acid and assess its stability in cosmetic products.
Agricultural Research
In agricultural research, fumaric acid and its derivatives are studied for their potential as plant growth regulators and crop protection agents. Analyzing the presence and concentration of fumaric acid in plant tissues or agricultural samples is important for understanding its impact on plant physiology and overall crop health. Sample preparation techniques, such as extraction and purification, are often required to isolate and concentrate fumaric acid from complex matrices before analysis. Analytical methods such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) can provide valuable insights into fumaric acid's role in agricultural applications.
Sample Requirements for Fumaric Acid Analysis
To ensure accurate fumaric acid analysis, specific sample quantities need to be considered. The following are examples of typical sample quantities used for fumaric acid analysis:
- Body Fluid Samples:
Blood: 1 mL
Urine: 10 mL
- Plant Tissue Samples:
Leaf Samples: 10 g
Root Samples: 5 g
Fruit Samples: 20 g
- Pharmaceutical Samples:
Tablet Formulation: 100 mg
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API): 20 mg
- Food Samples:
Fruit Juice: 100 mL
Bakery Products: 10 g
Dairy Products: 50 g
- Cosmetic Samples:
Cream/Lotion: 5 g
Shampoo: 10 mL
It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and sample quantities may vary depending on the specific analysis method, required sensitivity, and sample characteristics.
Feedback to Customers
- Experimental steps
- Related mass spectrometry parameters
- Part of the mass spectrum picture
- Raw data