Humic Acid Analysis
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Humic Acid?
Humic acids are naturally occurring organic molecules that originate from the decomposition of plant and animal matter. They are fundamental constituents of soil organic matter and are known for their remarkable ability to influence soil structure, nutrient availability, and microbial activity. Humic acids are characterized by their high molecular weight, dark color, and intricate structure, which is composed of various functional groups such as carboxylic, phenolic, and hydroxyl groups. The complexity of humic acid molecules has intrigued scientists for decades, spurring the need for advanced analytical techniques to unravel their secrets.
Humic acid analysis holds immense significance in understanding the intricate interplay between these organic molecules and the surrounding environment. By deciphering the composition and structure of humic acids, researchers can gain insights into soil health, nutrient cycling, and carbon sequestration. Moreover, humic acid analysis provides valuable information for optimizing agricultural practices, enhancing crop productivity, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. In a world where sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship are paramount, humic acid analysis emerges as a crucial tool for informed decision-making.
Humic Acid Analysis in Creative Proteomics
Characterization of Humic Acid Metabolites
At Creative Proteomics, we employ advanced mass spectrometry-based techniques to meticulously characterize humic acid metabolites. Our state-of-the-art methodologies enable us to identify and quantify the diverse array of compounds involved in humic acid metabolism. Through detailed metabolite profiling, we unveil the chemical transformations that shape the synthesis and degradation of humic acids, offering insights that drive scientific discovery.
Humic Acid Quantitative Analysis
Our humic acid metabolic analysis services extend beyond characterization to include quantitative insights. Leveraging our cutting-edge instrumentation, including the highly sensitive HPLC-MS, we provide accurate quantification of humic acid metabolites. This quantitative perspective allows us to discern not only the relative abundances of metabolites but also the dynamics of their changes over time. By delving into the quantitative aspects of humic acid metabolism, we enable a deeper understanding of the underlying processes.
Isotope Labeling Studies
Creative Proteomics employs stable isotope labeling techniques to trace the origins and transformations of humic acid molecules. Through the introduction of stable isotopes such as 13C and 15N into metabolic precursor molecules, we follow the journey of these isotopes as they become incorporated into humic acids. This approach provides insights into the sources of carbon and nitrogen atoms within humic acid molecules, shedding light on turnover rates and contributing to a holistic understanding of humic acid metabolism.
Microbial Interactions
Microorganisms are key players in humic acid metabolism, influencing processes such as synthesis, degradation, and transformation. At Creative Proteomics, we explore the intricate interactions between microorganisms and humic acids, unraveling the microbial contributions to humic acid metabolism. By identifying specific microbial taxa associated with humic acid-related processes, we enhance our comprehension of soil microbial ecology and unearth opportunities for leveraging microbial partnerships to optimize humic acid-related processes.
Humic Acid Assay Platforms
Advanced High-Resolution Mass Spectrometers
Our cutting-edge high-resolution mass spectrometers, exemplified by the renowned Thermo Scientific Orbitrap series, deliver exceptional analytical performance for humic acid analysis. These instruments are globally recognized for their superior precision and sensitivity. They excel in accurately resolving and quantifying the intricate assortment of compounds present within complex humic acid samples. By integrating them with sophisticated chromatography techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), these instruments facilitate multidimensional humic acid analysis, unveiling the intricate composition and structure of these organic molecules.
Enhanced Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) Capabilities
Our advanced mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry technology, embodied by the distinguished Thermo Scientific Q-Exactive series, amplifies the depth of insights attainable through humic acid analysis. This approach combines mass spectrometry with tandem mass spectrometry, enabling highly precise analysis and identification, especially for intricate mixtures. Renowned for their elevated resolution, precision, and sensitivity, these instruments empower rapid and accurate identification and quantification of diverse metabolites within humic acid samples.
Spatially Resolved Mass Spectrometry Imaging Techniques
Exploring new frontiers, our mass spectrometry imaging techniques, including the innovative Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS), offer spatially resolved analysis of humic acids. This groundbreaking method permits direct examination of sample surfaces, enabling visualization of humic acid distribution and dynamic changes. By synergizing mass spectrometry imaging with high-resolution mass spectrometry data, we attain a holistic understanding of the intricate dynamics that govern humic acid behavior.
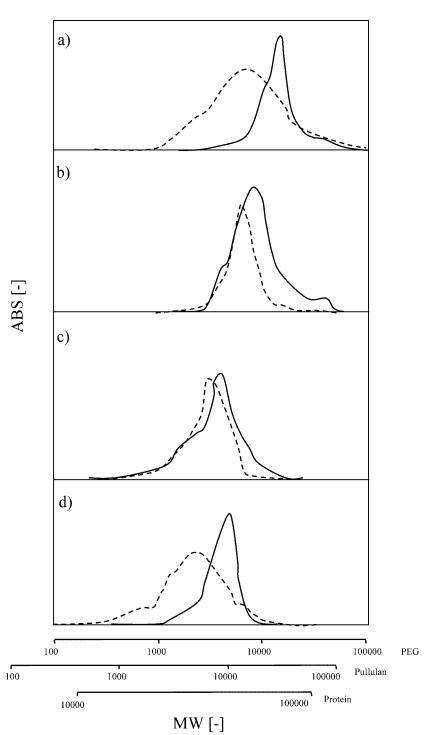 Molecular Weight Characterization of Humic Substances by MALDI-TOF-MS [1]
Molecular Weight Characterization of Humic Substances by MALDI-TOF-MS [1]
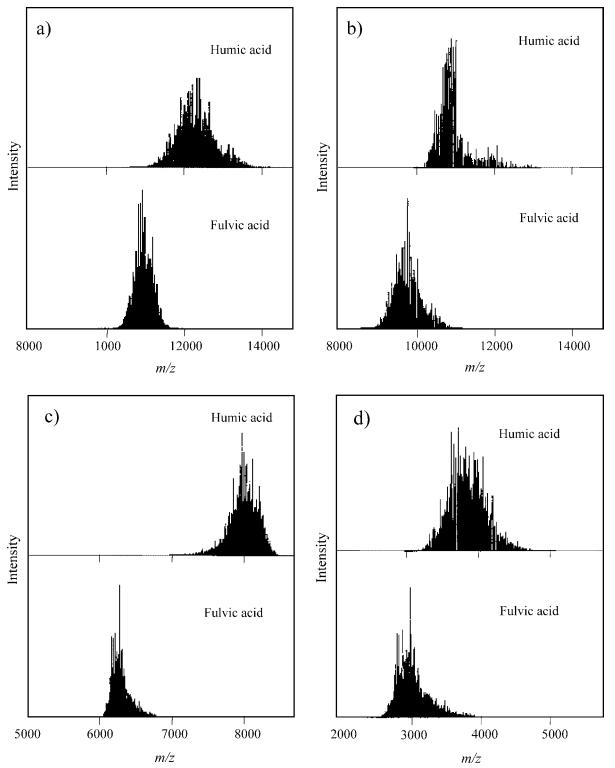 MALDI-TOF mass spectra of humic and fulvic acids from various sources [1]
MALDI-TOF mass spectra of humic and fulvic acids from various sources [1]
Sample Requirements for Humic Acid Assay
| Sample Type | Recommended Quantity |
|---|---|
| Soil | 100-200 g |
| Plant Material | 50-100 g |
| Leaves | 50-100 g |
| Stems | 50-100 g |
| Roots | 50-100 g |
| Flowers | 50-100 g |
| Fruits | 50-100 g |
| Seeds | 50-100 g |
| Shoots | 50-100 g |
| Algae | 50-100 g |
| Tubers | 50-100 g |
| Mushrooms | 50-100 g |
| Plant Root Systems | 50-100 g |
| Plant Pollen | 1-2 g |
| Plant Bark | 50-100 g |
| Plant Leaves | 50-100 g |
| Plant Branches | 50-100 g |
| Plant Petals | 1-2 g |
| Plant Stem Leaves | 50-100 g |
| Plant Buds | 50-100 g |
| Plant Rhizomes | 50-100 g |
| Water | 1-2 L |
| Sediment | 100-200 g |
| Compost | 100-200 g |
| Manure | 50-100 g |
| Fecal Matter | 50-100 g |
| Peat | 100-200 g |
| Aquatic Plants | 50-100 g |
Applications of Humic Acid Analysis
Agriculture and Soil Health
Understanding humic acid composition and dynamics is pivotal for optimizing soil health and nutrient management. Our advanced analysis helps tailor fertilization strategies, enhance nutrient uptake, and promote sustainable agriculture practices, ultimately bolstering crop yield and quality.
Environmental Monitoring and Remediation
Humic acid analysis serves as a powerful tool for monitoring environmental health. By assessing humic acid levels in water bodies, soils, and sediments, we contribute to early pollution detection and facilitate effective remediation strategies, safeguarding ecosystems and human well-being.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
Unraveling the intricate interactions between humic acids and carbon storage is crucial for mitigating climate change. Our analysis aids in deciphering carbon sequestration mechanisms, guiding strategies to enhance carbon capture and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Bioremediation and Biotechnology
Humic acids' unique properties make them valuable assets in bioremediation endeavors. By exploring their interactions with microbial communities, we unlock opportunities for innovative biotechnological applications, including pollutant degradation and ecosystem restoration.
Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Research
The bioactive potential of humic acids fuels research in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical fields. Our analysis aids in uncovering bioactive compounds, paving the way for drug discovery and the development of health-enhancing products.
Ecological Studies and Biodiversity
Studying humic acid interactions in natural ecosystems sheds light on biodiversity and ecological health. Our analysis contributes to preserving natural habitats, understanding ecosystem dynamics, and safeguarding the delicate balance of our planet.
If you would like to analyze other organic acids or learn more, please contact us. We look forward to working with you.
Reference
- Shinozuka, Toshiyuki, Mitsuhiro Shibata, and Tatsuaki Yamaguchi. "Molecular weight characterization of humic substances by MALDI-TOF-MS." Journal of the Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan 52.1 (2004): 29-32.

