Mannose Type of O-glycan Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryOverview
Glycosylation is the most important post-translational modification in mammals. There are two main categories of glycosylation, O-glycosylation and N-glycosylation, according to the glycan-peptide linkage sites. Recently, researches have suggested that O-mannose glycan, an O-glycan, plays an important role in brain and muscle development. Lack of O-mannose glycans lead to congenital muscular dystrophy, or alpha-dystrophy. One of the most famous modified O-glycoproteins is α-dystroglycan (α-DG) in human, which is the main component of the muscular dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) isolated from the skeletal muscle membrane. α-DG is highly glycosylated, and its glycan plays an important role in the binding of laminin, neurotoxin, Perlecan and lectin to laminin, neurotoxin, G (LG) domain and other proteins.
At present, according to the binding sites of GlcNAc to Man residues, these polysaccharides can be classified into three core O-Man structures: core M1 (GlcNAc-β-1-2Man), core M2 [GlcNac-β-1-6 (GlcNAc-β-1-2) Man] and core M3 (GlcNac-β-1-3GlcNAc-β-1-4Man). The peripheral structures of core M1 and core M2 are synthesized by a series of glycosyltransferases, such as galactosyltransferase, sialic acid transferase, glucuronosyltransferase, sulfonyltransferase and α-1mer-3-fucosyltransferase in Golgi apparatus. The novel complete core M3 structure has recently been revealed, the characteristics include: 1) the phosphorylation of 6-position of Man; 2) tandem phosphate 5-ribose alcohol (Rbo5P) structure; 3) the repeated 3GlcAβ1-3Xylα1 structure; 4) single GlcAβ1-4Xylβ1-4 unit.
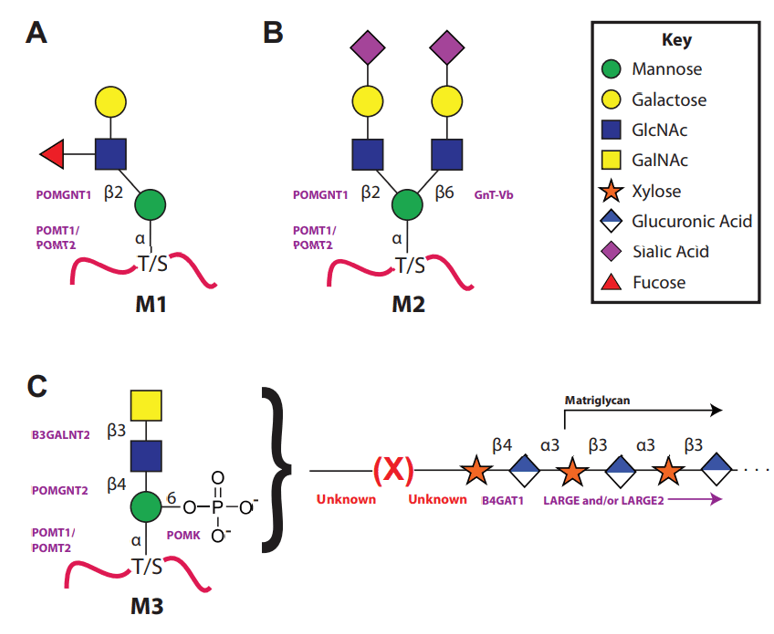 Fig 1. The three types of the O-Mannosylation pathway.
Fig 1. The three types of the O-Mannosylation pathway.
Advantage
- Short time-consuming
- High sensitivity and few detection restrictions
- High precision and good repeatability
- High throughput
- Customized service
Experimental process
O-mannose glycan analysis is usually carried out by LC-MS, which converts all hydroxyl groups into methyl ethers by permethylation and stabilizes the sialic acid by methyl esterification of their carboxyl groups, thus O-mannose glycan can be analysed in positive mode. O-glycan will be analysis as soon as infusion of O-mannose glycan of permethylation into the MS apparatus.
Service workflow
- Sample preparation
- O-glycan release
- Methylation of released polysaccharides
- Cleavage glycans with glycoside exonuclease or acid hydrolysis
- Reduction and derivation of free hydroxyl groups
- Through LC-MS analysis and quantification
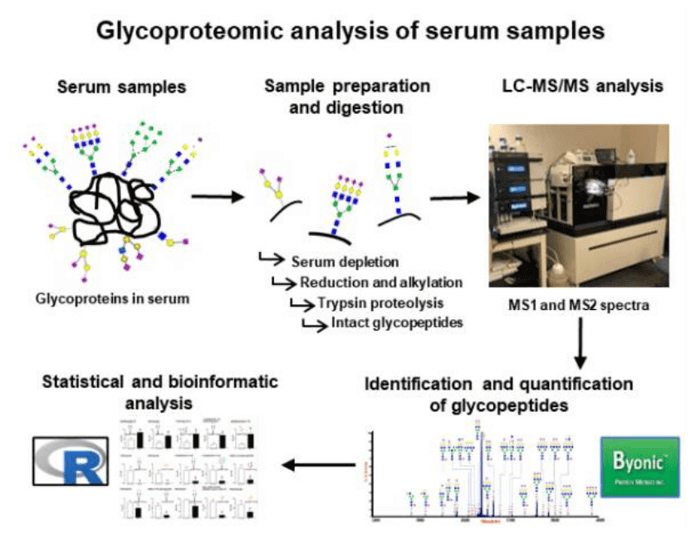 Fig 2. Workflow of common glycoproteomic analysis in serum.
Fig 2. Workflow of common glycoproteomic analysis in serum.
Sample requirement
- Serum/plasma: 500 μl/sample.
- Protein: 100 µg
- Anticoagulated blood (EDTA): 1 mL.
- Urine: 1 ml/sample.
- Animal tissues: 200 mg/sample.
- Cells: ≥ 1 × 107/sample.
- Feces: 500 mg/sample
Repeated freezing and thawing of samples must be avoided. The serum sample should be precipitated in the collection tube for 30 minutes at room temperature, then transported to the centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 5 minutes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was equally divided into a freezing tube of 500 uL / sample.
Anticoagulants and preservatives must be added immediately after collection and then frozen at -80 °C.
Urine samples should be equally divided into centrifuge tubes with 1 mL per tube, each tube is added with 1/100 (w/v) sodium azide and stored at -80 °C.
Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately and then transported to -80 °C for storage after collected.
Cytoactive should be terminated immediately to maintaining cell integrity.
In general, to assure enough sample to fulfill the whole project, the volume of the single sample need to be offered as much as possible. The remaining samples will be stored for one year free of charge and returned at any time if necessary. All samples need to be stored and transported at -80°C and try to avoid using surfactants (SDS, Triton-X) and inorganic salts.
Clinical samples are repeated in no less than 30 cases in a single group.
Animal samples are repeated in no less than 9 cases in a single group.
Report delivery
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- Raw data, chromatograms and mass spectra
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Service cycle
- Sample testing: 5-10 working days
- Data analysis: 5-10 working days
Creative Proteomics metabolism analysis platform is committed to the all-around, reliable and accurate analysis service for a variety of target substances, which is suitable for life-science research, drug exploration, biological determination and other fields. We sincerely hope to cooperate with you to assistant your scientific research.
References
- T. Endo. Glycobiology of alpha-dystroglycan and muscular dystrophy. J Biochem, 2015, 157(1):1-12.
- T. Endo. Mammalian O-mannosyl glycans: Biochemistry and glycopathology. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, 2019, 95(1):39-51.
- J.L. Praissman, T. Willer, M.O. Sheikh, et al. The functional O-mannose glycan on alpha-dystroglycan contains a phospho-ribitol primed for matriglycan addition. Elife, 2016, 5.
- Sharma, J. Cox, J. Glass, et al. Serum Glycoproteomic Alterations in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. Proteomes, 2020, 8(3).