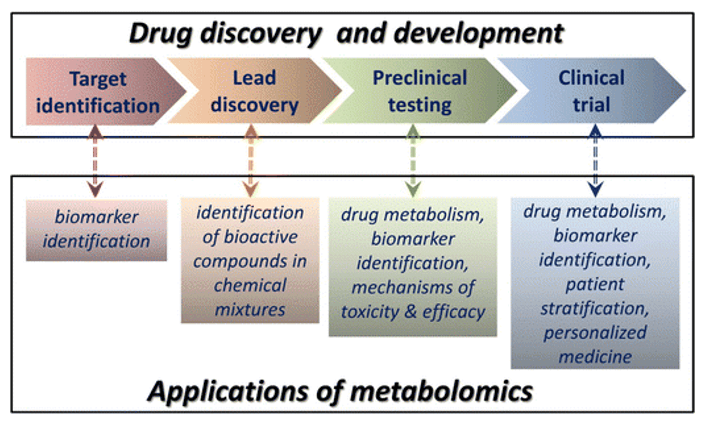
Keratan Sulfate Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryKeratan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (GAGs) that has been extensively studied in corneal and skeletal tissues. Glycosaminoglycans, also known as mucopolysaccharides, are negatively charged polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. They are present in every mammalian tissue and encompass a wide range of functions determined by their molecular structure. Historically, the functions of GAG have been considered limited to cellular hydration and structural scaffolds. However, recent evidence suggests that GAG also plays a key role in cellular signaling, regulating a wide range of biochemical processes. The four main groups of GAG are classified based on their core disaccharide units, including heparin/heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, hyaluronic acid, and keratin sulfate. Among them, keratin sulfate (KS) was the only GAG type with galactose as the structural component.
Based on tissue specificity, most importantly based on chemical structure, three classes of KS are defined, which vary depending on the degree of sulfation, the sulfation pattern, and the type of linked oligosaccharide that binds keratin sulfate to the core protein. Form I KS is an N-chain KS chain with variable degrees of sulfation (non-sulfate, mono-sulfate and di-sulfate) and is mainly present in the cornea. Type II KS is an almost completely sulfated KS chain that connects to the core protein O-type through GalNAc, and is mainly present in cartilage tissue. KS Form III is also highly sulfated, but is attached to its core protein by a 2-O-mannose bond and is the most abundant in the central nervous system.
Creative Proteomics offers qualitative and quantitative keratin sulfate assays based on ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) technology.
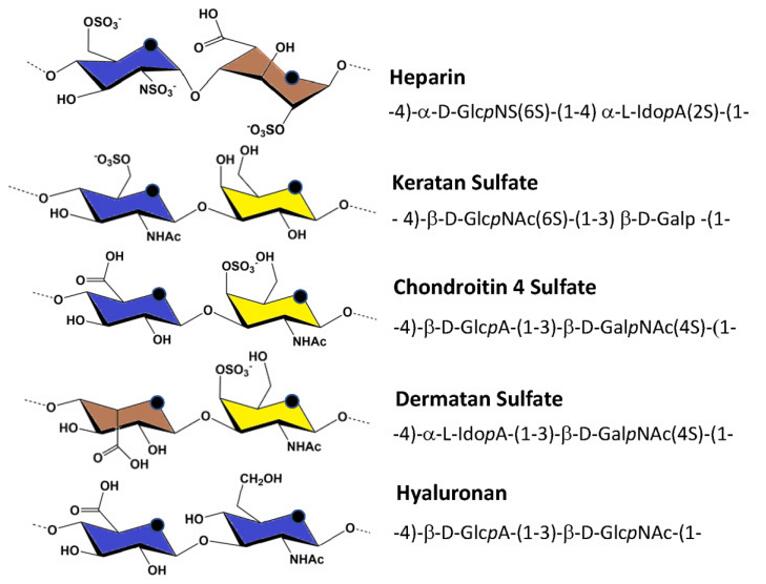 Fig 1. Major repeating unit of glycosaminoglycans. The color coding of the constituent monosaccharides was in accordance with the SNFG term. The abbreviations are as follows: Glc represents glucose, Ido represents galactose, Gal represents galactose, N represents amine, S represents sulfate, A represents acid, and NAc represents N-acetyl.
Fig 1. Major repeating unit of glycosaminoglycans. The color coding of the constituent monosaccharides was in accordance with the SNFG term. The abbreviations are as follows: Glc represents glucose, Ido represents galactose, Gal represents galactose, N represents amine, S represents sulfate, A represents acid, and NAc represents N-acetyl.
Advantage of Keratan Sulfate Analysis Service
- Short time-consuming
- High sensitivity and few detection restrictions
- High precision and good repeatability
- High throughput
- Customized service
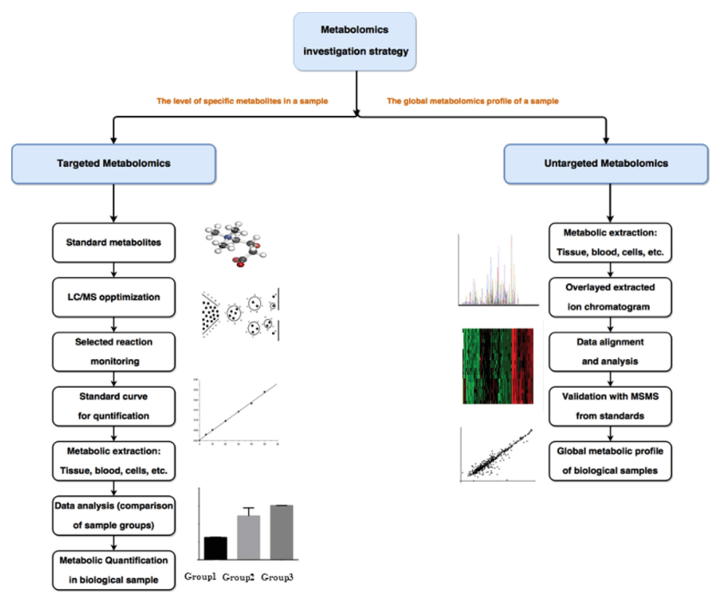
Service Workflow
- Extract and purifying glycosphingolipid from cell membrane or serum
- Release that glycosphingolipid glycan with the glucosidase
- The total methylation of glycan
- Sample detection by UPLC-MS
- Data analysis
 Fig 2. Workflow for the discovery-based proteomics.
Fig 2. Workflow for the discovery-based proteomics.
Sample Requirements
- Serum/plasma: 500 μl/sample
- Protein: 100 µg
- Anticoagulated blood (EDTA): 1 mL
- Urine: 1 ml/sample
- Animal tissues: 200 mg/sample
- Cells: ≥ 1 × 107/sample
- Feces: 500 mg/sample
In general, it is necessary to provide as many single samples as possible in order to ensure enough samples to complete the entire project. The remaining samples will be stored for one year free of charge and returned at any time if necessary. All samples need to be stored and transported at -80°C and try to avoid using surfactants (SDS, Triton-X) and inorganic salts.
Clinical samples are repeated in no less than 30 cases in a single group.
Animal samples are repeated in no less than 9 cases in a single group.
Report Delivery
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- Raw data, chromatograms and mass spectra
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Service Cycle
- Sample testing: 5-10 working days
- Data analysis: 5-10 working days
Creative Proteomics metabolism analysis platform is committed to the all-around, reliable and accurate analysis service for a variety of target substances, which is suitable for life-science research, drug exploration, biological determination and other fields. We sincerely hope to cooperate with you to assistant your scientific research.
References
- W. Wang, L. Shi, Y. Qin, et al. Research and Application of Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate-Degrading Enzymes. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8:560442.
- Z. Wang, K. Arnold, Y. Xu, et al. Quantitative analysis of heparan sulfate using isotopically labeled calibrants. Commun Biol, 2020, 3(1):425.