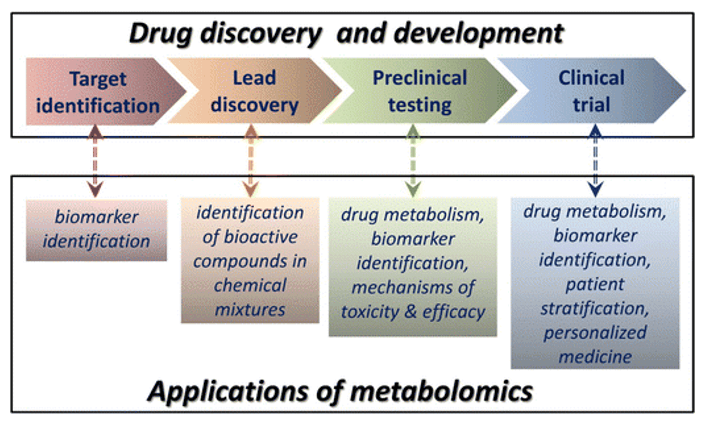
Various Types of N-glycan Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryOverview
The synthesis of N-glycan requires the formation of lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursors, which are transported to new proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, and N-glycan are linked to ASN asparagine in the common sequence ASN-X-Ser/Thr. All eukaryotes produce N-glycan and retain the first step in the synthesis of this polyterpenoid alcohol-oligosaccharide precursor and the sequential processing reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum.
The diversity of N-glycan, that is, high-mannose N-glycan in Golgi apparatus can be transformed into all kinds of hybrid and complex N-glycan subtypes, which is due to the presence of enzymes encoded by vertebrate genomes, including glycosyltransferases and glycosidases present in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. These enzymes show significant substrate specificity and unique expression patterns, so the structure of N-glycan changes in certain types of cell.
Creative Proteomics, as a leading biotechnology company, provides various types of N-glycan analysis service in animal, including high-mannose, hybrid and complex N-glycan metabolism analysis service. Relying on the advanced mass spectrometry and experienced research team, Creative Proteomics testing platform provides high-quality, fast and accurate one-stop testing service to support your scientific research.
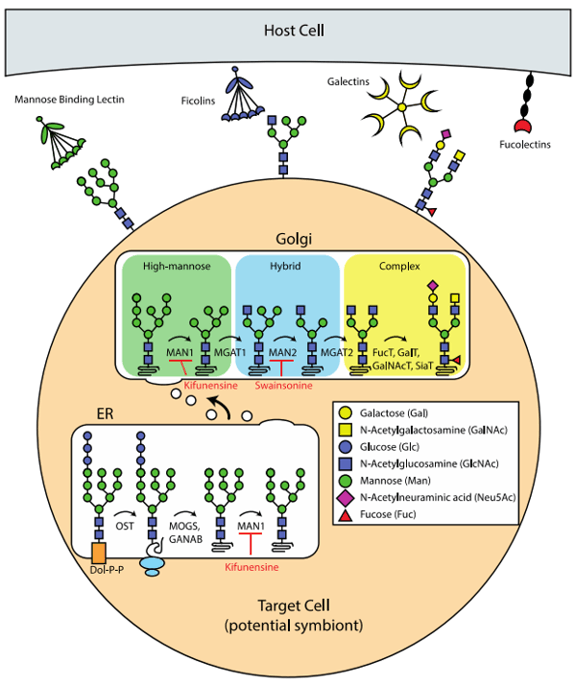 Fig 1. Various types of N-glycan biosynthesis and N-glycan recognition in animals (Tivey et al., 2020).
Fig 1. Various types of N-glycan biosynthesis and N-glycan recognition in animals (Tivey et al., 2020).
Advantage
- High coverage of N-glycans
- High sensitivity and few detection restrictions
- High precision and good repeatability
- Analysis for compounds which are difficult to be separated
Experimental process
Creative Proteomics provides various types of N-glycan analysis to identify linkage sites, monitor specific glycan types and determine the relative content of specific glycan groups.
- Sample preparation
- N-glycan release
- Glycan purification
- Methylation of released N-glycan
- Cleavage glycans with glycoside exonuclease or acid hydrolysis
- Reduction and derivatization
- Analysed and quantified by HPLC or LC-MS
Samples are offered according to the following requirement.
Glycans are released by enzymatic digestion, such as PNGase F, thus various types of N-glycan are released and to be sorted.
Various types of N-glycan are purified to remove interfering material before labelling.
A methyl group is introduced onto each free hydroxyl group.
Glycosidic linkages are cleaved to produce partially methylated monosaccharides.
Methylated monosaccharide are ring-opened and labelled.
Detection of released N-glycan by apparatus.
Service workflow
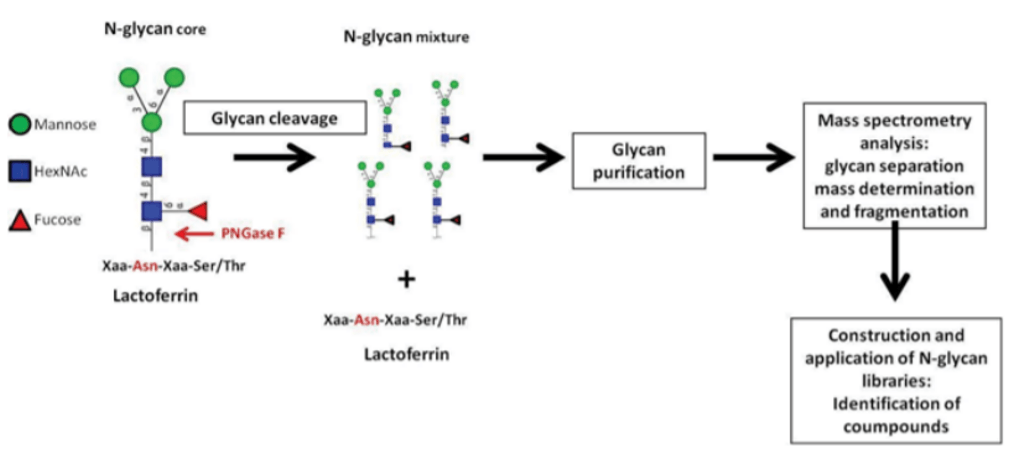 Fig 2. Schematic of enzymatic N-glycan released from protein and workflow for characterization of the released glycans (Dallas, Lee, Parc, de Moura Bell, & Barile, 2013).
Fig 2. Schematic of enzymatic N-glycan released from protein and workflow for characterization of the released glycans (Dallas, Lee, Parc, de Moura Bell, & Barile, 2013).
Sample requirement
- Serum/plasma: 500 μl/sample.
- Protein: 100 µg
- Anticoagulated blood (EDTA): 1 mL.
- Urine: 1 ml/sample.
- Animal tissues: 200 mg/sample.
- Cells: ≥ 1 × 107/sample.
- Feces: 500 mg/sample
Repeated freezing and thawing of samples must be avoided. The serum sample should be precipitated in the collection tube for 30 minutes at room temperature, then transported to the centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 5 minutes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was equally divided into a freezing tube of 500 uL / sample.
Anticoagulants and preservatives must be added immediately after collection and then frozen at -80°C.
Urine samples should be equally divided into centrifuge tubes with 1 mL per tube, each tube is added with 1/100 (w/v) sodium azide and stored at -80°C.
Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately and then transported to -80°C for storage after collected.
Cytoactive should be terminated immediately to maintaining cell integrity.
In general, to assure enough sample to fulfill the whole project, the volume of the single sample need to be offered as much as possible. The remaining samples will be stored for one year free of charge and returned at any time if necessary. All samples need to be stored and transported at-80°C.
Clinical samples are repeated in no less than 30 cases in a single group.
Animal samples are repeated in no less than 9 cases in a single group.
Report delivery
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- Raw data, chromatograms and mass spectra
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Service cycle
- Sample testing: 5-10 working days
- Data analysis: 5-10 working days
Creative Proteomics metabolism analysis platform is committed to the all-around, reliable and accurate analysis service for a variety of target substances, which is suitable for life-science research, drug exploration, biological determination and other fields. We sincerely hope to cooperate with you to assistant your scientific research.
References
- Dallas, D. C., Lee, H., Parc, A. L., de Moura Bell, J. M., & Barile, D. (2013). Coupling Mass Spectrometry-Based "Omic" Sciences with Bioguided Processing to Unravel Milk's Hidden Bioactivities. J Adv Dairy Res, 1(2), 104. doi:10.4172/2329-888X.1000104.
- Mereiter, S., Balmana, M., Gomes, J., Magalhaes, A., & Reis, C. A. (2016). Glycomic Approaches for the Discovery of Targets in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Front Oncol, 6, 55. doi:10.3389/fonc.2016.00055.
- Tivey, T. R., Parkinson, J. E., Mandelare, P. E., Adpressa, D. A., Peng, W., Dong, Loesgen, S. (2020). N-Linked Surface Glycan Biosynthesis, Composition, Inhibition, and Function in Cnidarian-Dinoflagellate Symbiosis. Microb Ecol, 80(1), 223-236. doi:10.1007/s00248-020-01487-9.