Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryOverview
Chondroitin sulfate (CS) and dermatan sulfate (DS) are widely distributed on the cell surface and extracellular matrix in the form of proteoglycans, and they are involved in a variety of physiological processes. The functional diversity of CS/DS is mainly attributed to its high structural variability. As a major member of the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) family, chondroitin sulfate (CS)/dermatan sulfate (DS) chain covalently binds to the core protein to form CS/DS proteoglycan (CS/DSPG).
It has been shown that the abnormal expression of CS/DS is closely related to the occurrence and development of various diseases, such as glial scar formation, tumor metastasis, bone disease and virus infection after brain injury, which indicates that the treatment of CS/DS- degradation enzymes should affect the progression of related diseases. The abnormal expression of CS/DS or CS/DSPGs in cells and tissues is also closely related to many carcinogenic processes, including cell growth and survival, adhesion, migration and invasion. A series of studies have shown that CSases has potential application value in anti-tumor.
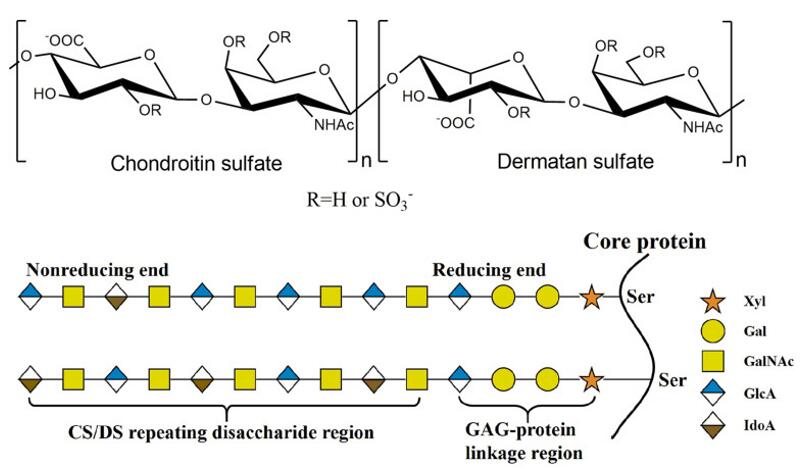 Fig 1. Structure of CS/DS. The CS/DS chain consists of either D-glucuronide (GlcA) or L-Aidoo uronic acid (IdoA) glycosylation linked to N-acetylgalactosamine (GLANCA) [(-4gLCAβ1-3GaLNACβ1-) or (-4IdoAα1-3GalNAcβ1-). The CS/DS chain is covalently attached to the core protein via the GAG- protein junction tetrasaccharide
Fig 1. Structure of CS/DS. The CS/DS chain consists of either D-glucuronide (GlcA) or L-Aidoo uronic acid (IdoA) glycosylation linked to N-acetylgalactosamine (GLANCA) [(-4gLCAβ1-3GaLNACβ1-) or (-4IdoAα1-3GalNAcβ1-). The CS/DS chain is covalently attached to the core protein via the GAG- protein junction tetrasaccharide
Advantages
- High coverage of glycans
- High sensitivity and few detection restrictions
- High precision
- Advanced platforms and strategies
Experimental process
- Extract and purifying glycosphingolipid from cell membrane or serum
- Release that glycosphingolipid glycan with the glucosidase
- The total methylation of glycan
- Analysis based on 2-AB labeling
- Analyzing the fully methylated glycan by a time-of-flight mass spectrum
Service workflow
The biosynthesis of CS/DS is a complex, multi-step, enzymatic adaptive process, which occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi apparatus and starts with the synthesis of GAG protein junction regions covalently linked to serine residues embedded in different core proteins. The modified synthesis process is connected by a specific tetrasaccharide structure GlcAβ1-3Galβ1-3Galβ1-4Xylβ1, in which Gal- and Xyl- represent galactose and xylose residues respectively. The structure is catalyzed by the corresponding glycosyltransferase in the tetrasaccharide sequence. Firstly, a Xyl- residue is linked to a specific Ser- residue of the core protein through the catalysis of xylose transferase; then, β1Maginol4-galactosyltransferaseI and β1Maginol 3-galactosyltransferase II successively catalyze the ligation of the two Gal- residues. Finally, the residue of GlcUA is added to the residue of glucuronyltransferase I to form the tetrasaccharide junction region.
 Fig 2. Workflow of glycosaminoglycan metabolism service.
Fig 2. Workflow of glycosaminoglycan metabolism service.
Sample requirement
- Serum/plasma: 500 μl/sample
- Protein: 100 µg
- Anticoagulated blood (EDTA): 1 mL
- Urine: 1 ml/sample
- Animal tissues: 200 mg/sample
- Cells: ≥ 1 × 107/sample
- Feces: 500 mg/sample
Repeated freezing and thawing of samples must be avoided. The serum sample should be precipitated in the collection tube for 30 minutes at room temperature, then transported to the centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 5 minutes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was equally divided into a freezing tube of 500 uL / sample.
Anticoagulants and preservatives must be added immediately after collection and then frozen at -80 °C.
Urine samples should be equally divided into centrifuge tubes with 1 mL per tube, each tube is added with 1/100 (w/v) sodium azide and stored at -80 °C.
Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately and then transported to -80 °C for storage after collected.
Cytoactive should be terminated immediately to maintaining cell integrity.
In general, to assure enough sample to fulfill the whole project, the volume of the single sample need to be offered as much as possible. The remaining samples will be stored for one year free of charge and returned at any time if necessary. All samples need to be stored and transported at -80°C and try to avoid using surfactants (SDS, Triton-X) and inorganic salts.
Clinical samples are repeated in no less than 30 cases in a single group.
Animal samples are repeated in no less than 9 cases in a single group.
Report delivery
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of HPLC and MS
- Raw data, chromatograms and mass spectra
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom analysis report
Service cycle
- Sample testing: 5-10 working days
- Data analysis: 5-10 working days
Creative Proteomics metabolism analysis platform is committed to the all-around, reliable and accurate analysis service for a variety of target substances, which is suitable for life-science research, drug exploration, biological determination and other fields. We sincerely hope to cooperate with you to assistant your scientific research.
References
- S. Ashworth, J. Harrington, G.M. Hammond, et al. Chondroitin Sulfate as a Potential Modulator of the Stem Cell Niche in Cornea. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8:567358.
- W. Wang, L. Shi, Y. Qin, et al. Research and Application of Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate-Degrading Enzymes. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8:560442.