N-glycan Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhy Analysis N-glycan?
Glycans promote proper folding and transport of proteins during the period of protein synthesis. After maturation of glycoprotein processing, the solubility and folding energetics of the protein are improved through the interaction of glycan chains and amino acid sequences. It has been shown that due to the rigidity and hydrophilicity of N-glycans, the denaturation and aggregation of glycoproteins are effectively prevented and the homeostasis of glycoproteins is improved. N-linked glycans are also associated with cancer development and metastasis. Tumor cells exhibit extensive glycosylation differences compared to their corresponding normal cells. The development and maturation of the mammalian immune system is accompanied by a process of reconstitution of the cellular glycan structure. The glycosome of immune cells undergoes important changes during cell differentiation, activation and apoptosis, which are closely related to the maintenance of immune system homeostasis, antigen recognition, and immune cell maturation.
The correct glycosylation structure is an important guarantee that the antibody drug will work. Monoclonal antibodies with abnormal glycosylation structures not only fail to treat disease but may also cause immunogenic reactions.
Assessment of N-glycan levels and the conformation and location of glycosidic bonds will help provide new insights into the study of N-glycans in basic biological functions, drug development, and disease biomarkers.
Creative Proteomics provides reliable, rapid and cost-effective qualitative and quantitative N-glycan analysis and N-glycan structural analysis services. We rely on our advanced liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry platform (HPLC-MS) and experienced research team to provide high quality, rapid and accurate one-stop testing services for researchers.
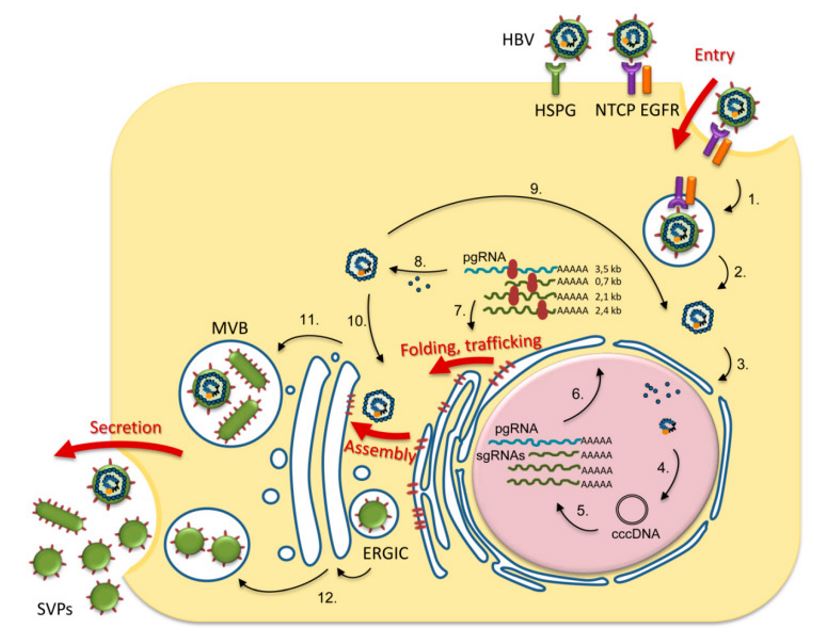 Fig 1. An overview of the role of N-glycosylation in the life cycle of HBV. The HBV life cycle steps regulated by N-glycosylation / N-glycan processing are indicated by a thick red arrow (Dobrica, Lazar et al. 2020).
Fig 1. An overview of the role of N-glycosylation in the life cycle of HBV. The HBV life cycle steps regulated by N-glycosylation / N-glycan processing are indicated by a thick red arrow (Dobrica, Lazar et al. 2020).
Advantage of N-glycan Analysis Service
- Suitable for a wide range of analysis of compounds
- High sensitivity and few detection restrictions
- High precision
- Analysis for compounds which are difficult to be separated
Service Workflow of N-glycan Assay
Data acquisition
HPLC-MS is the most widely used analytical technology at present. With the help of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), Creative Proteomics identify the samples and carry out quantitative analysis with high efficiency and precision.
Quantitative analysis
The data are processed by the quantitative analysis software installed with the instrument, and the chromatogram of the relative abundance of N-glycan was obtained simultaneously.
Data statistics and report generation
Generate the final service report through data analysis.
Turnaround time: About 1-4 weeks.
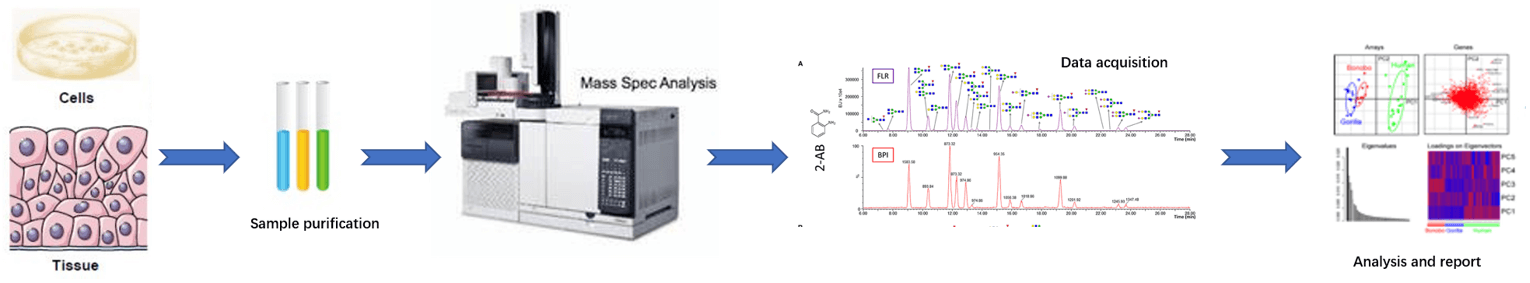 Fig 2. Overall workflow of N-glycan metabolism analysis service.
Fig 2. Overall workflow of N-glycan metabolism analysis service.
Experimental Process for N-glycan Analysis
- Release N-glycans. PNGase F is an amidase that releases complete double-stranded Homozygous and heterozygous N-polysaccharides by cutting between the innermost layer of N-glycans, GlcNAc and N-polysaccharides. The digested time of PNGase F is only a few minutes, which greatly shorten the sample preparation process of N-polysaccharide in the latest protocol.
- Clean-up and purification. Aim to separate polysaccharides from the mixture, which remove salts and detergents and improve the labeling efficiency of fluorescence.
- 2-AB labeling. The released N-glycans are often labeled with fluorophores to enhance the separation and detection of glycan. Frequently used markers include 2-aminobenzamide (2-AB) and 2-aminobenzoic acid (2-AA).
- Purification after labeling. Purify the labeled glycans and remove excess dyes and salts.
- HILIC-HPLC or LC-MS analysis. HPLC and LC-MS are the most widely used analytical techniques at present, which realize the identification of samples and carry out quantitative analysis efficiently and accurately.
Sample Requirement
- Serum/plasma: 500 μl/sample
- Urine: 1 ml/sample
- Tissue: 200 mg/sample
- Cells: ≥ 1 × 107/sample
- Feces: 500 mg/sample
In general, to assure enough sample to fulfill the whole project, the volume of the single sample need to be offered as much as possible. The remaining samples will be stored for one year free of charge and returned at any time if necessary. All samples need to be stored and transported at-80°C.
Clinical samples are repeated in no less than 30 cases in a single group.
Animal samples are repeated in no less than 9 cases in a single group.
Report Delivery
- Experimental procedures
- Related parameters of apparatus
- Quantitative or quantitative information for identifying substances
- Mass spectrometry figures
- Raw data files and detailed summary report
Creative Proteomics metabolism analysis platform is committed to the all-around, reliable and accurate analysis service for a variety of target substances, which is suitable for life science research, drug exploration, biological determination and other fields. We provide personalized metabolism analysis service to support your science research.
References
- Dobrica, M. O., et al. (2020). "N-Glycosylation and N-Glycan Processing in HBV Biology and Pathogenesis." Cells 9(6).
- Gornik, O., et al. (2012). "Alternative glycosylation modulates function of IgG and other proteins - implications on evolution and disease." Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(9): 1318-1326.
- Keser, T., et al. (2018). "Comparison of 2-Aminobenzamide, Procainamide and RapiFluor-MS as Derivatizing Agents for High-Throughput HILIC-UPLC-FLR-MS N-glycan Analysis." Front Chem 6: 324.
- Yang, X., et al. (2018). "Serum Metabolomics Analysis in Wasp Sting Patients." Biomed Res Int 2018: 5631372.