Aflatoxin Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryAbout aflatoxin
Aflatoxin is a secondary metabolite secreted by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in nature, easily contaminating food crops and their products. Aflatoxin is mainly present in moldy peanuts, rice, corn and other crops and their related food, with strong toxicity and carcinogenic power, has a strong toxic effect on human and animal liver and central nervous system. A large number of one-time intake will cause acute poisoning and death of humans and animals, small doses of long-term intake can be teratogenic, carcinogenic and mutagenic. Aflatoxin colorless, tasteless, odorless, stable physicochemical properties, is by far the most stable physicochemical properties of fungal toxins found in nature, in the food processing process is difficult to be destroyed.
In order to ensure food safety, human health and international trade, the qualitative and quantitative detection of aflatoxin is necessary. Creative Proteomics is based on a high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) technology platform to detect aflatoxin levels in a variety of samples.
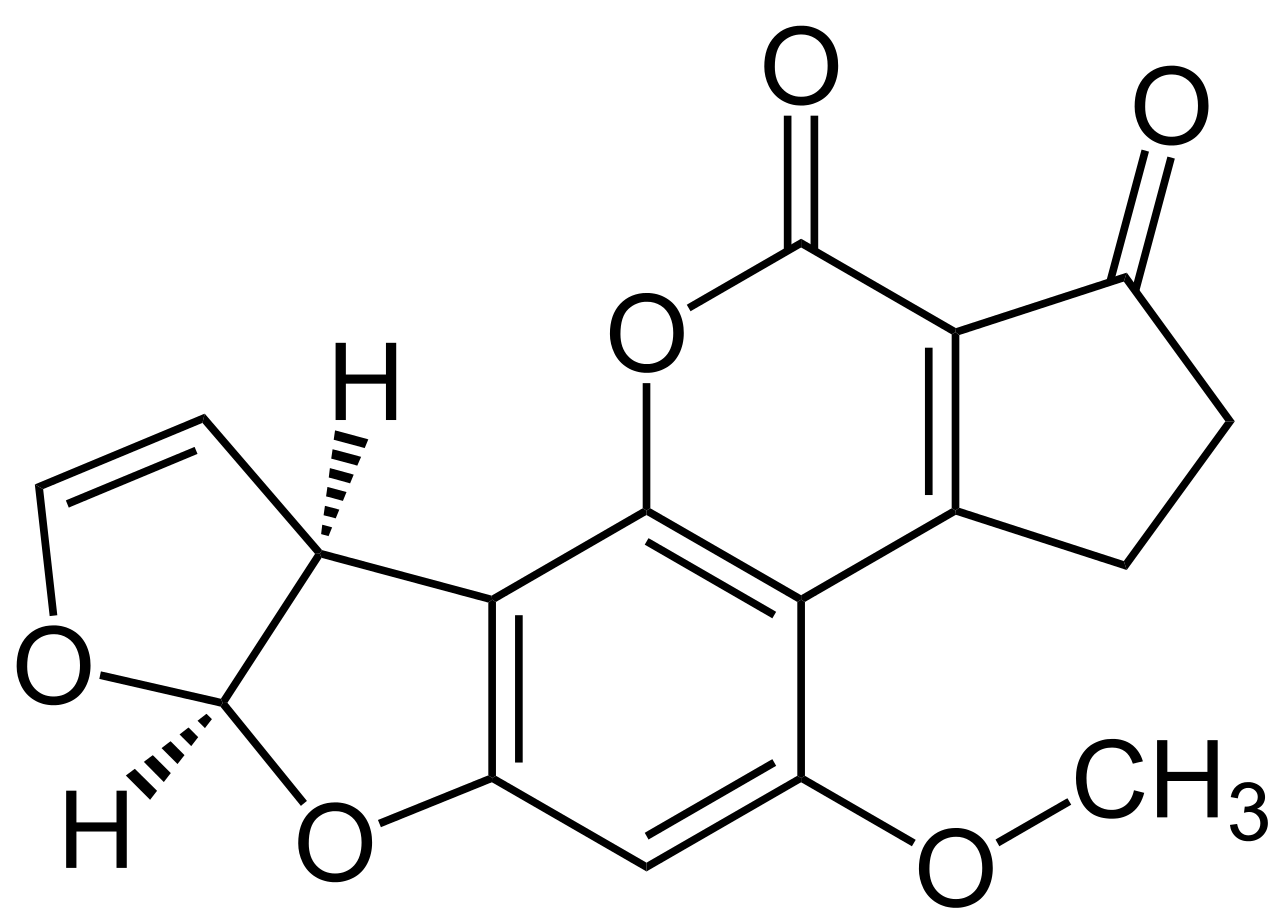 Chemical structure of aflatoxin
Chemical structure of aflatoxin
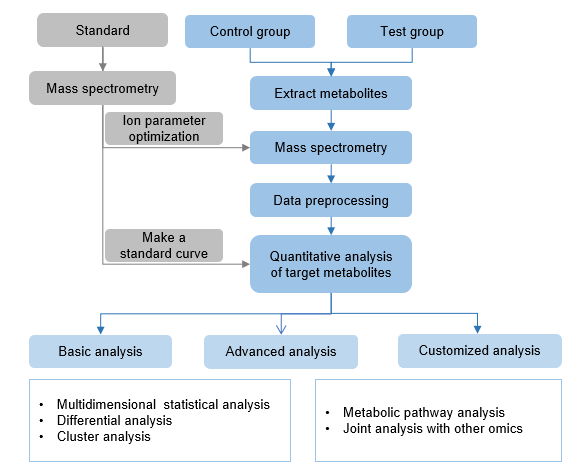
The technical route of targeted metabolomics of aflatoxin
Sample requirements
| Sample requirements |
|---|
| Sample type |
| Cell sample - please centrifuge after sampling, remove the medium, immediately put it in liquid nitrogen, and store it at -80℃. Tissue sample - please put it in liquid nitrogen immediately after separation and store it at -80℃. |
| Sample mixed |
| In order to ensure the accuracy of the samples and reduce systematic errors during sampling, it is necessary to select more than 3 materials with the same condition for each sample. ※ The same condition refers to the same period, basically the same phenotype, and the same part. |
| Sample weight and repeat |
| Samples that have been lyophilized are >0.5g. For samples with low water content, such as stems, flowers, seeds, dormant buds, etc., fresh samples >1g. For samples with middle water content, roots and leaves (especially young leaves), fresh samples >2g. For samples with water content >90%, if fruit (tomato, watermelon, citrus, etc.), fresh sample >5g. Blood ≥100 µl, Urine ≥100 μl, Tissue ≥50 mg, Fresh stool ≥50 mg, Freeze-dried stool ≥5 mg, Cell ≥1*107 It is recommended that prepare more than 6 biological replicates. |
| Storage and transportation |
| Quick-frozen preservation with liquid nitrogen can minimize the leakage time of plant samples at room temperature. Dry ice transportation (about 3~4kg dry ice is consumed every day, please use sufficient dry ice for transportation). There is no restriction on plant varieties. For varieties with special requirements or rare varieties, please contact our staff for more information. |
Creative Proteomics offers several approaches to plant metabolomics studies, delivers precise and detailed data and analysis report. We can also customize the methods or establish new methods together with our collaborators, so they are fit-for-purpose and meet your specific needs. If you have any questions or specific requirements, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Bhatnagar D, Rajasekaran K, Payne G, et al. The'omics' tools: genomics, proteomics, metabolomics and their potential for solving the aflatoxin contamination problem. World Mycotoxin Journal, 2008, 1(1): 3-12.
- Falade T, Chrysanthopoulos P K, Hodson M P, et al. Metabolites identified during varied doses of Aspergillus species in Zea mays grains, and their correlation with aflatoxin levels. Toxins, 2018, 10(5): 187.
- Mohammed A, Hussain R M, Ur R N, et al. De novo transcriptome sequencing and metabolite profiling analyses reveal the complex metabolic genes involved in the terpenoid biosynthesis in Blue Anise Sage (Salvia guaranitica L.). DNA Research (6):6.




