Cyanidin Analysis Service
Submit Your InquiryWhat is Cyanidin?
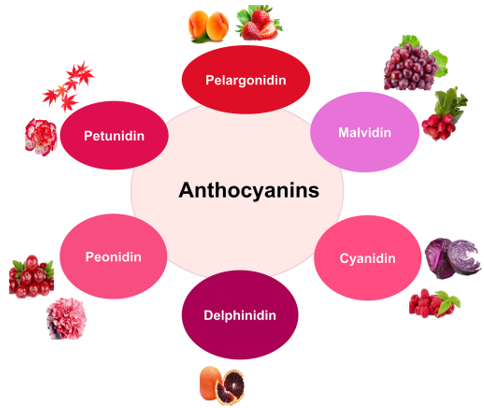
Cyanidin, a member of the anthocyanin family, is a natural plant pigment responsible for the red, purple, and blue hues seen in various fruits, vegetables, and flowers. Its chemical structure consists of a flavylium cation with two phenol rings and a positively charged oxygen atom. This compound is particularly abundant in foods like berries (e.g., blueberries, strawberries, blackberries), red grapes, cherries, and red cabbage, contributing not only to their vibrant coloration but also to their potential health benefits.
Research indicates that cyanidin possesses numerous beneficial properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities. Additionally, it has been observed to enhance cognitive function while protecting against age-related ailments.
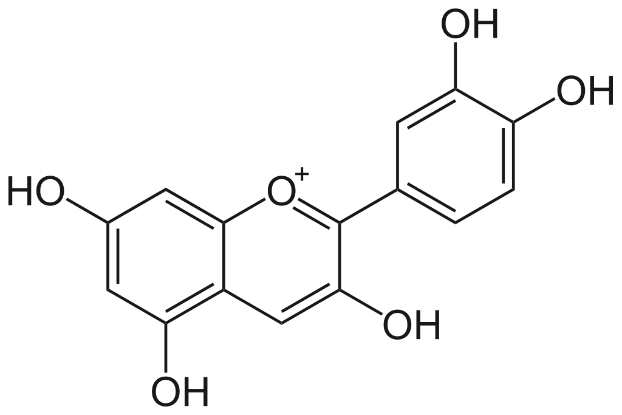 The molecular structure of cyanidin
The molecular structure of cyanidin
At Creative Proteomics, we offer a full suite of cyanidin analysis services based on mass spectrometry.
- Cyanidin Identification: We identify and characterize cyanidin metabolites, elucidating their chemical structures.
- Cyanidin Quantification: Accurate quantification of cyanidin and its metabolites in various biological matrices, facilitating pharmacokinetic studies.
- Metabolomic Pathway Analysis: We map the metabolic pathways of cyanidin, providing insights into its fate within the human body.
Our services present a vast array of advantages, foremost among them the use of cutting-edge equipment and techniques, which enable the identification of even minute quantities of cyanidin. We also customize our services to meet the unique needs of our clientele, offering everything from method development and validation to sample preparation and data analysis.
Cyanidin Analysis Platform at Creative Proteomics
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
One of the cornerstone techniques in cyanidin metabolomics is Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS). This method combines the separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the high sensitivity and specificity of mass spectrometry. At Creative Proteomics, we utilize industry-leading LC-MS instrument models, including:
- Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Series: Renowned for its exceptional resolution, accuracy, and sensitivity, the Thermo Scientific Q Exactive series allows us to detect and quantify cyanidin and its metabolites with the utmost precision.
- Waters ACQUITY UPLC-Xevo TQ-S: This high-performance system offers robust and efficient chromatographic separation coupled with the sensitivity of triple quadrupole mass spectrometry, enabling accurate quantification of cyanidin and its metabolites.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
For the analysis of volatile cyanidin derivatives and related compounds, Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) is an indispensable technique. Creative Proteomics employs state-of-the-art GC-MS instrument models, including:
- Agilent 7890B GC System with 5977B Mass Selective Detector: This combination offers exceptional sensitivity and selectivity for the analysis of volatile cyanidin compounds, ensuring reliable identification and quantification.
Sample Requirements for Cyanidin Analysis
| Sample Type | Sample Matrix | Recommended Sample Volume | Storage Conditions | Special Instructions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma/Serum | Blood | 100-200 μL per sample | -80°C or below | Collect samples in EDTA tubes to prevent coagulation. |
| Urine | Urine | 1-2 mL per sample | -80°C or below | Collect samples in sterile containers. |
| Tissues | Various (e.g., liver, etc.) | 20-50 mg per sample | Flash freeze in liquid nitrogen | Record tissue weight and source organ. |
| Cell Culture | Cell lysates | As needed | -80°C or below | Specify cell type and culture conditions. |
| Plant Extracts | Plant materials | As needed | Freeze-dried or -80°C or below | Provide details on plant species and growth conditions. |
| Food and Beverages | Various (e.g., juice, etc.) | As needed | -80°C or below or refrigerated | Include sample preparation methods and storage conditions. |
Applications of Cyanidin Analysis
Nutritional Research: Cyanidin analysis is fundamental in assessing the nutritional content of various foods and beverages, especially those rich in cyanidin, such as berries, red grapes, and red cabbage. This information is crucial for dietary recommendations and nutritional labeling.
Pharmacological Studies: Cyanidin's potent antioxidant properties make it a subject of interest in pharmacological research. Analyzing cyanidin content and its metabolites in various plant extracts or pharmaceutical formulations can assist in developing antioxidant-rich supplements or medications.
Cancer Research: The potential chemopreventive properties of cyanidin have garnered attention in cancer research. Analyzing its levels in tissues and studying its effects on cancer cells can provide valuable insights into its anti-cancer mechanisms.
Metabolism Studies: Understanding how cyanidin is metabolized in the human body is critical for pharmacokinetic studies. Analyzing its metabolism can help determine its bioavailability and the duration of its beneficial effects.
Food and Beverage Industry: Cyanidin analysis is used for quality control in the food industry. It ensures product consistency and verifies the cyanidin content in red wines, juices, jams, and fruit-based products.
Agricultural Research: Cyanidin analysis plays a pivotal role in agricultural research by aiding in the selection and breeding of plants with higher cyanidin content. This can lead to the production of crops with enhanced nutritional value and potential resistance to pests and diseases.
Pharmaceutical Development: Pharmaceutical companies may use cyanidin analysis to develop formulations that incorporate cyanidin for various therapeutic purposes.
Environmental Monitoring: Analyzing cyanidin in plants grown in different environments provides insights into the impact of environmental factors on plant metabolism and health.
Biomedical Research: Cyanidin analysis is crucial in cellular and molecular studies, helping researchers understand how cyanidin affects cellular processes and signaling pathways.