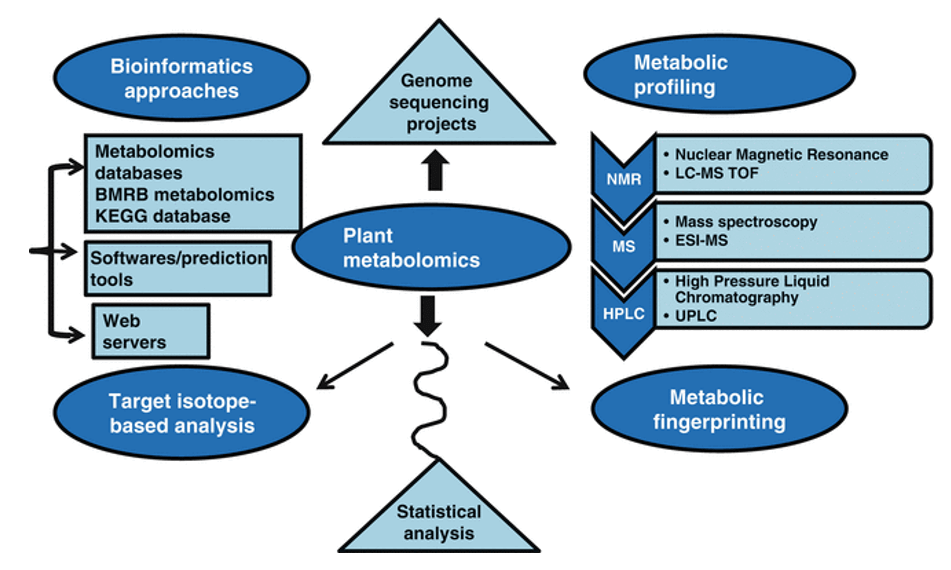
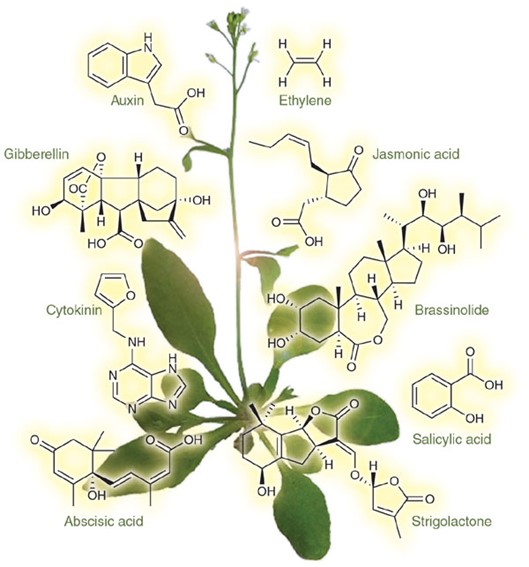
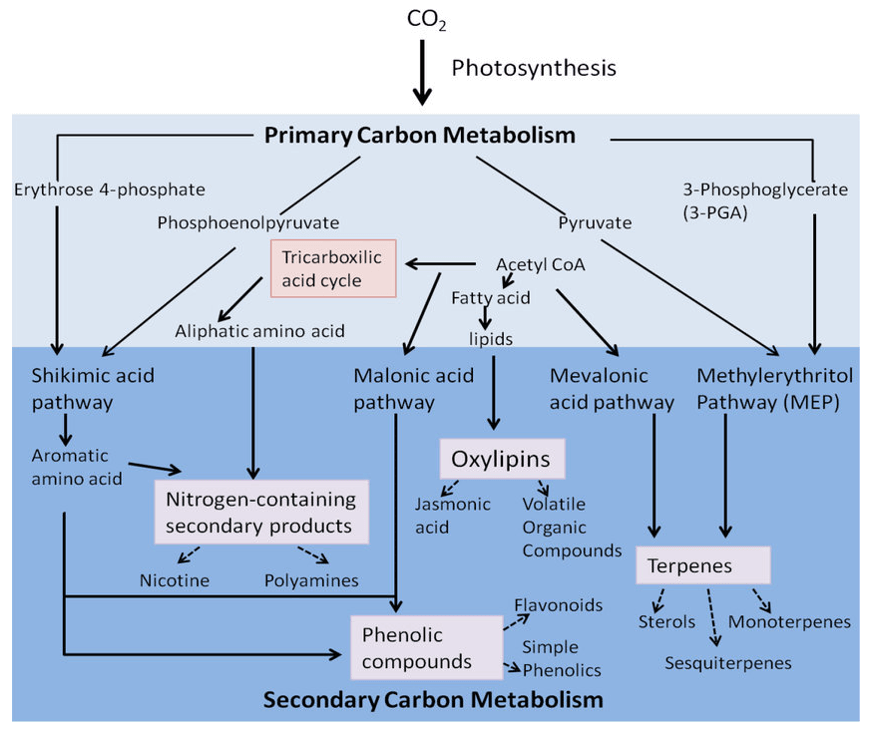
Overview
Untargeted metabolomics is an analytical approach used for the simultaneous, unbiased analysis of a vast array of compounds that an organism accumulates at a certain point in a given sample, which is used to investigate metabolic phenotypes involving a massive amount of metabolites and elucidate plant-pathogen interactions. Untargeted analyses are especially useful in some cases previous knowledge about the metabolome of the plants or compounds relevant to herbivores is not available. Plant specimens are complex matrices consisting of a myriad of metabolites. Thus, a significant challenge of metabolomics is to identify measured metabolites. Currently, liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is the most promising technique for metabolomics in terms of its sensitivity, resolution, precision, throughput, and metabolome coverage. UPLC coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) is the most commonly used method for untargeted plant metabolomics, which generates a massive amount of data generated. With an integrated set of separation, identification and quantification systems featured with excellent robustness and reproducibility, Creative Proteomics provides reliable, efficient and cost-effective plant untargeted metabolomics services.
Applications of Plant Untargeted Metabolomics
- Reveal metabolic phenotypes involving a massive amount of metabolites
- Identify candidate compounds involved in host plant interactions
- Elucidate metabolic pathways involved in different biological processes
- Safety assessment of genetically modified crops and crop improvement
Advantages of Our Plant Untargeted Metabolomics
- Unbiased measurement of plant metabolites
- High sensitivity, resolution, and precision
- High coverage of the metabolome at high throughput
- Decades of experience in offering plant metabolomics analyses services
- Fast turnaround time and competitive price
Service Workflow
Creative Proteomics employs state-of-the-art UPLC-MS/MS systems for plant untargeted metabolomics studies. A non-targeted metabolomic analysis generally consists of these steps: sample collection and homogenization, metabolites extraction, raw data acquisition, data processing, and bioinformatics analysis. We have strong expertise in handling a variety of sample types, and ensure the best recovery and unbiased metabolome measurement.
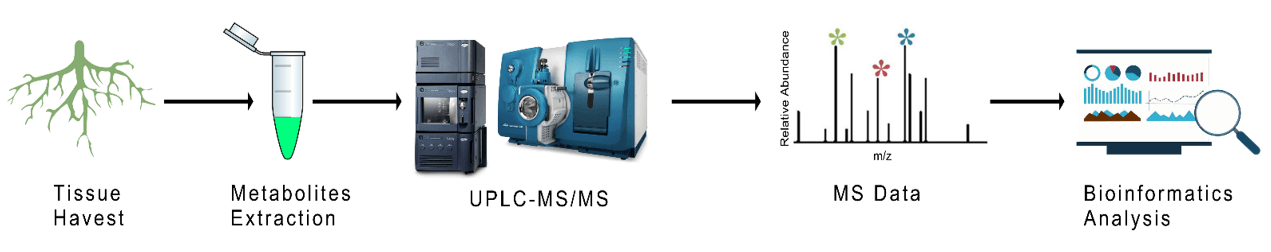
Our primary instruments include:
- Liquid chromatography system
- Orbitrap MS
- Triple Quad-MS
- Q-TOF-MS
Data Analysis
- Peak calling and metabolite annotation
- Principal component analysis (PCA) and the partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA)
- Metabolite enrichment and pathway analyses
- Modeling algorithms
- Integrate metabolomics data with lipidomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and phenomics data available
Sample Preparation
Fresh plant tissue or seed, weight > 1 g. Samples should be frozen in liquid nitrogen right after collection, and then transferred to -80°C for storage. At least 3 biological replicates.
Delivery
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of chromatography and MS
- Extracted mitochondria and purified protein sample
- Purity analysis report
- MS raw data files and MS data quality checks
- Metabolites quantification data
- Custom bioinformatics analysis report
Creative Proteomics is proud to offer high-efficient and accurate plant untargeted metabolomics analysis service by applying advanced UPLC- MS/MS systems and techniques. We have extensive experience in the field of plant metabolomics and offer custom service to meet customer's specific research needs, and guarantee comprehensive analysis service with accuracy.
References
- Silva E, Perez da Graça J, Porto C, et al. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis by UHPLC-MS/MS of Soybean Plant in a Compatible Response to Phakopsora pachyrhizi Infection. Metabolites, 2021, 11(3): 179.
- Gevi F, Fanelli G, Zolla L, et al. Untargeted Metabolomics of Plant Leaf Tissues. High-Throughput Metabolomics. Humana, New York, NY, 2019: 187-195.
- Sanchez-Arcos C, Kai M, Svatoš A, et al. Untargeted metabolomics approach reveals differences in host plant chemistry before and after infestation with different pea aphid host races. Frontiers in plant science, 2019, 10: 188.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.