What Are Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)?
BCAAs—L-leucine, L-isoleucine, L-valine—are essential amino acids with branched aliphatic side chains. They are central to nitrogen handling, carbon routing, and anabolic signaling. In applied settings (food, feed, fermentation, and discovery research), accurate BCAA quantification supports formulation control, process stability, and mechanistic insight.
What Problems We Solve for Our Clients
What We Offer — Branched-Chain Amino Acids Analysis from Creative Proteomics
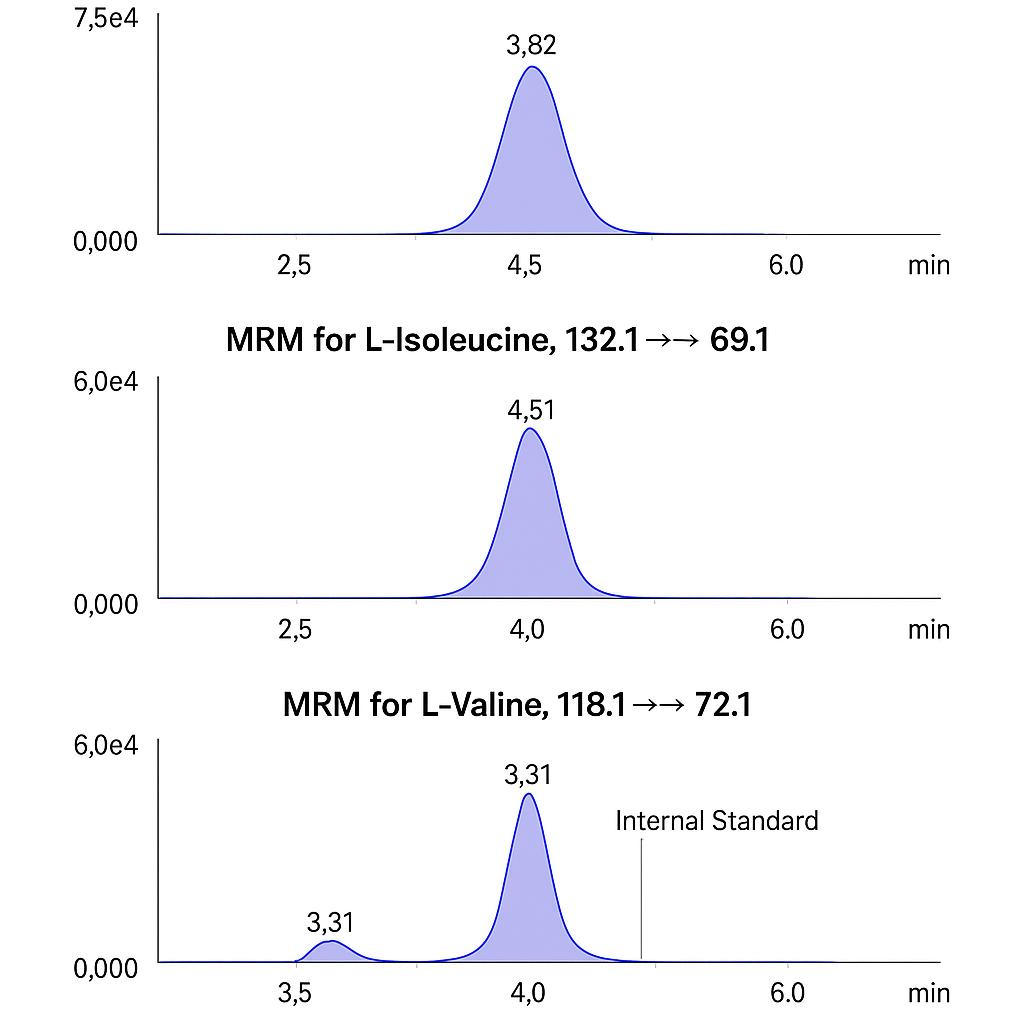
- Targeted BCAA quantification (primary panel): Absolute concentrations of leucine, isoleucine, valine using stable-isotope internal standards.
- BCKA add-on panel: α-ketoisocaproate (KIC), α-keto-β-methylvalerate (KMV), α-ketoisovalerate (KIV).
- Acylcarnitine add-on: Isovaleryl-, isobutyryl-, and 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine for catabolic read-through.
- Extended amino-acid bundle: ≥20 amino acids for nutritional and process context.
- Isotope-tracing (research): ^13C/^15N-BCAA tracers to examine pathway flux in cells, tissues, or fermenters.
- Cross-platform confirmation (as needed): GC–MS on derivatized analytes for challenging matrices.
- Data analysis options: Time-course trend plots, PCA across groups, correlation with your process variables (e.g., pH, DO, glucose).
Full Panel of Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Related Metabolites
| Category |
Analyte |
Description / Research Relevance |
| Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) |
L-Leucine |
Essential amino acid; key in protein synthesis and metabolic regulation |
| L-Isoleucine |
Essential amino acid; involved in energy production and hemoglobin synthesis |
| L-Valine |
Essential amino acid; supports muscle metabolism and tissue repair |
| Branched-Chain Keto Acids (BCKAs) |
α-Ketoisocaproate (KIC) |
Leucine transamination product; indicator of BCAA catabolism |
| α-Keto-β-methylvalerate (KMV) |
Isoleucine transamination product |
| α-Ketoisovalerate (KIV) |
Valine transamination product |
| Acylcarnitines |
Isovalerylcarnitine (C5) |
Leucine catabolism intermediate |
| 2-Methylbutyrylcarnitine (C5) |
Isoleucine catabolism intermediate |
| Isobutyrylcarnitine (C4) |
Valine catabolism intermediate |
| Other Related Amino Acids |
Alanine |
Transamination partner; nitrogen shuttle |
| Threonine |
Essential amino acid; metabolic network context |
| Methionine |
Sulfur amino acid; methylation donor |
| Phenylalanine |
Aromatic amino acid; precursor to neurotransmitters |
| Nitrogen/Carbon Metabolism Markers (Optional) |
Glutamate / Glutamine |
Nitrogen transfer intermediates |
| Urea / Ammonium |
Nitrogen excretion indicators |
| Lactate / Pyruvate |
Energy metabolism context |
Why Choose Our Branched‑Chain Amino Acids Analysis: Key Advantages
- Validated Sensitivity for Multiple Matrices: Matrix-qualified LOQs as low as 5–50 nM in biofluids and 0.5–5 µM in food/feed/tissue samples, ensuring detection even in low-abundance scenarios.
- Wide Quantification Range: Linear response across 3–4 orders of magnitude (r² ≥ 0.995) to accommodate both trace-level and high-concentration samples without re-analysis.
- High Precision and Accuracy: Intra- and inter-batch precision typically RSD ≤ 10%; spike-recovery results within 85–115%, delivering reproducible data for confident comparisons.
- Matrix Effect Control: Isotope-dilution quantification combined with matrix-matched calibration minimizes ion suppression/enhancement for true concentration values.
- Batch-to-Batch Consistency: Calibrator bracketing and QC monitoring throughout the run safeguard consistency across large sample sets and multi-batch studies.
- Traceable, Auditable Data: Each reported value is linked to its chromatogram, integration file, and QC record, enabling transparent verification for reports, publications, or audits.
Technical Specifications You Can Rely On
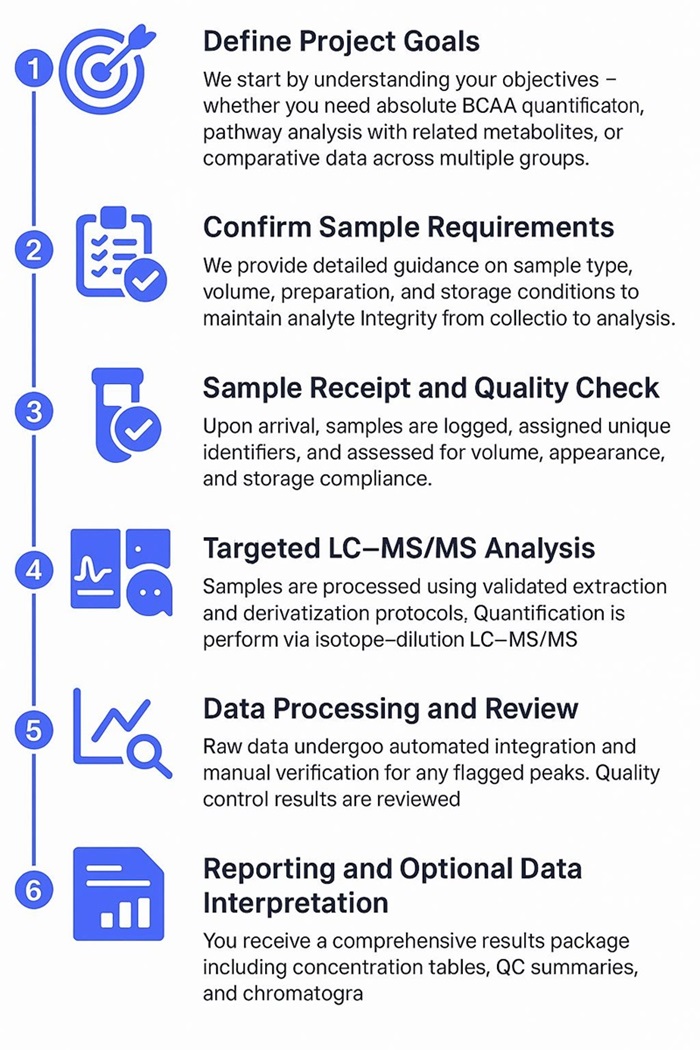
How Our BCAA Analysis Works — Step-by-Step Process
Accepted Sample Types and Collection Instructions for BCAA Quantification
| Sample Type |
Minimum Volume / Weight |
Collection & Preparation |
Storage & Shipping |
| Plasma / Serum |
≥ 50 µL |
Plasma: collect in EDTA or heparin tube, centrifuge promptly to separate plasma. Serum: collect in clot activator tube, allow clotting, centrifuge to separate. Avoid hemolysis. |
Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice. |
| Urine |
≥ 50 µL |
Collect midstream urine without preservatives; mix gently before aliquoting. |
Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice. |
| Cell Culture Supernatant |
≥ 100 µL |
Remove cells by centrifugation or filtration; transfer supernatant to a clean tube. |
Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice. |
| Cell Pellets |
≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells |
Wash once with cold PBS; remove all supernatant; snap-freeze immediately. |
Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice. |
| Tissue (animal/plant) |
10–50 mg |
Rinse plant tissues briefly; blot dry. For animal tissues, dissect rapidly; snap-freeze immediately. |
Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice. |
Deliverables: What You Get from Our Branched‑Chain Amino Acids Assay
- BCAA concentration data(L-Leucine, L-Isoleucine, L-Valine)
- Optional related metabolites(BCKAs, acylcarnitines, other amino acids, if selected)
- QC summary(calibration curve, accuracy, precision)
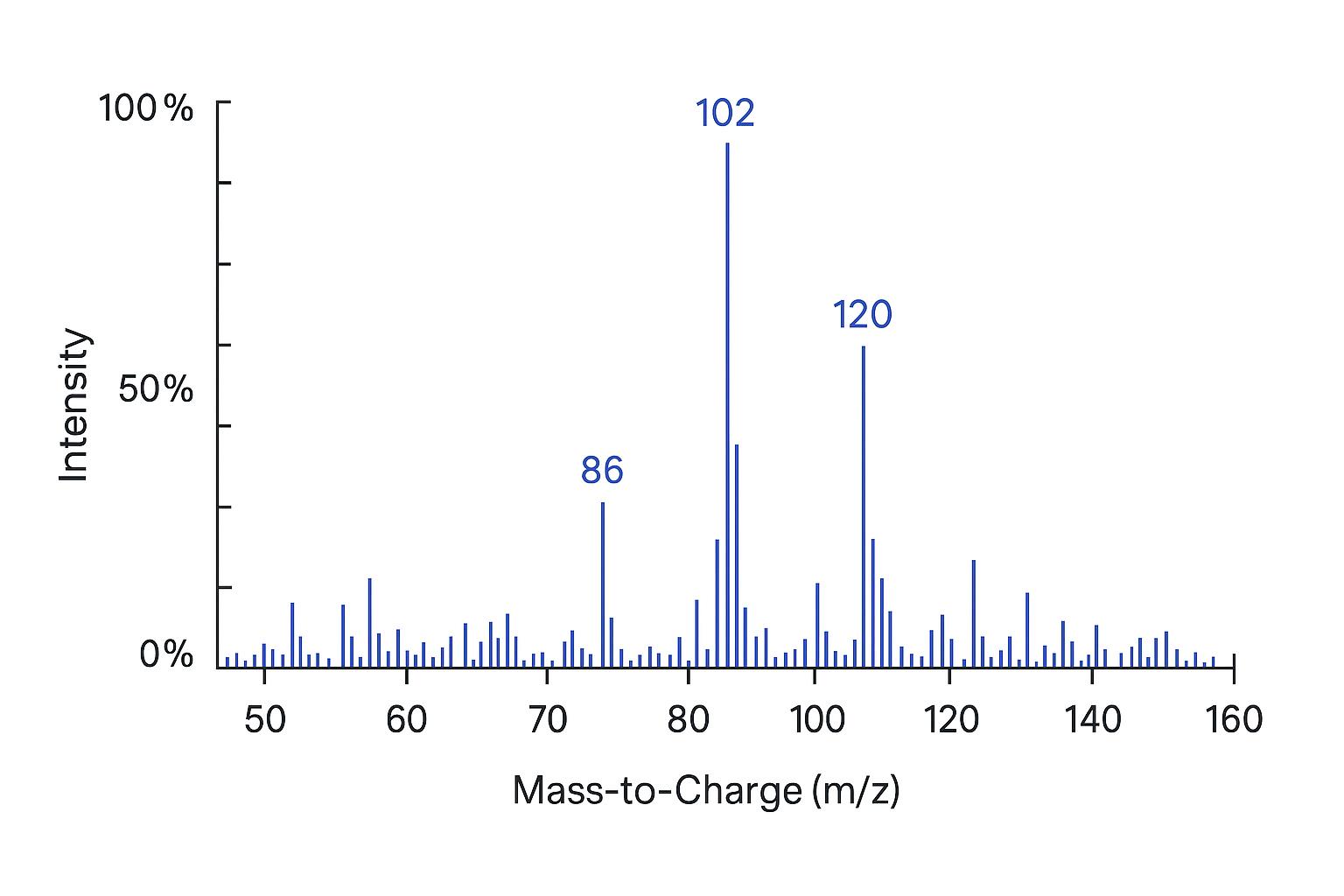
- Representative chromatograms
- Data files:Excel/CSV & PDF report
- Optional charts:trend plots, group comparisons
Untargeted metabolomics reveal sex-specific and non-specific redox-modulating metabolites in kidneys following binge drinking
Rafferty, D., de Carvalho, L. M., Sutter, M., Heneghan, K., Nelson, V., Leitner, M., et al.
Journal: Redox Experimental Medicine
Year: 2023